Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Synovial fluid (SF) provides nutritional support for cartilage and contains numerous catabolic and anabolic cytokines, chemokines and proteins. The precise role of these proteins in joint inflammation and cartilage injury in RA and OA, however, are not well understood. Advances in fluoresce bead based multiplex technology allows the measurement of multiple proteins from volumes < 200 mcL. Easier access to SF can allow investigators to identify patient specific wet biomarkers since most of these key regulatory cytokines in the peripheral blood correlate poorly with those measured simultaneously in the SF.
Methods: We performed 54 knee aspirations from 26 symptomatic RA and 8 primary OA patients using an external pneumatic compression device and ultrasound guidance. SF was transferred into heparin containing tubes with WBC levels counted by hemacytometer, then samples were centrifuged and cryopreserved within 60 minutes. Levels of 54 separate cytokines/chemokines and proteins were quantitated in batches of 20 using Luminex or ELISA assays. A significant correlation between log-transformed cytokine levels and WBC counts was determined by a p < 0.05 using Pearson’s product moment between log 10 concentration of specific cytokines and SF WBC levels whereas between group differences was performed using R and SAS programs.
Results: Demographic and clinical features are presented in Table 1. 92% of the OA samples had SF WBC levels < 300 cells/mm3 as did 31% of RA patients. 93% of this RA cohort were receiving prednisone, DMARD or a biologic; yet all had symptomatic knee pain. There was a significant correlation, p<0.05, between all RA and OA patient’s SF 10 WBC counts and log concentration of IL-1, IL-1ra, IL-6, MMP-3, MMP 8 and MMP-9 levels, but not with the other cytokines, chemokines, and proteins. Table 2 displays those specific SF proteins which were higher in either RA or OA patients whereas 43 cytokine/chemokine/protein levels did not differ statistically between both groups of patients.
Conclusion: Sufficient SF volumes were obtained using pneumatic external compression and US to measure 54 separate cytokines, chemokines and proteins from cryopreserved samples from all RA and OA patients using multiplex assays. There was a significant correlation between SF WBC levels and 6 different cytokines, chemokines and proteins, but not in 43 others; yet some biomarkers were higher in OA than RA SF samples. Despite SF WBC < 300 levels in OA and well controlled RA patients, the pro-inflammatory catabolic SF profile suggests an ongoing risk for continued cartilage injury. 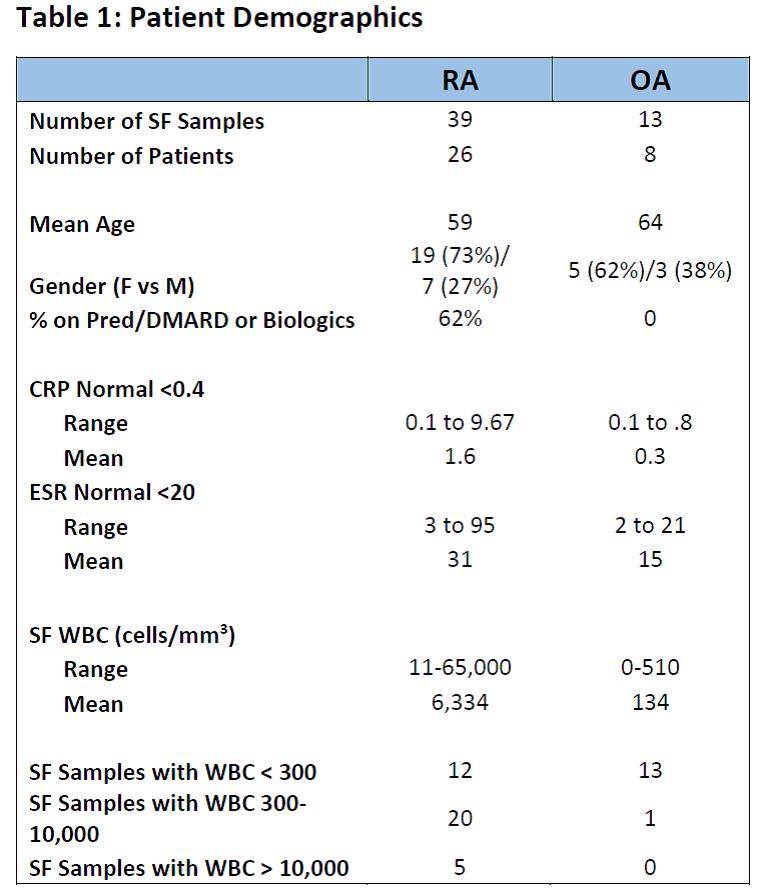

To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Meehan R, Hoffman E, Wolf M, Regan E, Parmar P, Pacheco K, Crooks J, Knight V. Synovial Fluid Cytokines /Chemokines and Proteins from the Knees of Symptomatic RA and OA Patients Which Correlate with the Magnitude of the Inflammatory Response As Measured By Synovial Fluid WBC Levels [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synovial-fluid-cytokines-chemokines-and-proteins-from-the-knees-of-symptomatic-ra-and-oa-patients-which-correlate-with-the-magnitude-of-the-inflammatory-response-as-measured-by-synovial-fluid-wbc-lev/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synovial-fluid-cytokines-chemokines-and-proteins-from-the-knees-of-symptomatic-ra-and-oa-patients-which-correlate-with-the-magnitude-of-the-inflammatory-response-as-measured-by-synovial-fluid-wbc-lev/
