Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Dysregulated humoral immunity is a hallmark of primary Sjögren’s Syndrome (pSS). This dysregulation involves aberrant B-lymphocyte activity resulting in abnormally high immunoglobulin G (IgG) levels and the production of autoantibodies, particularly those reactive with Ro/La ribonuclear complexes. pSS can affect almost any organ system, and current evidence-based therapies only offer some symptom relief, but no treatment has been shown to alter the disease course. Nipocalimab is a high-affinity, fully human monoclonal antibody that reduces circulating IgG levels by selectively blocking the interactions of IgG, including pSS autoantibodies, with the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn). Nipocalimab has previously induced rapid, safe, and durable serum IgG reductions in healthy volunteers (NCT02828046)1 and in autoantibody-driven generalized myasthenia gravis (gMG) in adults (Vivacity-MG; NCT03896295)2, suggesting that nipocalimab may treat a broad range of autoimmune disorders associated with autoantibodies, immune complexes and B-lymphocyte hyperactivity, including pSS. This abstract describes key data from Vivacity-MG that illustrate the therapeutic potential of nipocalimab in IgG autoantibody-driven conditions and reviews the design of a phase 2 study evaluating the efficacy and safety of nipocalimab in patients with pSS (NCT04968912).
Methods: Study feasibility assessments involved evaluating results from the phase 2 placebo-controlled trial Vivacity-MG. Of the 68 patients enrolled, 54 were randomized 1:1:1:1:1 to 4 treatment groups or a placebo group.
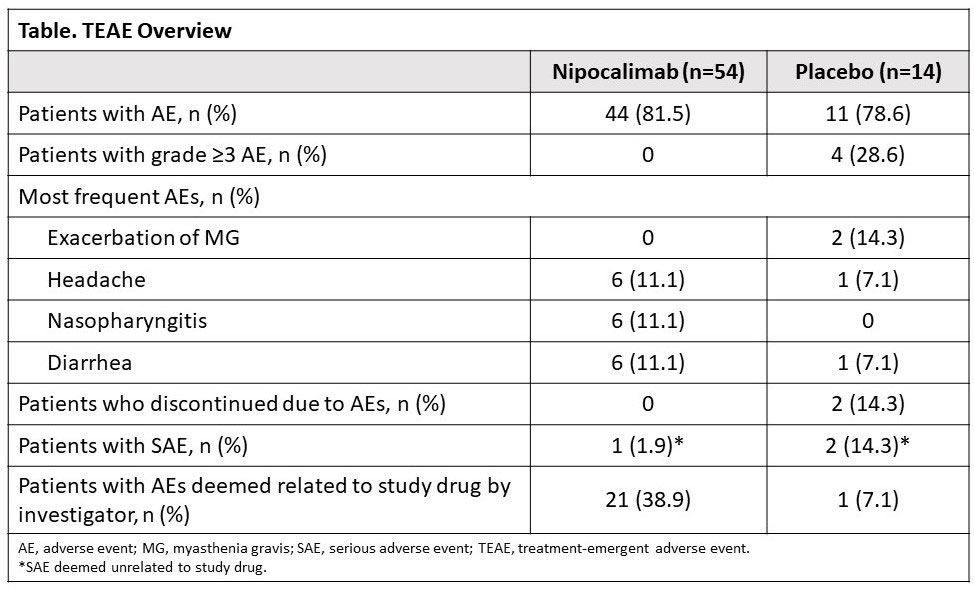
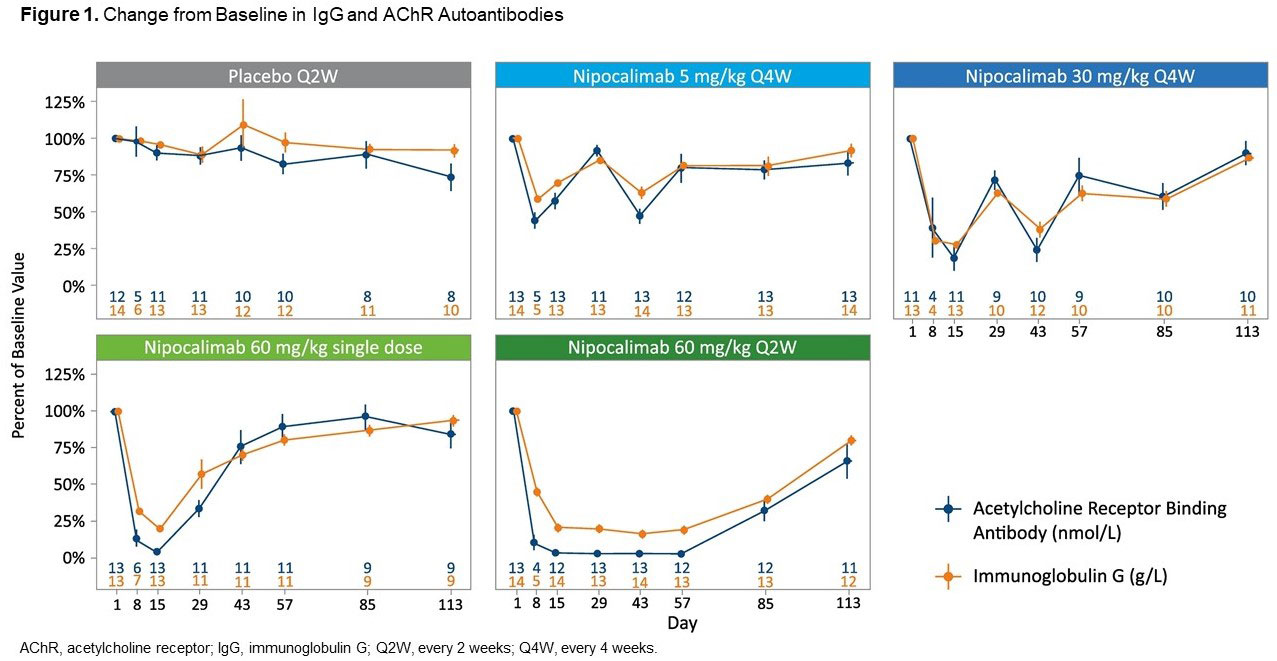
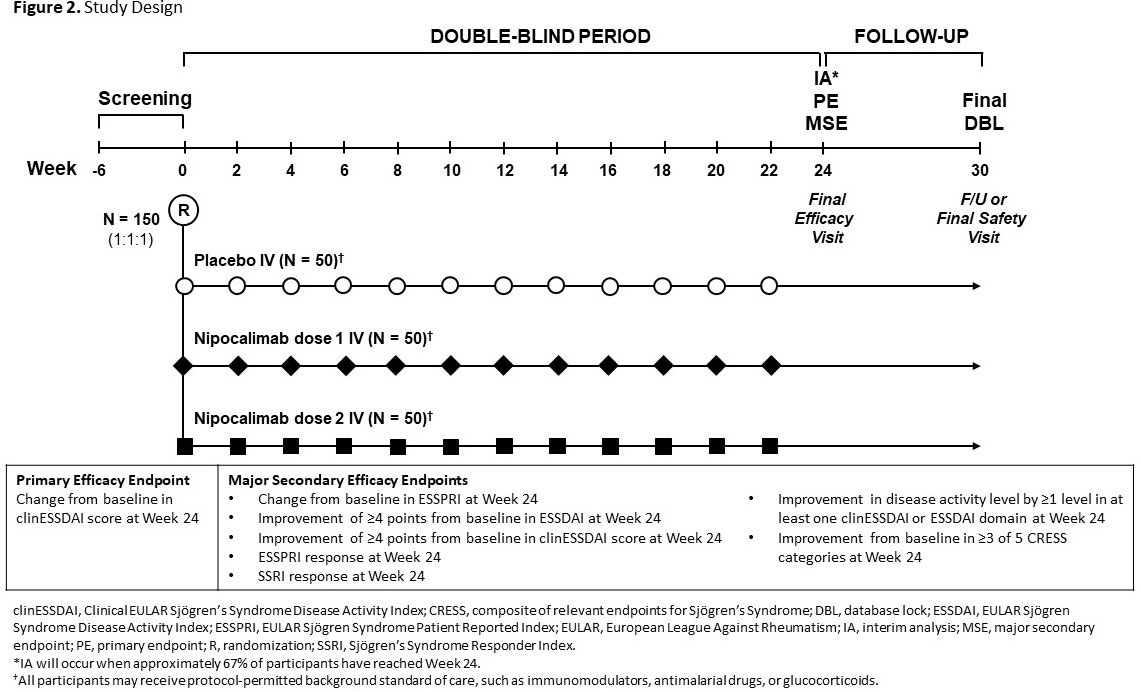
Results: In Vivacity-MG, there were no discontinuations due to TEAEs, severe AEs, or related SAEs with nipocalimab. The incidence of infections and headaches with nipocalimab were comparable to placebo (Table). Treatment with nipocalimab resulted in rapid, and dose-dependent reductions in serum total IgG levels and anti-AChR IgG autoantibodies (Figure 1), as compared to placebo. These safety and pharmacodynamic data from Vivacity-MG support the hypothesis that nipocalimab has the potential to treat pSS through lowering pathogenic IgGs. As such, we developed a phase 2, multicenter, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study enrolling adults with moderately-to-severely active pSS (Figure 2). The pSS study consists of a ≤6-week screening period, 24-week double-blind treatment period, and a 6-week follow-up period. Participants are randomized 1:1:1 to treatment every 2 weeks with intravenous nipocalimab (low or high dose), or placebo, through Week 22. The primary efficacy endpoint is change from baseline in clinESSDAI score at Week 24. Safety assessments include AEs, abnormal vital signs, and laboratory parameters.
Conclusion: Vivacity-MG demonstrated that nipocalimab has the potential to offer an important new and targeted treatment option for patients with IgG-mediated diseases. The ongoing phase 2 study evaluates the safety and efficacy of treatment with nipocalimab in patients with moderately-to-severely active pSS.
References:
1. Ling LE, et al. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2019;105(4):1031-1039.
2. Ramchandren S, et al. MGFA 2022. Poster 90.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hubbard J, Campbell K, Sivils K, Hoffman R, Lo K, Leu J, Liva S, Zuraw Q, Stevens A, Ling L, Karcher K, Ramchandren S, Sun H, Scofield H, Wallace D, Seror R. Designing of a Phase 2, Multicenter, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of Nipocalimab, an FcRn Inhibitor, in Adults with Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/designing-of-a-phase-2-multicenter-randomized-placebo-controlled-double-blind-study-to-assess-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-nipocalimab-an-fcrn-inhibitor-in-adults-with-primary-sjogrens-sy/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/designing-of-a-phase-2-multicenter-randomized-placebo-controlled-double-blind-study-to-assess-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-nipocalimab-an-fcrn-inhibitor-in-adults-with-primary-sjogrens-sy/