Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in SSc causes significant disease burden and requires invasive diagnosis with right heart catheterization (RHC). Comprehensive work-up is needed to identify patients at risk for PH.(1) Vectorcardiography may represent a novel tool to increase the precision of identification. It can be derived from the 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) and has been shown to be a promising tool. (2) In our study, we sought to determine the accuracy of the “ventricular gradient projected on the optimal direction for detection of right ventricular pressure overload” (VG-RVPO) to identify patients with SSc at risk for PH who should be referred for RHC.
Methods: Consecutive SSc patients from the Leiden Combined care in SSc cohort were included. Patients with skin involvement, without known PH, who underwent an RHC in 2021 and 2022 and had an ECG available were included. Data was collected prospectively including history, six-minute walk distance (6MWD), laboratory testing, trans-thoracic echocardiography (TTE), pulmonary function testing and RHC. Standard 10-second 12-lead ECG around the time of the RHC were recorded in the supine position, subsequently collected and processed in Extensible Markup Language (XML) format. A dedicated software program was used to calculate the VG-RVPO, which is defined as the the 3D integral of the heart vector over the QT interval. PH was defined as a mean pulmonary arterial pressure (mPAP) of >20 mmHg. Difference in VG-RVPO between PH status was tested with an unpaired t-test. The association of VG-RVPO with clinical determinants such as 6MWD and diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide (DLCO) was assessed with linear regression. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis was conducted to assess diagnostic accuracy.
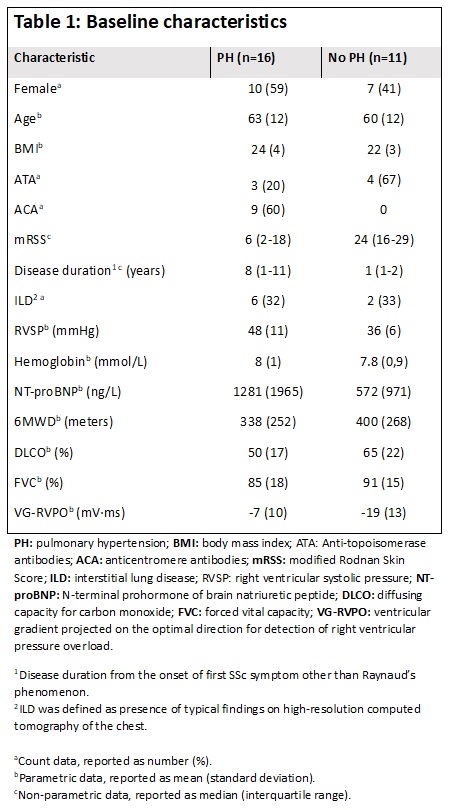
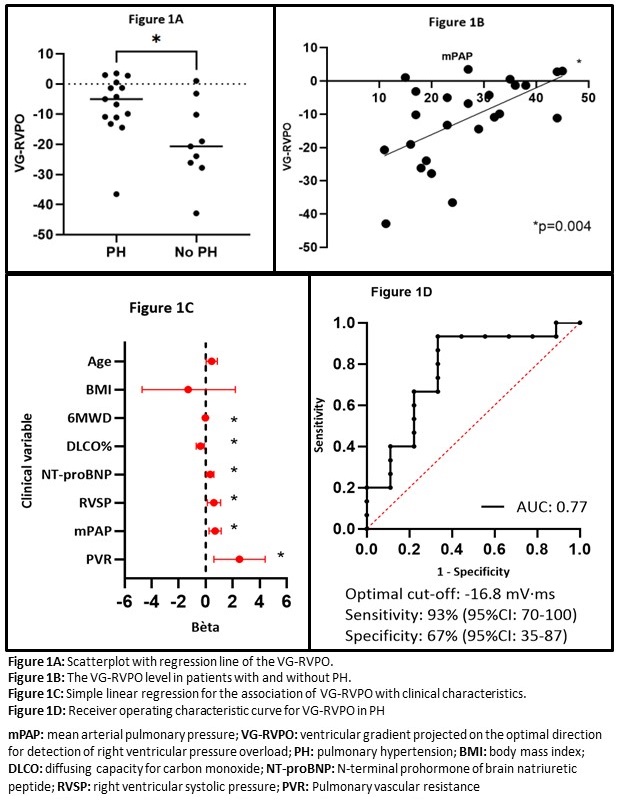
Results: The baseline characteristics of the 27 patients that were included, are presented in table 1. The VG-RVPO was higher in patients with PH (-7 millivolt·millisecond [mV·ms]) than in patients without (-19.2 mV·ms) (p=0.02, figure 1A). The VG-RVPO was significantly associated with the 6MWD, DLCO, right ventricular systolic pressure (RVSP) on TTE, NT-proBNP, mPAP and pulmonary vascular resistance (figure 1B and 1C). ROC analysis yielded an area-under-the-curve (AUC) of 0.77, with the optimal cut-off at -16.8 mV·ms. At this cut-off, VG-RVPO held a sensitivity of 93% (95%CI: 70-100) and a specificity of 67% (95%CI: 35-87) (figure 1D).
Conclusion: In this preliminary study, the VG-RVPO is substantially higher in patients with PH and displays promising abilities to identify SSc patients at risk for PH. However, present sample size is too small. Therefore, more cases are being added to determine the independent diagnostic properties of the VG-RVPO to the current standards.
References:
1. Naranjo M, Hassoun PM. Systemic Sclerosis-Associated Pulmonary Hypertension: Spectrum and Impact. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021;11(5).
2. Kamphuis VP, Haeck ML, Wagner GS, Maan AC, Maynard C, Delgado V, et al. Electrocardiographic detection of right ventricular pressure overload in patients with suspected pulmonary hypertension. J Electrocardiol. 2014;47(2):175-82.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ahmed S, Hoekstra E, van der Wouden K, Man S, Swenne K, Vonk M, Hoffmann-Vold A, Bruni C, Mulder U, Huizinga T, Vliegen H, de Vries-Bouwstra J. Vectorcardiography for Identification of Systemic Sclerosis Patients at Risk for Pulmonary Hypertension [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vectorcardiography-for-identification-of-systemic-sclerosis-patients-at-risk-for-pulmonary-hypertension/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vectorcardiography-for-identification-of-systemic-sclerosis-patients-at-risk-for-pulmonary-hypertension/