Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Calcinosis is a complication of the idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) in which calcium salts are deposited in and around soft tissue, which can impact activities of daily living and reduce quality of life. Currently, patient-reported outcome measures (PROM) have not been developed for myositis patients with calcinosis. The Mawdsley Calcinosis Questionnaire (MCQ) was originally developed for Systemic Sclerosis Related Calcinosis (SSc-Ca) and consists of 4 domains: Quantity/Frequency, Pain/Sensation, Physical Function, and Psychological Impact of calcinosis. The objective of our study was to investigate the performance of the MCQ for DM/JDM patients with calcinosis.
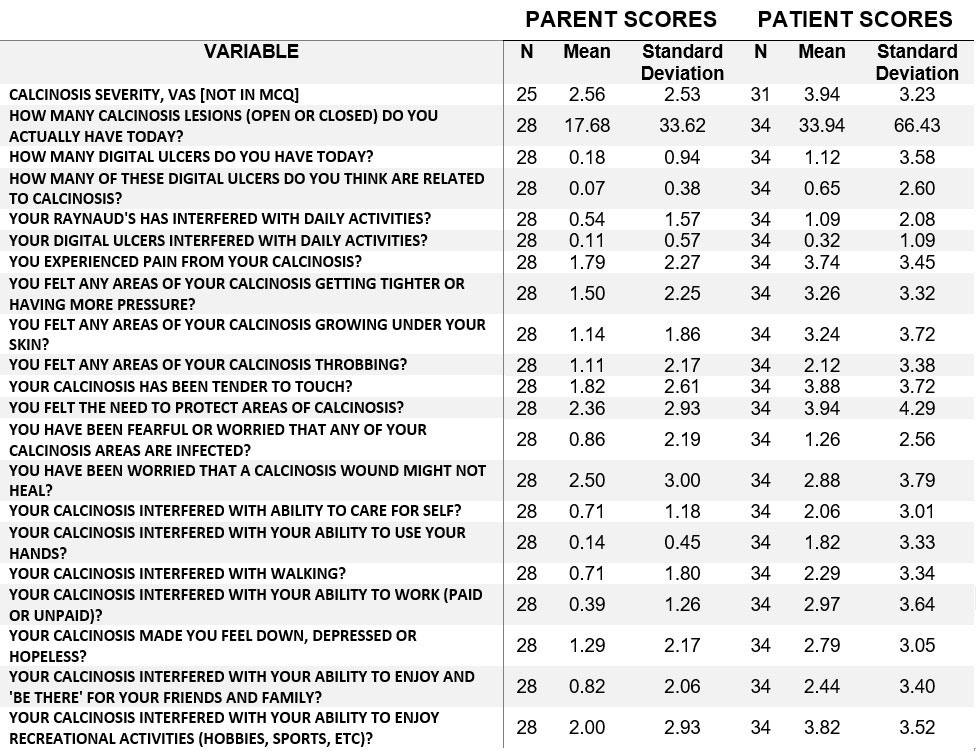
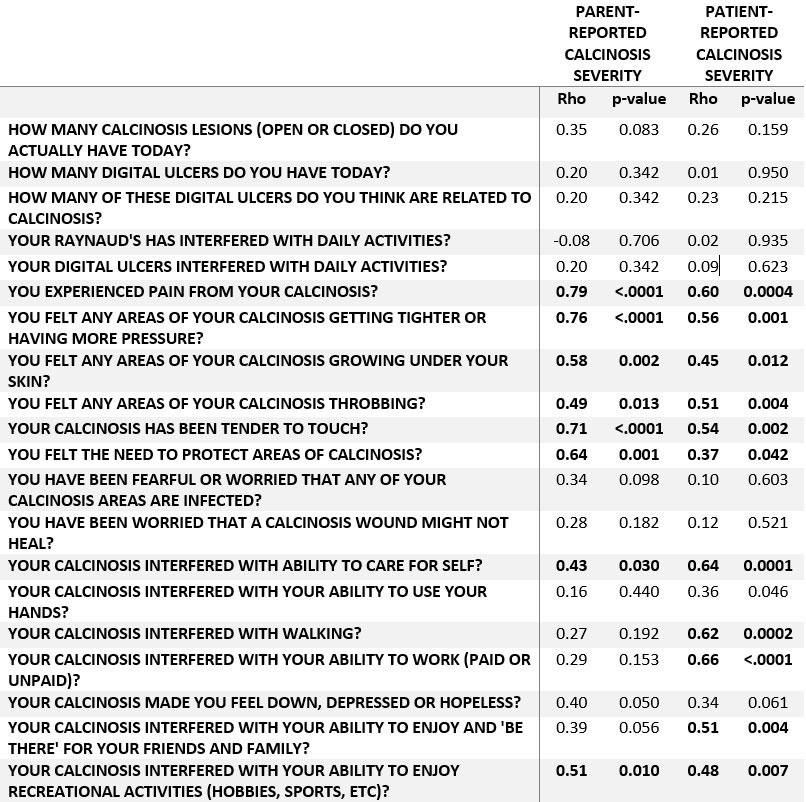
Methods: Patients with probable or definite DM/JDM by Bohan and Peter criteria completed the MCQ and a visual analog scale of calcinosis severity. Four items on the MCQ are quantitative, and 17 items are scored on a 11-point scale with higher scores being more severe. Patient forms were used for adults (n=31), while parent forms were used for pediatric patients (n=25). Correlations between MCQ items and overall calcinosis severity were assessed by Spearman’s correlation coefficient (Rho). Rho values between 0.75-1.00 were considered strong, 0.5-0.75 moderate, 0.25-0.5 weak, and < 0.25 poor. Maximizing the adjusted R-squared value in multiple linear regression models predicting overall calcinosis severity was used for MCQ item selection.
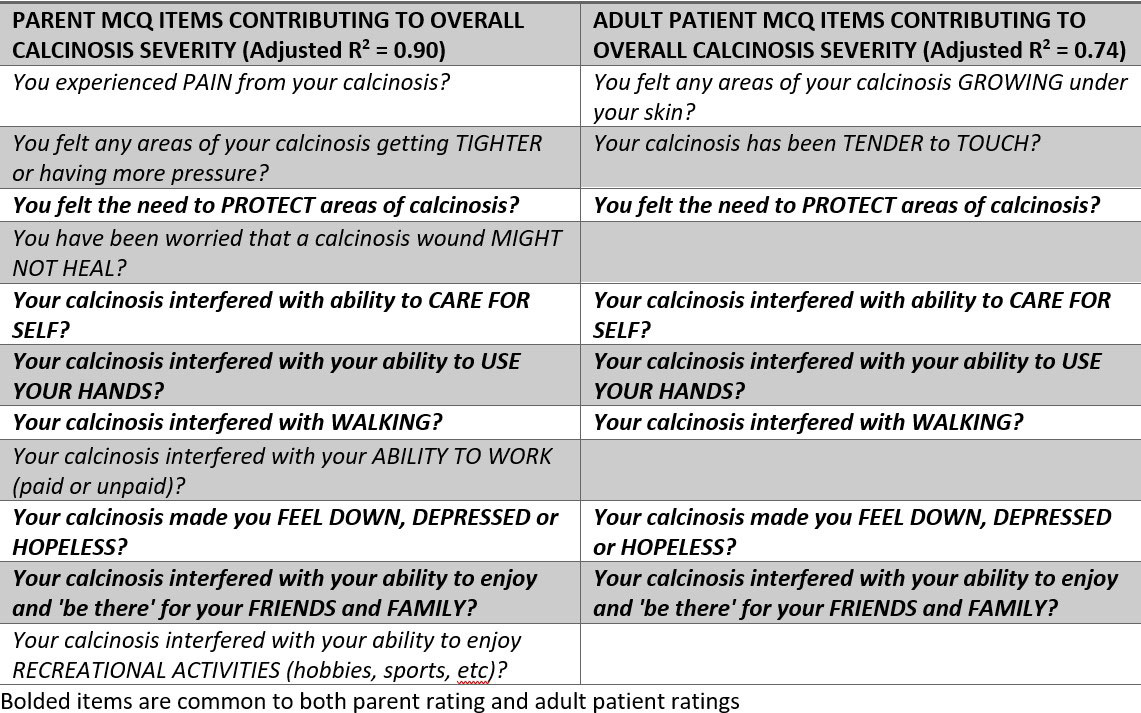
Results: 56 IIM patients (mean age 25.9 years) were evaluated: 15 DM, 41 JDM. At least one patient or parent scored > 0 for each item on the MCQ, and several items had a mean >2 (Table 1). Many MCQ items correlated with overall calcinosis severity (Table 2), while four items correlated poorly (excluded from the multiple linear regression model). MCQ items showed strong internal consistency, with Cronbach α of 0.91 for adults and 0.90 for parent raters. In the multiple linear regression model for parents, twelve MCQ items contributed to overall calcinosis severity (adjusted R2 of 0.90); in the adult patient model, 8 MCQ items contributed to overall calcinosis severity, (adjusted R2 of 0.74) (Table 3). An analysis of 18 patients that had both patient and parent scores revealed that 6 MCQ items correlated poorly between them, suggesting that their scores cannot be combined.
Conclusion: Many items on the MCQ individually exhibited moderate to strong correlations with calcinosis severity. Multivariate modeling identified several MCQ items for both parents and patients with DM/JDM that predict overall calcinosis severity. Overall, the MCQ may be an effective PROM for assessing calcinosis in DM/JDM patients.
Acknowledgements: IRP of NIH, CC, NIAMS, NIEHS.
Permission for Mawdsley from Lesley Saketoo, [email protected]
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nazir S, Rouster-Stevens K, Fuller J, Kim H, Do V, Volochayev R, Jansen A, Bayat N, Rider L, Schiffenbauer A. Validity of the Mawdsley Calcinosis Questionnaire in Adult and Juvenile Dermatomyositis (DM, JDM) Patients with Calcinosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validity-of-the-mawdsley-calcinosis-questionnaire-in-adult-and-juvenile-dermatomyositis-dm-jdm-patients-with-calcinosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/validity-of-the-mawdsley-calcinosis-questionnaire-in-adult-and-juvenile-dermatomyositis-dm-jdm-patients-with-calcinosis/