Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Data from before the COVID-19 pandemic had shown persistently poor care for people with gout in many countries worldwide. Whether this was further exacerbated by the pandemic is not fully understood. Our objective was to investigate the impact of the pandemic on consultations and care quality for people with gout in England, using the OpenSAFELY Trusted Research Environment.
Methods: With the approval of NHS England, we performed a population-level cohort study using health data for 17.9 million adults in England (40% of the population) via the OpenSAFELY platform. We analysed trends in the following outcomes between 1 March 2018 and 28 February 2024: 1) the number of patients consulting for gout in primary care; 2) the initiation of ULT within 6 months of consultation; 3) the attainment of serum urate < 6 mg/dL (360 micromol/L) within 6 months of consultation.
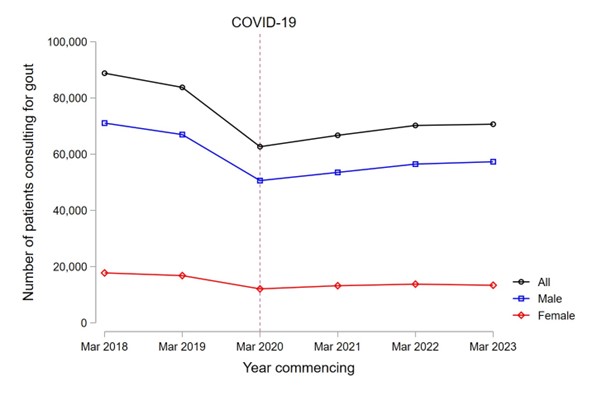
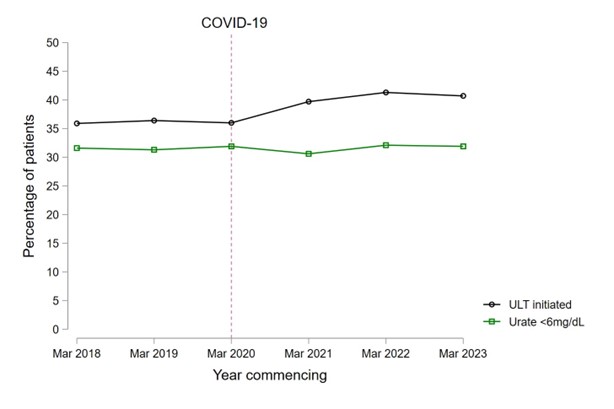
Results: Of 17.9 million adults from 2,530 general practices in England, an average of 73,805 patients per year consulted a primary care clinician for gout (4.1 patients per 1,000 population; 29.2 patients per practice). The mean age at consultation was 61.6 years, 80.4% were male, and 51.2% had prevalent gout diagnoses. Patients had an average of 1.3 primary care consultations for gout per year. The number of patients consulting for gout decreased by 25.2% in the first year of the pandemic (from 83,765 in 2019/20 to 62,665 in 2020/21). Consultations remained 15.6% lower than pre-pandemic levels in 2023/24 (Figure 1). 17.1% of patients had been prescribed ULT within 6 months prior to their consultation. Of patients not already prescribed ULT at the time of their consultation, 38.3% initiated ULT within 6 months (intraclass correlation for general practices: 0.077). ULT initiation improved modestly after the onset of the pandemic, from 35.9% in 2018 to 40.7% in 2023 (Figure 2). 38.0% of patients had serum urate levels measured within 6 months of consultation, of whom 31.6% achieved serum urate levels < 6 mg/dL. Urate target attainment remained stable throughout the pandemic (31.6% in 2018; 31.9% in 2023; Figure 2).
Conclusion: The number of consultations for gout decreased by 25% during the early pandemic, and remained 15% below pre-pandemic levels as of 2023/24. ULT initiation improved modestly during the pandemic, while urate target attainment remained stable. Despite this, absolute levels of ULT initiation and urate target attainment remain far below an acceptable standard. Importantly, we have demonstrated the potential for routinely-collected data to transform how care quality is monitored for rheumatic diseases at a national level.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Russell M, Massey J, Roddy E, MacKenna B, Bacon S, Goldacre B, Andrews C, Hickman G, Mehrkar A, Mahto A, Rutherford A, Patel S, Adas M, Alveyn E, Nagra d, Bechman K, Ledingham J, Hudson J, Norton S, Cope A, Galloway J. Trends in Management and Consultations for Gout: A Study of 18 Million Adults Using the OpenSAFELY Platform [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/trends-in-management-and-consultations-for-gout-a-study-of-18-million-adults-using-the-opensafely-platform/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/trends-in-management-and-consultations-for-gout-a-study-of-18-million-adults-using-the-opensafely-platform/