Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Axial Spondyloarthritis (AxSpA) is a chronic inflammatory arthritis primarily affecting the axial skeleton and commonly coexists with gut and skin inflammation. Currently, patients with axSpA require lifelong treatment. Current biologics (TNFi, IL-17i, JAKi)improve symptoms but are not curative and cannot prevent disease progression.
With the help of AI technology highlighting several unique small molecules with the potential efficacy in axSpA, it was possible to identify a potential small molecule that acts on the binding site of lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1). The LFA-1/ICAM-1 interaction is known to enable both T-cell activation and pro-inflammatory cytokine release. Through previously associated work with computational science and a preclinical in vivo model using DBA/1 collagen induced arthritis model, we have seen significant effects, resulting in decreased arthritis score and paw thickness. It is with this ICAM-1-mimicing small molecule compound that this study reports on the effect blocking this interaction has on an axSpA murine model.
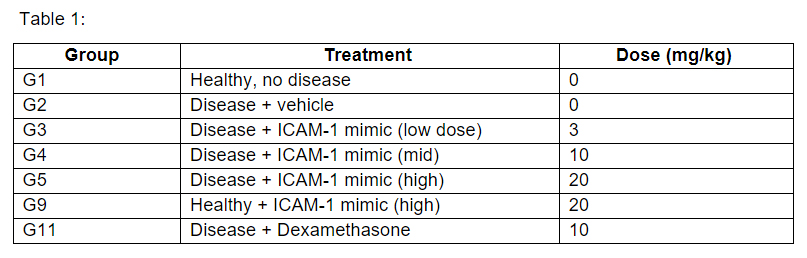
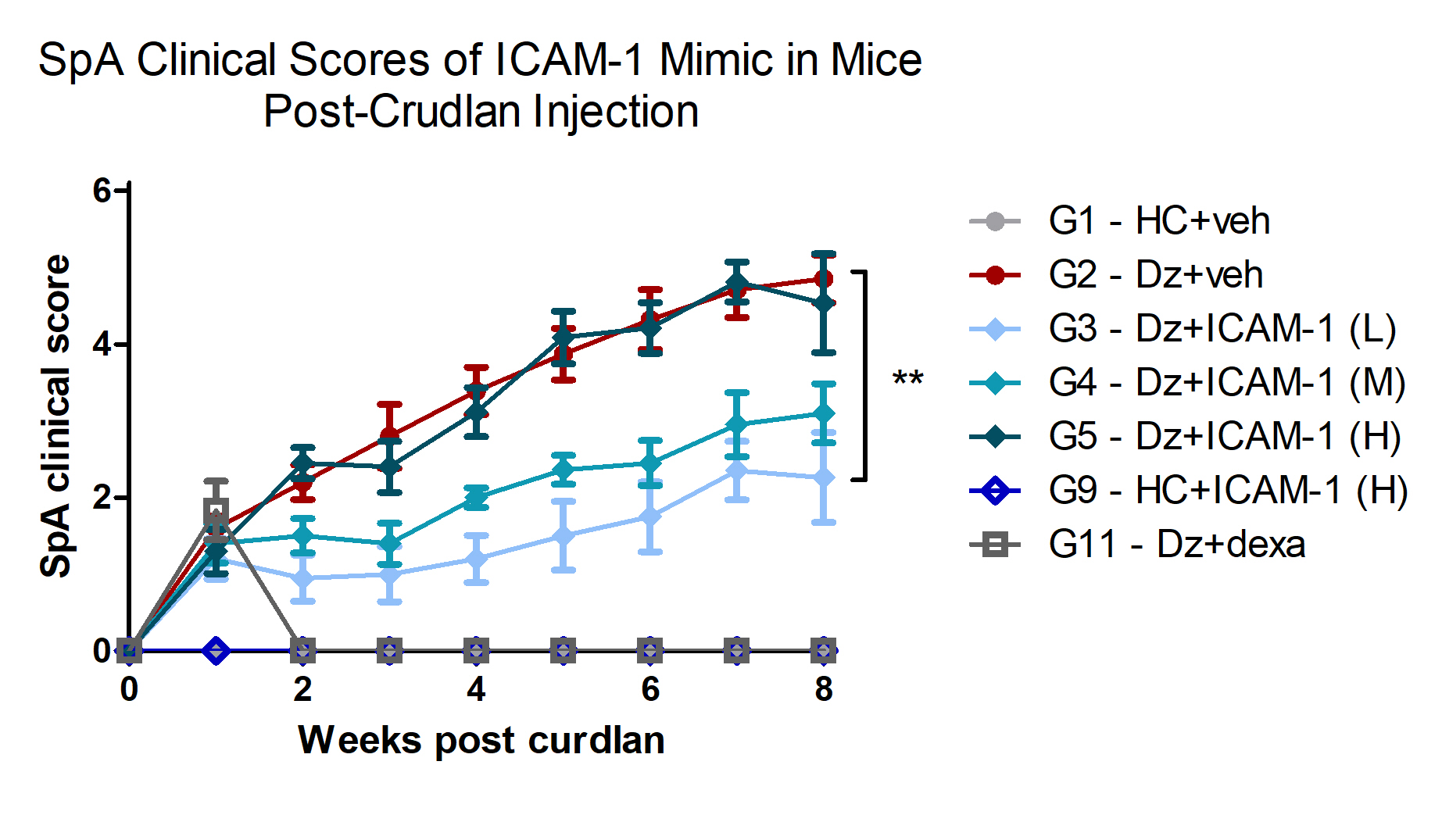
Methods: We employed the use of the SKG mouse, an IL-23- and IL17-dependent model leading to disease resembling human axSpA. SKG mice given a single dose 3mg curdlan (intraperitoneal) developed skin inflammation in ears and tail, blepharitis, and swelling of ankles and wrists and digits. Therapeutic intervention began one week post-curdlan disease induction. These mice were treated with varying doses of the ICAM-1 mimic via daily intraperitoneal (IP) injections and monitored for 8weeks.
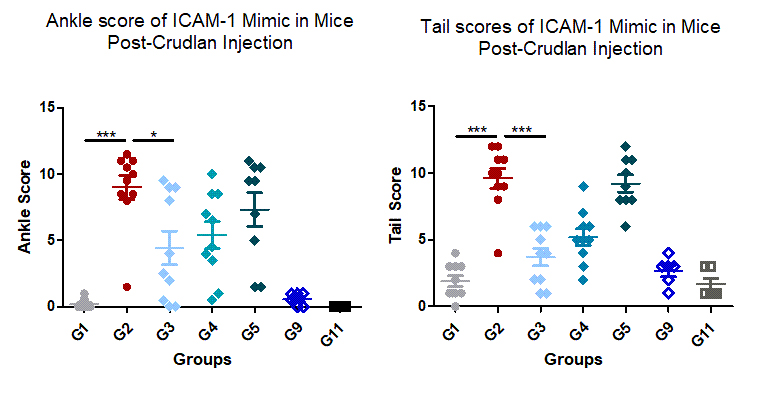
Results: With the SKG mice, theICAM-1 mimic showed excellent tolerability and showed a significant decrease in clinical scores, which was most pronounced in the low dose treatment group (G3 in Fig 1). Histological analysis with H&E staining indicated that animals treated with the compound had significantly reduced histological scores of tails, skin, ankle, and gut for the low dose treatment group (G3).
Conclusion: This small molecule ICAM-1 mimic, identified by an axSpA drug discovery approach, shows efficacy in this preclinical model. Follow-up studies will examine pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of the compound. This is promising data for application of this ICAM-1 mimic as a new therapeutic option for axSpA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lim M, Foroozan S, Qaiyum Z, Tang M, Yau E, Inman R. Therapeutic Effect of ICAM-1 Mimic on Experimental Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-effect-of-icam-1-mimic-on-experimental-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-effect-of-icam-1-mimic-on-experimental-axial-spondyloarthritis/