Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a persistent inflammatory disease primarily affecting the diarthrodial joints. Nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) is a family of inducible transcription factors responsible for regulating numerous genes involved in various aspects of immune and inflammatory diseases, including RA. This study aims to evaluate the potential anti-inflammatory properties of suppressor IκB (srIκB), an inhibitor of NF-κB when delivered by exosomes in the context of RA.
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were collected from both healthy controls (HCs) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients, and additional synovial fluid mononuclear cells (SFMCs) were collected from RA patients. Collected PBMCs and SFMCs were pretreated with Exo-srIκB or vehicle (Exo-Naïve) and then evaluated for cell viability. The subset of cells producing inflammatory cytokines, including IFN-γ, IL-17, and GM-CSF, was examined by flow cytometry and quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). To evaluate the therapeutic potential of Exo-srIκB in vivo, collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mouse model was used. Mice were treated with Exo-srIκB or vehicle, and arthritis scores were calculated for monitoring disease progression. Histological observations of ankle joints were performed using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining, and radiation damage scores were measured using micro-computed tomography micro-CT) imaging.
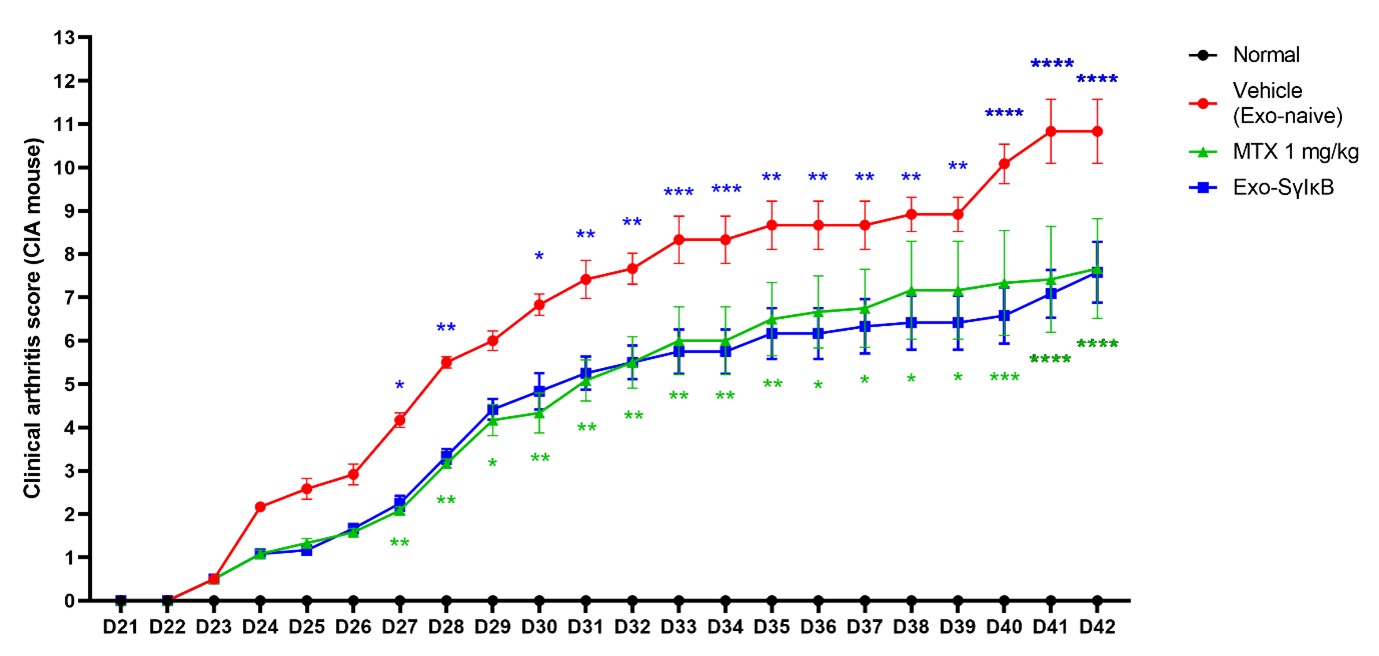
Results: Administration of Exo-SrlκB for 7, 24, and 48 hours had no significant effect on cell viability. However, treatment with Exo-SrlκB showed a significant reduction in the frequency of IL-17A- and GM-CSF-producing cells in PBMCs from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Exo-SrlκB treatment also reduced the frequency of GM-CSF-producing cells in SFMCs from RA patients. In the mouse experiment, Exo-SrlκB administration delayed the onset of arthritis and significantly reduced the severity of arthritis compared to the control group (Figure 1). In addition, radiographic arthritis scores were significantly lower in Exo-SrlκB treated mice than in Exo-Naïve treated mice.
Conclusion: Exo-srIκB, which contains IκB as an inhibitor, demonstrates the ability to inhibit inflammatory cytokines in vitro and exhibits inhibitory effects in animal models. These findings suggest that regulation of NF-κB signaling by Exo-srIκB may be a promising therapeutic target for the treatment of RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Park K, Kang J, Lee H, Lee Y, Kim M, Ahn S, Yoo J, Choi C, Kim T. The Delivery of the Super-repressor IκBα by Exosomes Has the Potential to Alleviate Inflammation Associated with Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-delivery-of-the-super-repressor-i%ce%bab%ce%b1-by-exosomes-has-the-potential-to-alleviate-inflammation-associated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-delivery-of-the-super-repressor-i%ce%bab%ce%b1-by-exosomes-has-the-potential-to-alleviate-inflammation-associated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis/