Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease (2043–2047)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 10:00AM-10:50AM
Background/Purpose: T cell-derived pro-inflammatory cytokines are major drivers of RA pathogenesis, and these cytokines have traditionally been attributed to CD4 T cells. However, single-cell RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) of RA synovial tissue has revealed that CD8 T cells, which represent nearly half of T cells in inflamed RA synovium, are the predominant expressors of IFNγ and TNF transcripts1. Here, we present data indicating that synovial CD8 T cells are major cytokine producers in response to both TCR-mediated and cytokine-mediated stimulation and have low cytotoxic potential.
Methods: Blood, synovial fluid, and synovial tissue were obtained from RA patients meeting the 2010 ACR criteria for RA. Single-cell RNA-seq data sets were generated by integrating new and publicly available data from synovial tissue and fluid from patients with RA and from blood from healthy controls. For stimulation assays, peripheral blood mononuclear cells or synovial fluid mononuclear cells were stimulated with IL-12 and IL-15 for 20 hours or with anti-CD3/CD28 antibody-coated beads for 4 hours, with brefeldin A and monensin included during the last 4 hours of culture. Cytokine production was assessed by intracellular cytokine staining and flow cytometry. Additional flow cytometry experiments were performed on unstimulated cells.
Results: The majority of CD8 T cells in synovial tissue and fluid from patients with seropositive RA express granzyme K (GzmK), either alone or together with granzyme B (GzmB), a marked enrichment compared to blood (Fig. 1A). These cells express lower levels of GzmB and perforin compared to classical GzmB+ CD8 cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) in blood (Fig. 1B), and they do not express high levels of CD57 or CX3CR1, two surface markers associated with cytotoxicity. GzmK itself does not cleave caspases to activate apoptotic cell death pathways but instead signals synovial fibroblasts to produce IL-6 and other inflammatory factors. Together, these results indicate that GzmK+ GzmB+ CD8 T cells have low cytotoxic potential.
In stimulation assays, GzmK+ GzmB+ CD8 T cells responded to stimulation with IL-12 and IL-15 as well as anti-CD3/CD28 antibody-mediated stimulation. CD8 T cells represented half or more of IFNγ-producing T cells in both conditions, matching or out-producing CD4 T cells. Antigen-independent stimuli are likely the predominant activation pathway for GzmK+ GzmB+ CD8 T cells in vivo, since they express low levels of Nur77, a marker of TCR-mediated stimulation, compared to the rare GzmB+ CD8 T cells.
Conclusion:
GzmK+ GzmB+ CD8 T cells are the largest CD8 T cell population in synovial fluid and tissue from patients with RA. These cells have low cytotoxic potential but produce cytokines such as IFNγ in response to antigen-independent stimulation. These findings argue that the dominant CD8 T cell population in RA synovium amplifies inflammation by producing IFNγ and other inflammatory mediators (including GzmK itself) in response to cytokines found in inflamed RA tissue. This antigen-independent activation of CD8 T cells may represent a major mechanism for breaking self-tolerance in RA and other autoimmune diseases.
1. Zhang, F. et al. Nat Immunol 20, 928-942 (2019).
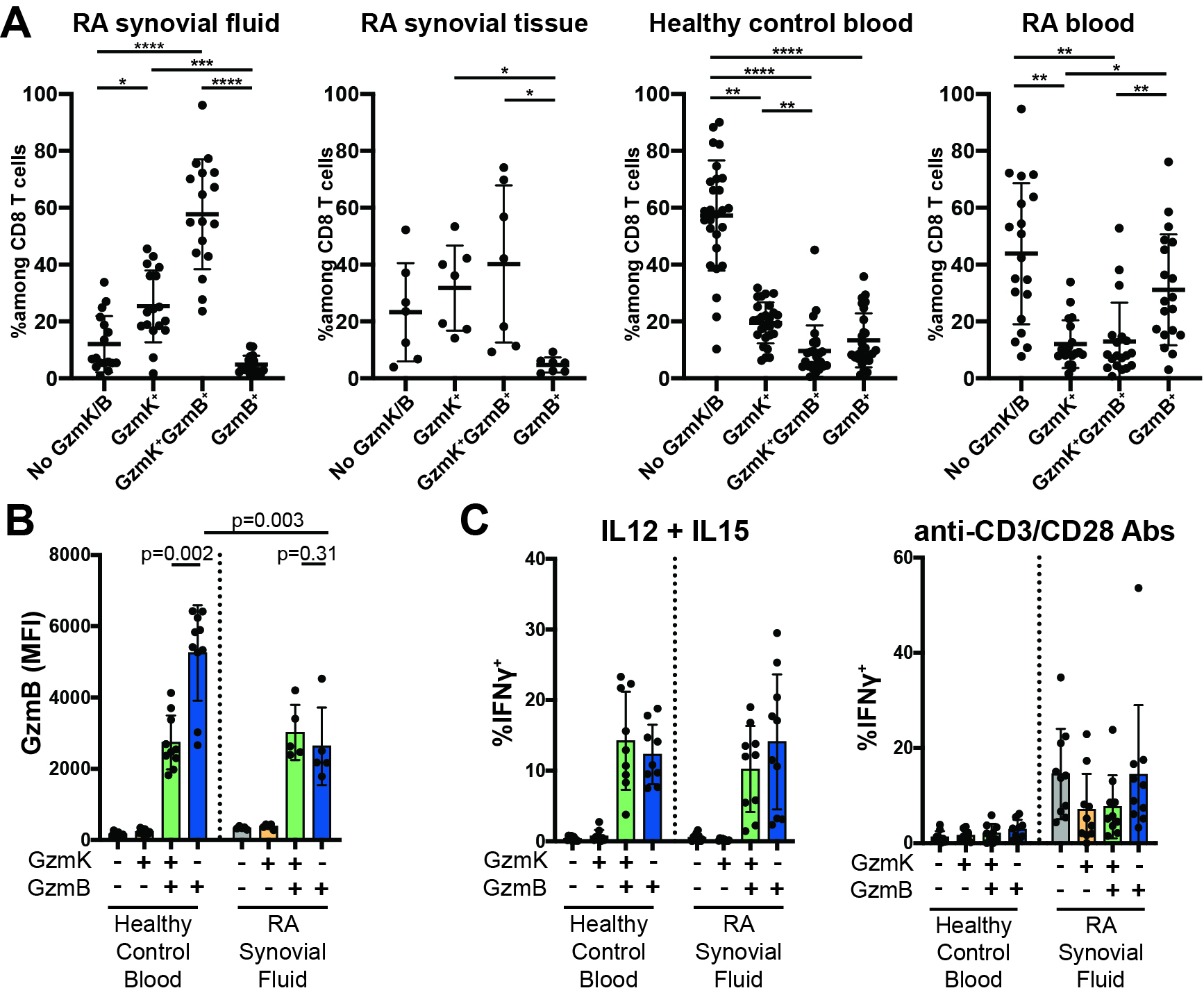 Figure 1. GzmK+ GzmB+ CD8 T cells, the predominant CD8 T cell population in RA synovial fluid and tissue, have low cytotoxic potential but can respond to antigen-independent stimulation. (A) Frequency of intracellular GzmK and GzmB expression among unstimulated CD8 T cells. (B) Mean fluorescence intensity of GzmB staining of unstimulated CD8 T cells categorized by GzmK and GzmB expression. (C) Intracellular cytokine staining after stimulation with IL-12 and IL-15 or anti-CD3/CD28-coated beads. Statistics by Friedman test (A) and Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon signed rank tests (B). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
Figure 1. GzmK+ GzmB+ CD8 T cells, the predominant CD8 T cell population in RA synovial fluid and tissue, have low cytotoxic potential but can respond to antigen-independent stimulation. (A) Frequency of intracellular GzmK and GzmB expression among unstimulated CD8 T cells. (B) Mean fluorescence intensity of GzmB staining of unstimulated CD8 T cells categorized by GzmK and GzmB expression. (C) Intracellular cytokine staining after stimulation with IL-12 and IL-15 or anti-CD3/CD28-coated beads. Statistics by Friedman test (A) and Mann-Whitney and Wilcoxon signed rank tests (B). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jonsson A, Zhang F, Gomez-Rivas E, Rupani K, Watts G, Wei K, Wang R, Rao D, Partnership (AMP) - RA/SLE A, Raychaudhuri S, Brenner M. Synovial CD8 T Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis Exhibit High Antigen-independent Cytokine Production and Low Cytotoxic Potential [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synovial-cd8-t-cells-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-exhibit-high-antigen-independent-cytokine-production-and-low-cytotoxic-potential/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synovial-cd8-t-cells-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-exhibit-high-antigen-independent-cytokine-production-and-low-cytotoxic-potential/
