Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (0934–0964) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Transitional B cells comprise a distinct population of B cells that have recently migrated to the periphery from the bone marrow. In systemic sclerosis (SSc),previous data from our laboratory has demonstrated that there are differences in the number and function of transitional B cells compared to healthy controls (HCs). In addition, we have previously isolated transitional B cells from SSc patients which are seropositive for anti-topoisomerase Iautoantibodies (ATA)demonstrating that these cells evade tolerance. To investigate why these autoreactive B cells are not tolerised in those withSSc,we performed a paired bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing study of the transitional B cell subsets in SSc and HCs.
Methods: 5000 CD19+CD24hiCD38hi transitional B cells were sorted from four HCs and four treatmentnaïveATA-positive SSc patients.Single-cell RNA-sequencing was performed on the sorted transitional B cells and the datawas analysed using Seurat in RStudio. Additionally, in a subset of this cohort paired bulk RNA-sequencing of the sorted transitional T1 (CD19+CD24hiCD38hiCD27–IgMhiIgDmed) and T2(CD19+CD24hiCD38hiCD27–IgMhiIgDhi) populations was carried out.
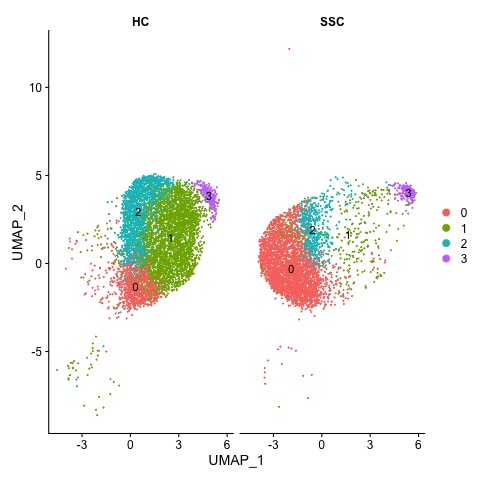
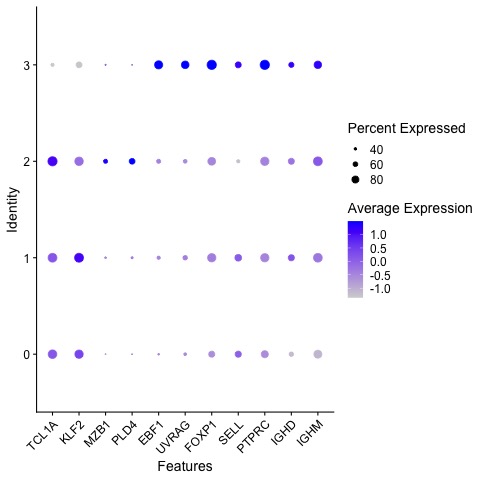
Results: As shown in Figure 1 single cell transcriptomics identified four distinct transitional B cell clusters in SSc patients and HCs. Notably, cluster 1 is diminished in the SSc group and cluster 0 is expanded in SSc compared to HCs. These clusters were characterised using relevant genes as shown in the dotplot in Figure 2. Clusters 0, 1 and 2 all share similar transcriptomic features whilst cluster 3 has upregulated expression of genes associated with commitment to the B cell lineage (EBF1). Thisindicates that cluster 3 is the earliest B cell emigrant from the bone marrow. Clusters 2, 1 and 0 can then be differentiated through expression of genes such as PLD4 and KLF2. Subsequent pathway analyses provided evidence for defective tolerance in SSc patients which may be mediated through dysregulated NF-κB signalling. In addition, differential gene expression analysis using bulk RNA-sequencing of sorted T1 and T2 transitional subsets have identified five candidate gene signatures which are significantly enriched in the T2 cells compared with the T1 cells. This finding was in concordance with the single cell data and provides further evidence to support the existence of a peripheral tolerance/selection checkpoint at the transitional B cell stage.
Conclusion: Through this data we have identified four transitional B cell subsets and have characterised their transcriptomic profile. Additionally, we have found further evidence for a potential breach in tolerance in the SSc patients. Studies are ongoing to explore biological pathways through which altered gene expression impacts peripheral tolerance in SSc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Beesley C, Goldman N, Abraham D, Denton C, Mageed R, Ong V. Single Cell Analysis of Transitional B Cells in Systemic Sclerosis Highlights Defective Peripheral Tolerance [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-analysis-of-transitional-b-cells-in-systemic-sclerosis-highlights-defective-peripheral-tolerance/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-analysis-of-transitional-b-cells-in-systemic-sclerosis-highlights-defective-peripheral-tolerance/