Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Accurate quantification of hip effusion volume may aid effective OA management as synovitis of the hip has been associated with pain and structural damage progression. Previous work has shown that volume quantification measures more closely correlate to clinical parameters than conventional measures like femoral neck fluid thickness (FTM). Recently, Artificial Intelligence (AI) based approaches have shown promise in measuring hip effusion volume from MRI sequences. This study examined the feasibility of using AI to quantify the change in effusion volume post intra-articular steroid injection (IASI) using Short-τ Inversion Recovery (STIR) MRI sequences.
Methods: We prospectively collected MRI images from 97 patients who met the ACR clinical classification criteria for hip OA at baseline (before IASI) and at 8 weeks follow-up (after receiving IASI). Two human readers measured the difference in effusion volumes in each image using an interactive tool developed inhouse.
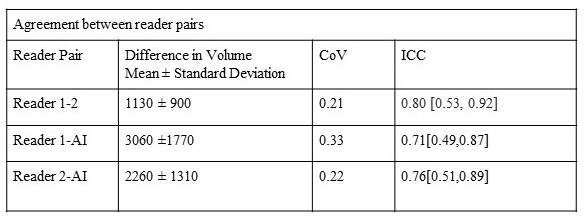
Manually segmented masks of effusion regions from 72 patients were used to train a Mask R-CNN [8] AI model. Changes in effusion volume between baseline and follow-up measured from the remaining 25 patients was used to compare and validate AI measurements vs 2 human readers. The agreement was assessed using the difference in volume (DV), Coefficients of Variation (CoV), and intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC).
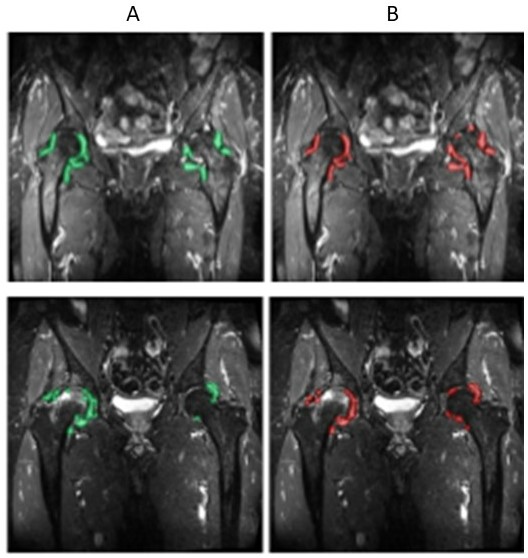
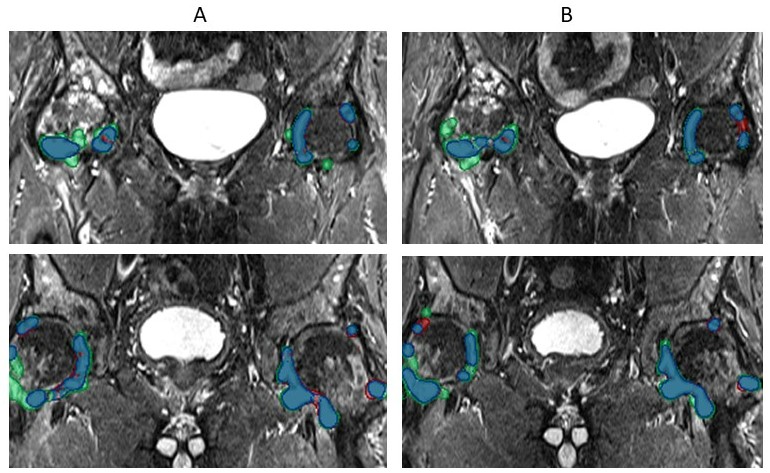
Results: The AI model automatically detected effusion regions successfully (Fig 1). Regions of effusion identified by the model both at baseline and follow-up correlated well with human assessment (Fig 2). Agreement in change of effusion volume (DV) measured between human readers was good (ICC=0.80 [0.53, 0.92]). Similarly, ICC between each human reader vs AI predicted ranged between moderate to good (ICC = 0.71-0.76) as summarized in Table 1.
Conclusion: Initial results of automatic quantification of change in effusion volume post -IASI shows moderate to high agreement between AI and human experts. This approach could potentially save expert time in OA MRI assessment resulting in overall improvement in OA care.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jaremko J, Felfeliyan B, Hareendranathan A, Thejeel B, Quinn-Laurin V, Ostergaard M, Conaghan P, Lambert R, Ronsky J, Maksymowych W. Quantitative Assessment of Volumetric Change in Hip Effusion Using Artificial Intelligence in Patients with Osteoarthritis of the Hip [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantitative-assessment-of-volumetric-change-in-hip-effusion-using-artificial-intelligence-in-patients-with-osteoarthritis-of-the-hip/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/quantitative-assessment-of-volumetric-change-in-hip-effusion-using-artificial-intelligence-in-patients-with-osteoarthritis-of-the-hip/