Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Polypharmacy, drug-drug interactions (DDI) and related adverse drug reaction (ADR) are understudied in SSc. The aim of this work was to determine the prevalence and determinants of DDI and ADR in a real-life prospective cohort of SSc patients.
Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of the drug prescriptions of the first hundred consecutive SSc patients admitted to the daily scleroderma clinic of Cochin Internal Medicine University Hospital between January 2020 and April 2022 who met inclusion criteria. Patients were included if they met the criteria for SSc according to the ACR/EULAR 2013 criteria, had an informatics-based drug prescription, and had a one-year follow-up. DDI were identified using 2 prescription analysis applications and classified into 4 types (contraindicated, not recommended, precaution for use, and warning). To assess ADR, all adverse events (AE) occurring during follow-up were evaluated by two medical experts experienced in SSc and AE were graded according to the Common Terminology Criteria for AE based on their severity. Any AE considered was adjudicated by a pharmacovigilance expert committee using the World Health Organization – Uppsala Monitoring Centre. Risk factors for DDI and ADR were then identified using multivariate analysis.
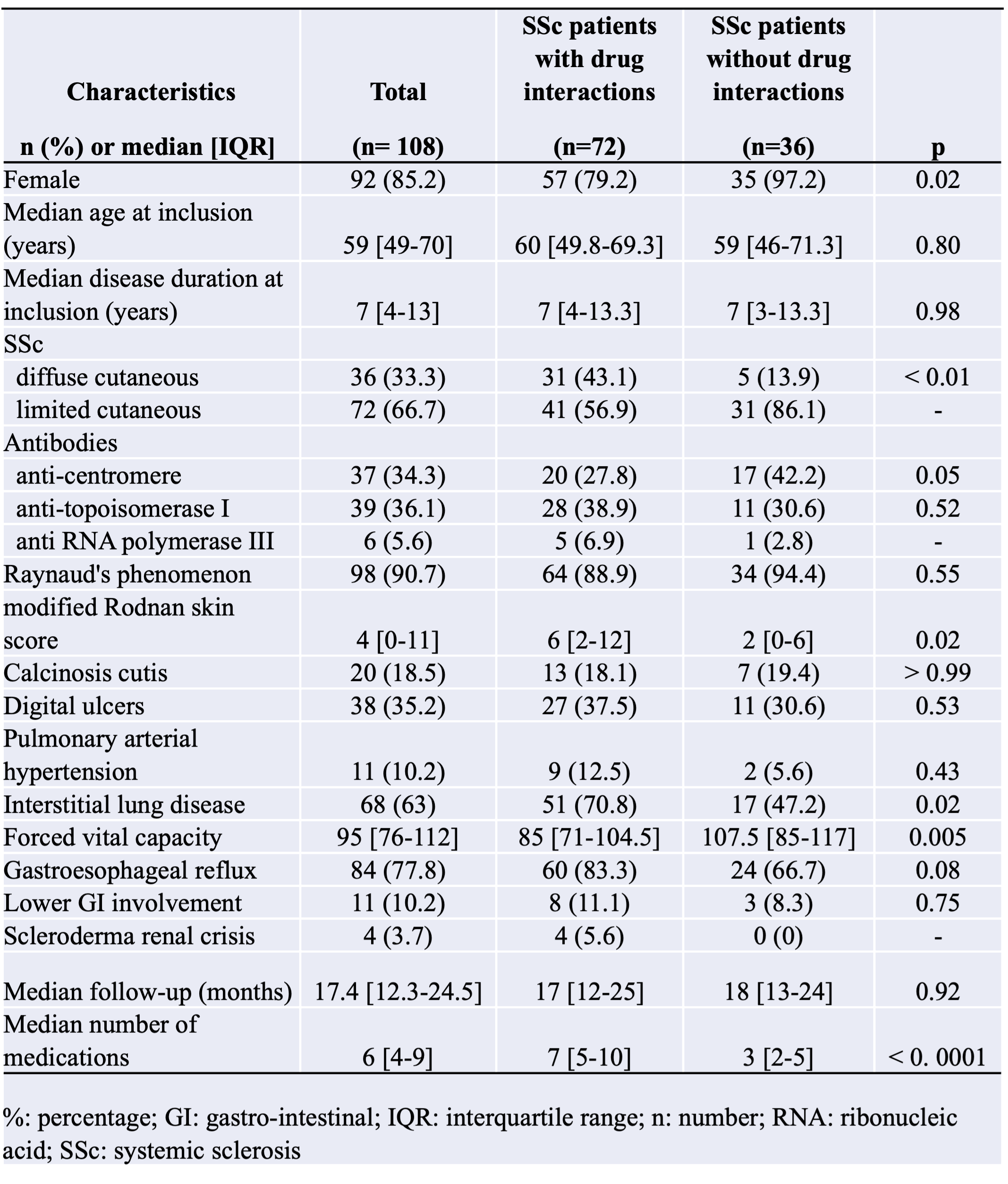
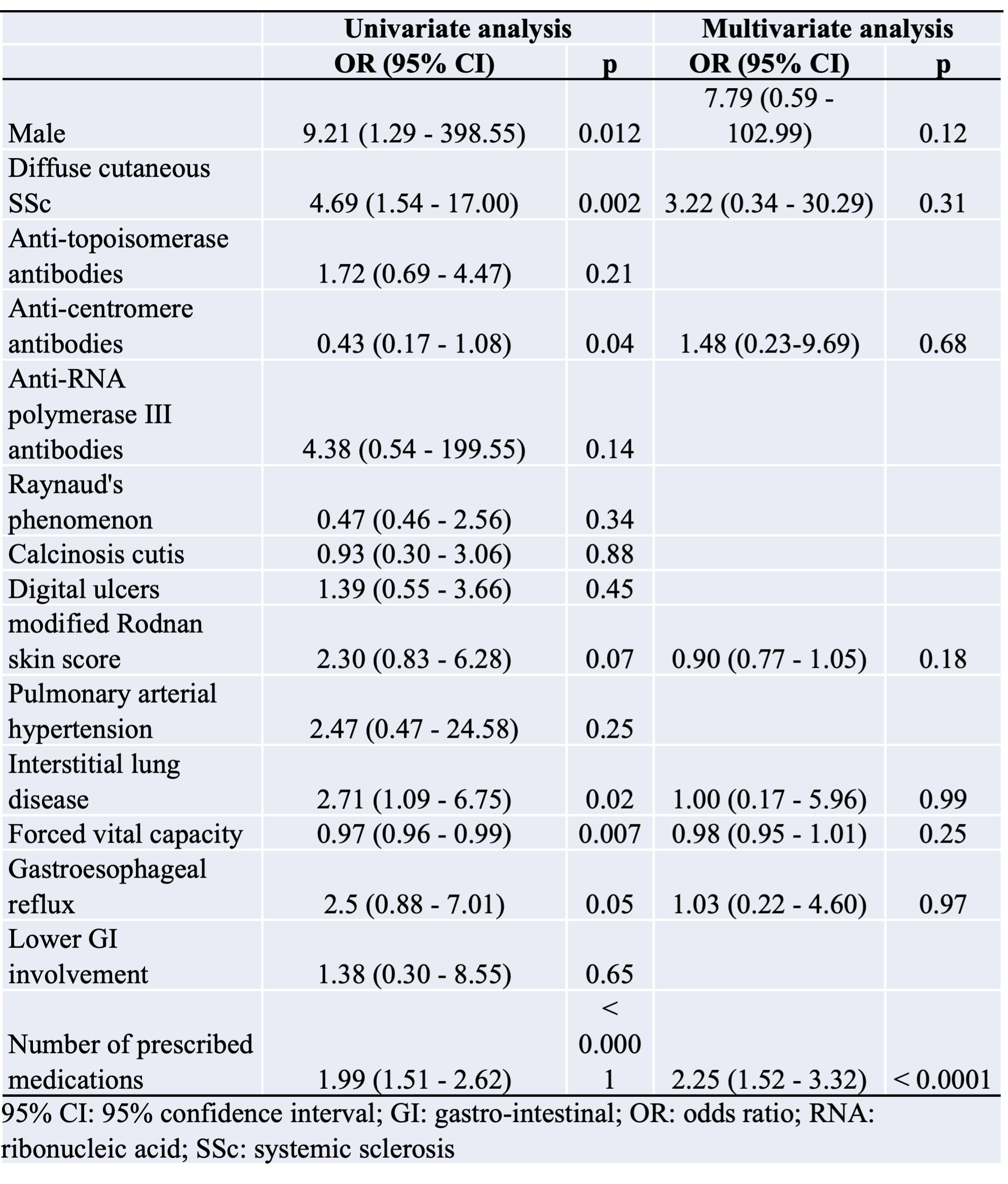
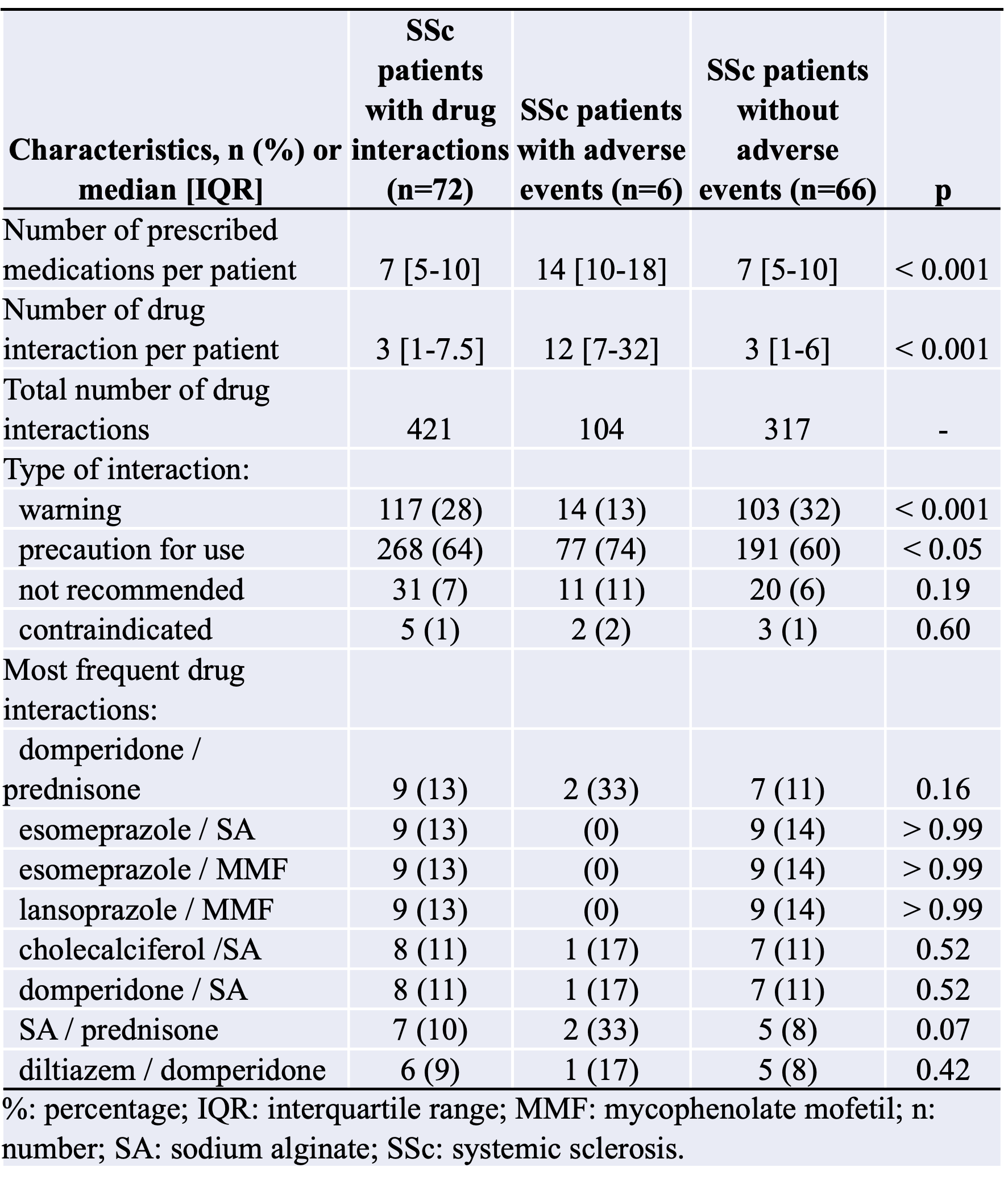
Results: One hundred and eight SSc patients were included. The median number of medications per patient was 6 [4-9]. One hundred and one (93.5%) patients had at least 2 medications on their prescriptions. Seventy-one (65.7%) patients had 5 or more medications, and 23 (21.3%) had 10 or more. Seventy-two (66.7%) patients had DDIs on their prescriptions at inclusion.The median number of DDI per patient was 3 [1-8], with a total number of 421 DDIs in the study (117 (28%) warning, 268 (64%) precautions for use, 31 (7%) recommended, and 5 (1%) contraindicated). Patients with DDIs had more medications than patients without DDIs (7 [5-10] versus 3 [2-5], p< 0.0001). Patients with DDI received significantly more proton-pump inhibitors (p < 0.0001), prednisone (p < 0.0001), MMF (p < 0.001), sodium alginate (p < 0.001), lipid-lowering drugs (p < 0.05), and domperidone (p < 0.01) than patients without.The main DDI involved domperidone-prednisone, esomeprazole-sodium alginate, esomeprazole-MMF, and lansoprazole-MMF. Six (8.3) patients experienced ADRs during the one-year follow-up.One ADR (1.4% of SSc patients with DDI) was classified as grade IV according to CTCAE (cardiac arrest due to ventricular tachycardia), 4 (5.6%) were grade III (falls, orthostatic hypotension, and tendon rupture), and 1 (1.4%) was grade II (Bowen’s disease). Patients with ADRs had more medications (14 [10-18] versus 7 [5-10] p< 0.001) and more DDIs (12 [7-32] versus 3 [1-6]; p< 0.001) than patients without ADRs. Multivariate analysis confirmed that the number of prescribed medications was independently positively associated with DDIs (OR: 2.25 [1.52-3.32], p< 0.0001) as well as with ADRs (OR: 1.68 [1.17 - 2.40], p< 0.01).
Conclusion: SSc patients are significantly exposed to polypharmacy, DDIs and related ADRs, particularly in cases of severe illness, and especially if 5 or more medications are prescribed. Patients with SSc should be routinely screened for polypharmacy, DDI, and ADR.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Boukhlal S, Chouchana L, Saadi M, Casadevall m, cohen P, Dunogue b, Murarasu A, Régent A, Mouthon L, Chaigne B. Polypharmacy, Drug-drug Interactions, and Adverse Drug Reactions Among Systemic Sclerosis Patients: A Cross-sectional Risk Factor Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/polypharmacy-drug-drug-interactions-and-adverse-drug-reactions-among-systemic-sclerosis-patients-a-cross-sectional-risk-factor-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/polypharmacy-drug-drug-interactions-and-adverse-drug-reactions-among-systemic-sclerosis-patients-a-cross-sectional-risk-factor-study/