Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1306–1346) Rheumatoid Arthritis – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The mechanisms of heart failure (HF) risk in RA remain incompletely understood. HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is over-represented in RA, which may be a result of chronic inflammation leading to cardiac remodeling and fibrosis. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are involved in extracellular matrix remodeling, upregulated in RA circulation and synovium, and associate with RA-interstitial lung disease, another fibrotic extra-articular manifestation in RA. We aimed to evaluate the association of plasma MMP concentrations with HF and HF subtype risk in RA.
Methods: In a multicenter, prospective cohort of US Veterans with RA, MMP-1, -3, -7, and -9 were measured from banked plasma at enrollment, using R-PLEX immunoassays (MesoScale Diagnostics). Analyte concentrations were log-transformed and standardized, categorized into quartiles, and dichotomized as high (quartile 4) vs. low (quartiles 1-3). Incident HF was defined as an outpatient HF diagnosis (2+ diagnostic codes at least 30 days apart), HF hospitalization or HF-related death in linked VA, Medicare, and National Death Index data. HF subtypes (HF with reduced EF [HFrEF] < 40%, HFpEF ≥50%) were defined using the most proximate left ventricular EF prior to or < 30 days after HF event (if prior EF was missing), extracted from clinical notes using a validated natural language processing tool. Participants without HF at baseline were followed to incident HF, death, or end of study period (4/2022). The association of MMPs with incident HF and HF subtypes was estimated in multivariable Cox regression models adjusted for age, sex, race, smoking status, BMI, ischemic heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, and DAS28 at baseline. Among patients with prevalent HF, the association of MMPs with risk of future HF hospitalization and HF-related death was tested using similar multivariable Cox regression models.
Results: Among 2,855 participants without HF at baseline (mean age 63 years, 86% male, mean DAS28 3.5) 488 HF diagnoses (Nf115 HFrEF, 246 HFpEF) were identified over a median follow up of 7 years. In fully adjusted models, MMP-7 was associated with incident HF risk (per 1 SD aHR 1.21 [1.09-1.35]; Table 1) in a dose-dependent manner (quartile (Q)4 vs. Q1 aHR 1.68 [1.27-2.22], p-for-trend < 0.01). This was driven by a stronger association with HFpEF (high vs. low aHR 1.45 [1.10-1.91]; Figure 1) compared with HFrEF (high vs. low aHR 0.97 [0.63-1.49]). While a trend toward higher HF risk was observed with higher MMP-1 (Q4 vs. Q1 aHR 1.26 [0.96-1.67], p-for-trend = 0.08) and MMP-3 quartiles (Q4 vs. Q1 aHR 1.24 [0.94-1.64], p-for-trend = 0.07), these were not significant (Table 1). Among patients with prevalent HF (Nf349), MMP-7 was associated with future HF hospitalization and HF-related death (high vs. low aHR 1.91 [1.23-2.97]; Table 2).
Conclusion: MMP-7 was associated with incident HFpEF and a higher risk of HF hospitalization or HF-related death in RA patients with prevalent HF, independent of traditional risk factors and RA disease activity. These findings support MMPs may play a role in cardiac remodeling and dysfunction in RA. Continued research is needed to incorporate these findings into clinical risk stratification and HF prevention strategies in RA.
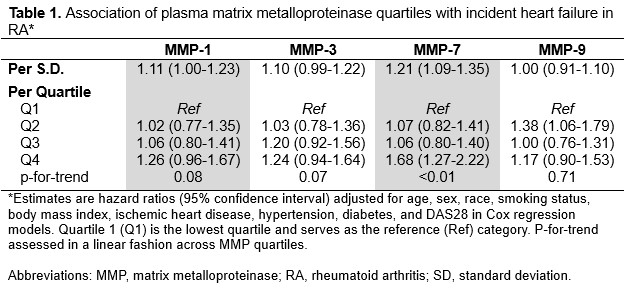 Table 1. Association of Plasma MMP Quartiles with Incident Heart Failure in RA
Table 1. Association of Plasma MMP Quartiles with Incident Heart Failure in RA
.jpg) Figure 1. Association of high (quartile 4) vs. low (quartiles 1-3) MMP concentrations with HF subtypes in RA.
Figure 1. Association of high (quartile 4) vs. low (quartiles 1-3) MMP concentrations with HF subtypes in RA.
.jpg) Table 2. MMP Concentrations and risk of HF-related hospitalization or death in RA patients with prevalent HF.
Table 2. MMP Concentrations and risk of HF-related hospitalization or death in RA patients with prevalent HF.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Johnson T, Duryee M, Roul P, Cannon G, Kunkel G, Wallace B, Smith I, Richards J, Wysham K, Kerr G, Reimold A, Schwab P, Anderson D, Baker J, Thiele G, Mikuls T, England B. Plasma Matrix Metalloproteinases and Heart Failure Outcomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/plasma-matrix-metalloproteinases-and-heart-failure-outcomes-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/plasma-matrix-metalloproteinases-and-heart-failure-outcomes-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/
