Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Although immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) cancer treatments are known to activate cytotoxic T-cells, autoantibodies may also contribute to the development of immune-related adverse events (irAE). Patients with ICI-associated myositis are said to rarely have autoantibodies. We performed a systematic literature review of irAE cases and case series to determine the prevalence of autoantibodies in patients with ICI-induced myositis, myasthenia gravis (MG) and/or myocarditis, and to identify characteristics of seropositive and seronegative patients.
Methods: PubMed, Embase and Cochrane databases were searched for reports of ICI-induced irAE. Publications were included if they provided results of autoantibody testing at the individual patient level. Here we report on the subset of publications describing ICI-induced myositis, MG and/or myocarditis. Descriptive statistics were used to summarize results.
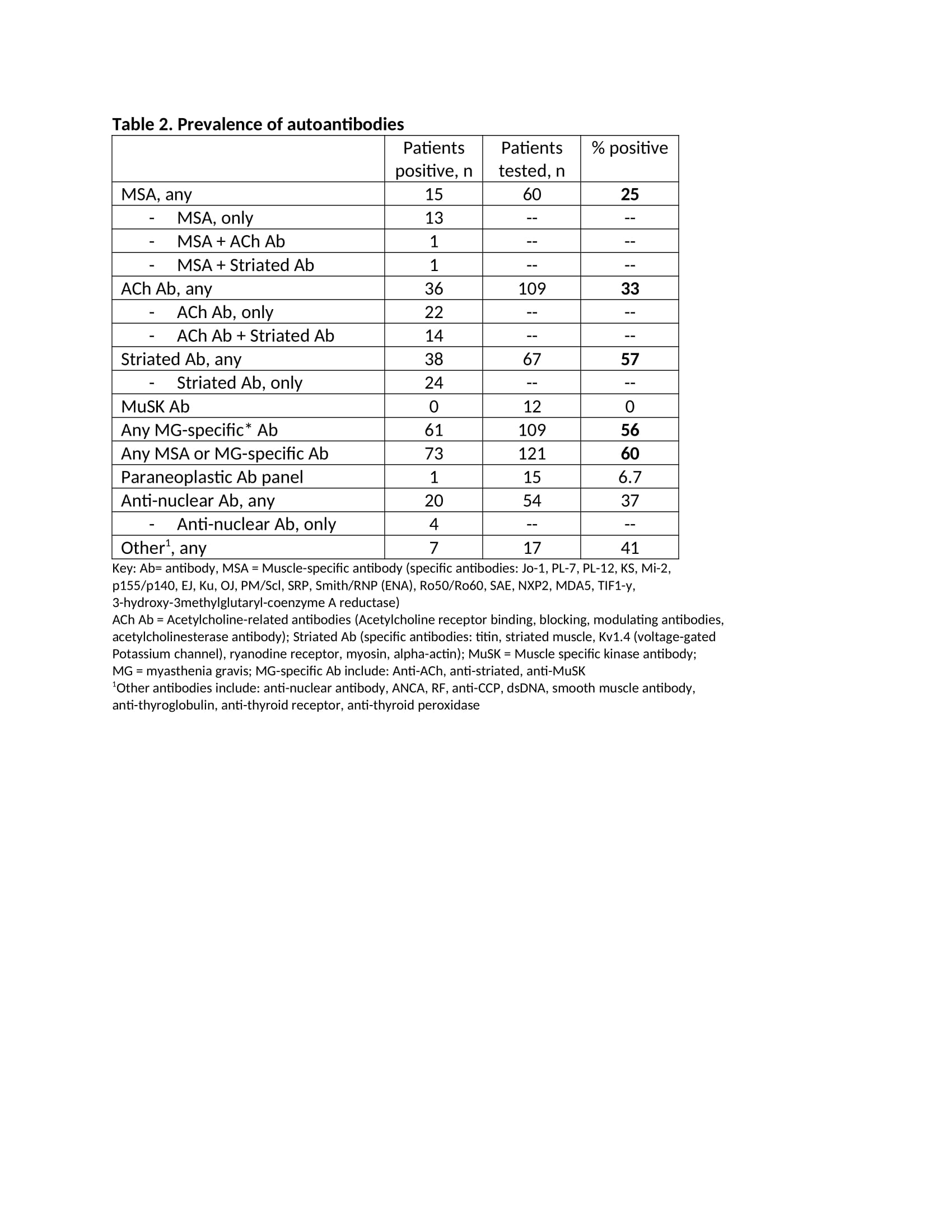
Results: We screened 12,207 articles and subsequently, 1249 full texts. We included 69 publications that described autoantibody testing in 150 patients with myositis, MG and/or myocarditis. Eighty-nine patients (59%) had at least one autoantibody, including 4 of 5 tested patients with myocarditis alone, and 5 of 6 with the combination of myositis, MG and myocarditis (Table 1). The prevalence of autoantibodies was the same across ICI and cancer types. Seropositive patients had a higher median creatinine phosphate kinase (CPK) (4300 u/L vs. 1959 u/L), a slightly earlier time of irAE onset (3.6 weeks vs. 4.1 weeks) and were less likely to resolve their irAE (27% vs 45%). Sixty percent of tested patients had a muscle-specific antibody (MSA) (25%) and/or MG-specific (56%) antibody (Table 2). Only 1/15 tested patients had a paraneoplastic autoantibody, while 20/54 (37%) tested were ANA positive. Over 90% of patients with MSA or striated antibodies presented with myositis, whereas 17/22 (77%) with only Acetylcholine-related antibodies (ACh) presented with MG (Table 3). A subset of patients (n=14) with both anti-striated and anti-ACh presented with variable myositis and MG symptoms. Patients with anti-ACh had worse irAE outcomes – only 10% with symptom resolution and 48% died.
Conclusion: Almost two-thirds of patients with ICI-induced myositis, MG and/or myocarditis have autoantibodies. Patients with myositis typically have MSA or striated antibodies. The presence of anti-ACh in isolation is found almost exclusively in patients presenting with MG and these patients tend to have a worse prognosis. Prospective studies are needed to determine whether autoantibodies are present prior to ICI and could serve as biomarkers of future serious irAE.
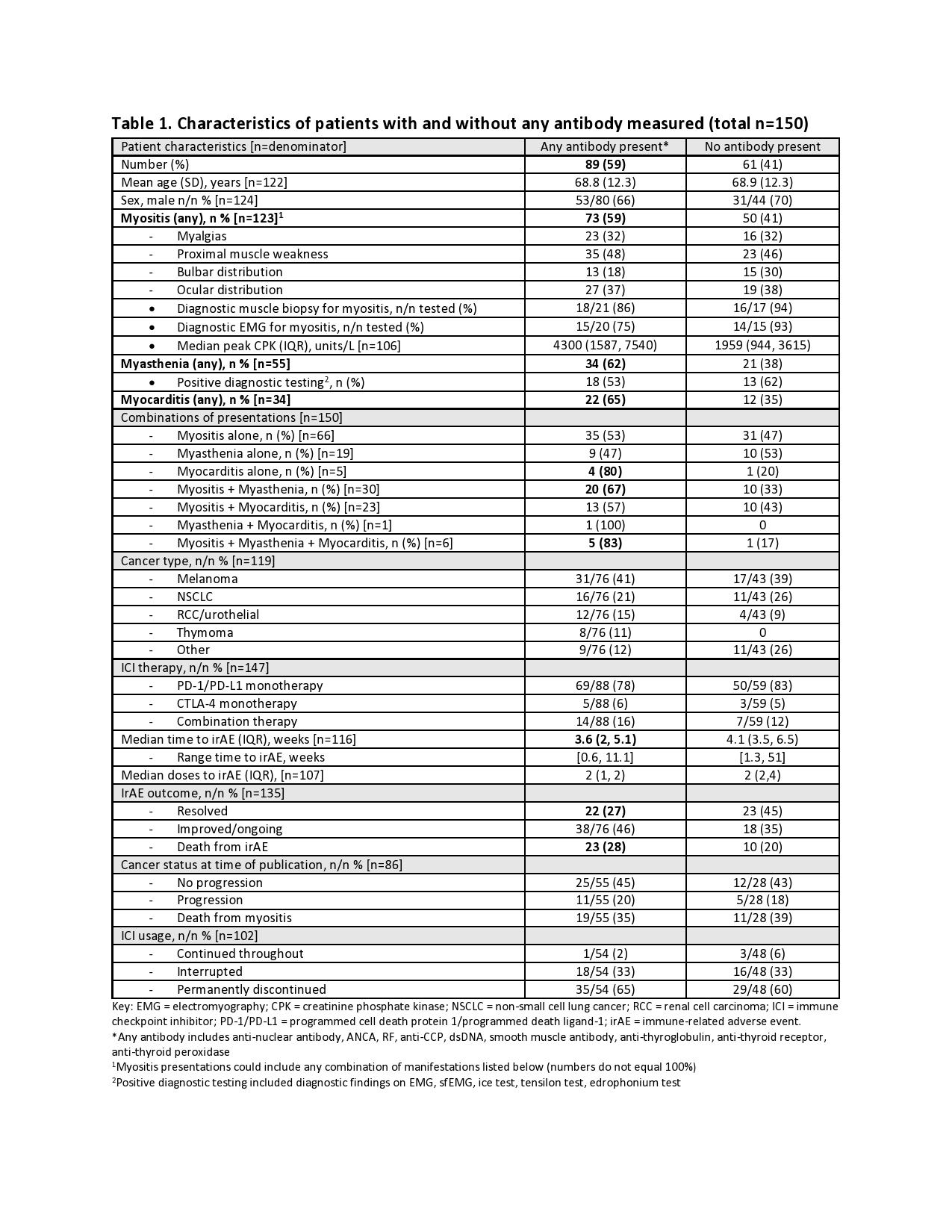 Characteristics of seropositive and seronegative patients
Characteristics of seropositive and seronegative patients
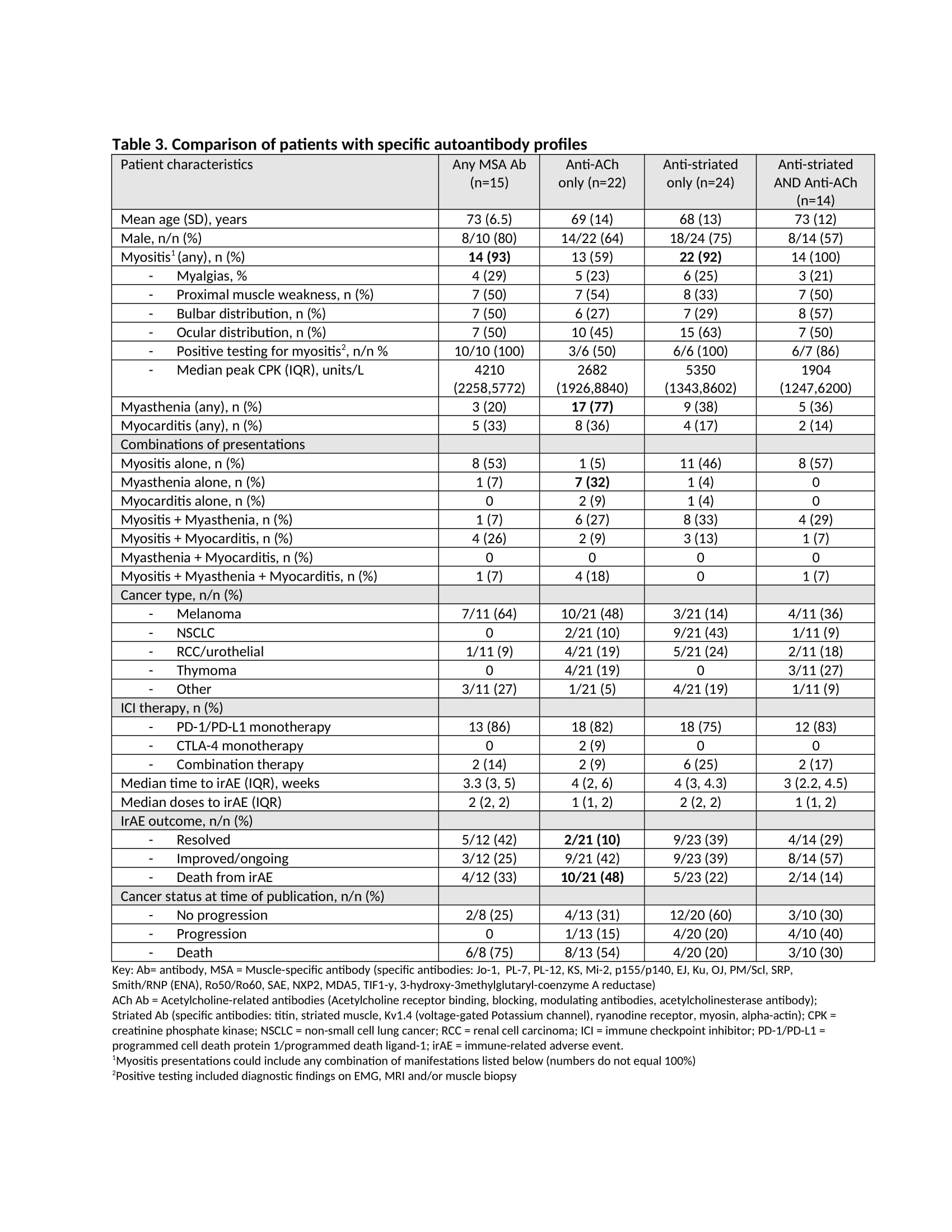 Characteristics of patients with specific autoantibody profiles
Characteristics of patients with specific autoantibody profiles
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ghosh N, Chan K, Jivanelli B, Bass A. Over Half of Patients with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-related Myositis, Myasthenia Gravis and/or Myocarditis Have Autoantibodies: Results from a Systematic Literature Review [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/over-half-of-patients-with-immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-related-myositis-myasthenia-gravis-and-or-myocarditis-have-autoantibodies-results-from-a-systematic-literature-review/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/over-half-of-patients-with-immune-checkpoint-inhibitor-related-myositis-myasthenia-gravis-and-or-myocarditis-have-autoantibodies-results-from-a-systematic-literature-review/