Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (0934–0964) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) and keloid are typical skin fibrotic diseases with unclear epigenetic mechanisms and clinical targets. As an important epigenetic regulatory factor, microRNAs play an important role in the occurrence and development of fibrosis in recent studies. This study aimed to assess the role of miR-3606-3p in skin fibrosis and the therapeutic potential.
Methods: The levels of miR-3606-3p were detected in SSc and keloid patients by qPCR and in situ hybridization. RNA-seq, in silico software and luciferase were performed to investigate the targets of miR-3606-3p. The effects of miR-3606-3p, GAB1 and ITGAV on fibroblast fibrogenesis, inflammation and migration were assessed in primary dermal fibroblasts by qPCR, western blotting, wound healing scratch assay. Histology, immunofluorescence analysis and in vivo imaging techniques were used to evaluate the effect of miR-3606-3p on alleviating skin fibrosis in keloid-bearing mice.
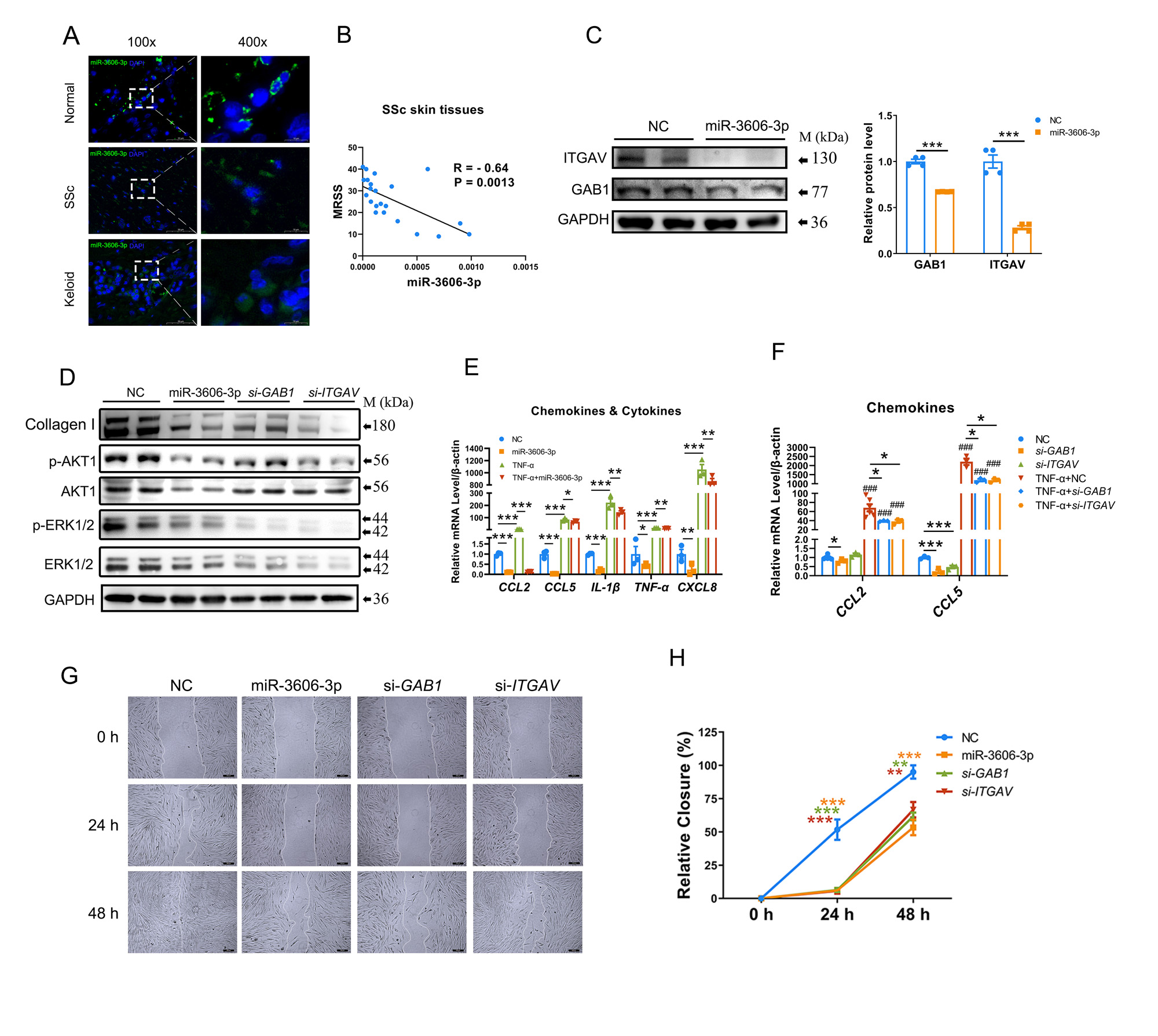
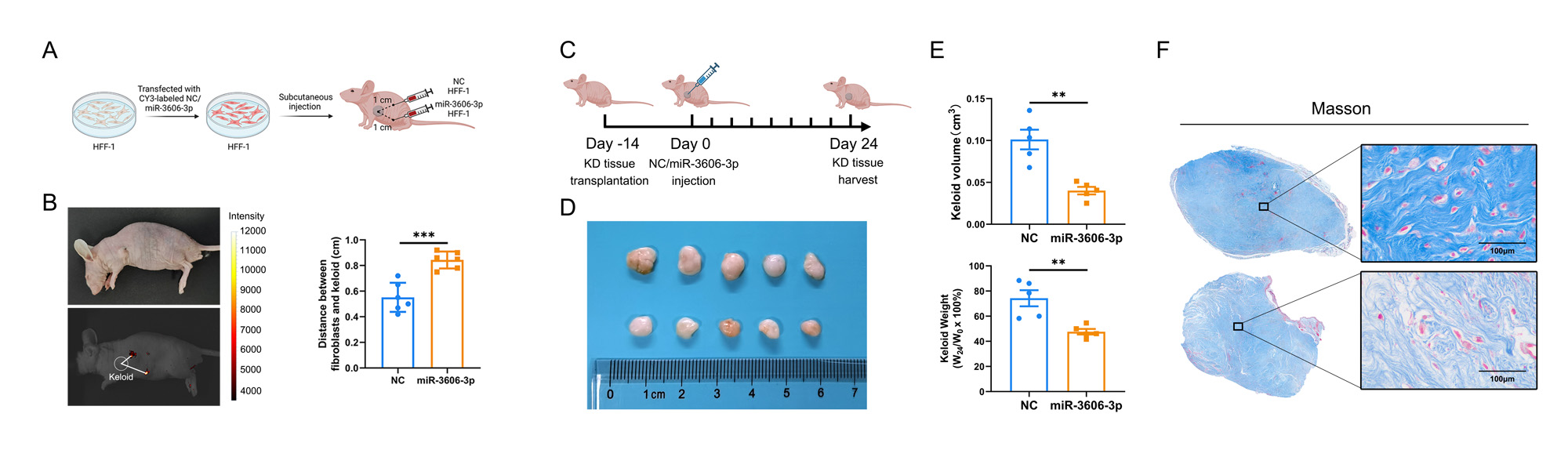
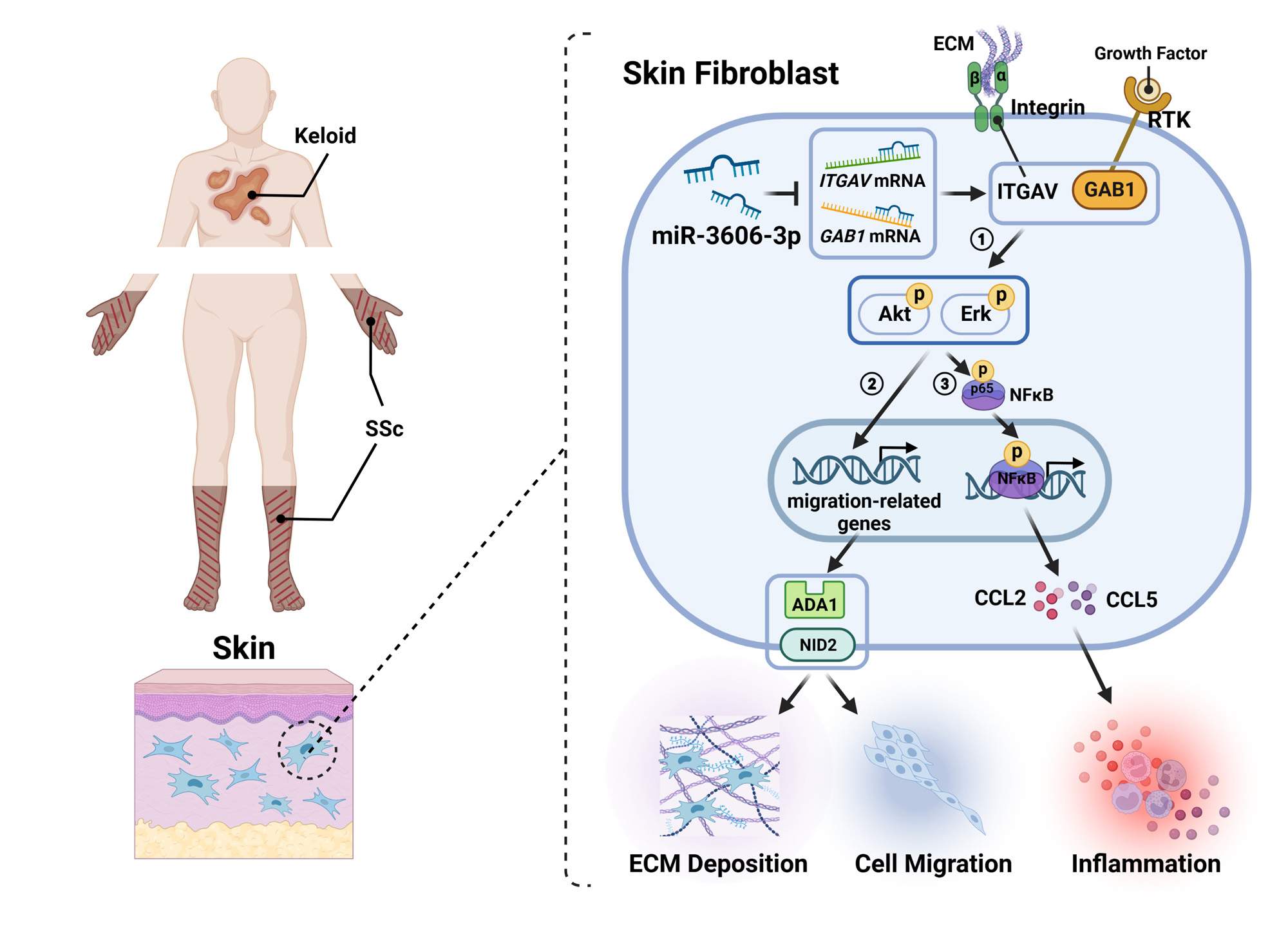
Results: MiR-3606-3p was reduced in the skin tissues and fibroblasts from both SSc and keloid patients and negatively correlated with disease severity. RNA-seq analysis and in silico prediction indicated GRB2 associated binding protein 1 (GAB1) and integrin subunit alpha V (ITGAV) were potential targets of miR-3606-3p. We then found that miR-3606-3p downregulated both GAB1 and ITGAV by directly targeting their 3′-UTRs, and further reduced p-AKT and p-ERK activities to inhibit collagen synthesis and NF-κB induced fibroblast inflammation. Furthermore, miR-3606-3p inhibited fibroblast migration in primary fibroblasts and keloid-bearing nude miceby wound healing scratch assay and in vivoimaging techniques respectively. In contrast, GAB1 and ITGAV were upregulated in SSc and keloid patients, and siRNA-mediated GAB1 or ITGAV knockdown replicated the phenotypes observed in miR-3606-3p-overexpressing fibroblasts, including inflammation, migration and fibrogenesis (Figure 1). Finally, by constructing the humanized mouse model of transplanted keloid graft, we found that miR-3606-3p treatment inhibits GAB1 and ITGAV leading to significantly alleviate skin fibrosis (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Our results indicated miR-3606-3p inhibits ECM deposition, inflammation, and migration of fibroblasts by downregulating GAB1 and ITGAV. miR-3606-3p-enhancing strategies may have beneficial effects on skin fibrosis through lowing p–AKT/p–ERK activity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
chen y, shi M, Wang W, Shi C, Xia X, Wu w, Wang J, Shi X. MiR-3606-3p Alleviates Skin Fibrosis by Suppressing Fibroblast Inflammation and Migration via Inhibiting GAB1 and ITGAV [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mir-3606-3p-alleviates-skin-fibrosis-by-suppressing-fibroblast-inflammation-and-migration-via-inhibiting-gab1-and-itgav/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/mir-3606-3p-alleviates-skin-fibrosis-by-suppressing-fibroblast-inflammation-and-migration-via-inhibiting-gab1-and-itgav/