Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Studies have found autoantibodies (Ab) directed against heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A2/B1 (anti-RA33), peptidyl arginine deiminase 4 (anti-PAD4) and carbamylated proteins (anti-CarP) each have diagnostic value for RA. However, it is not clear whether these Ab each recognize the same subset, or distinct subsets, of seronegative RA (SN-RA) patients. The present study evaluated the performance of these Ab individually and as a combined panel to determine the clinical validity in a U.S. cohort enriched for SN-RA.
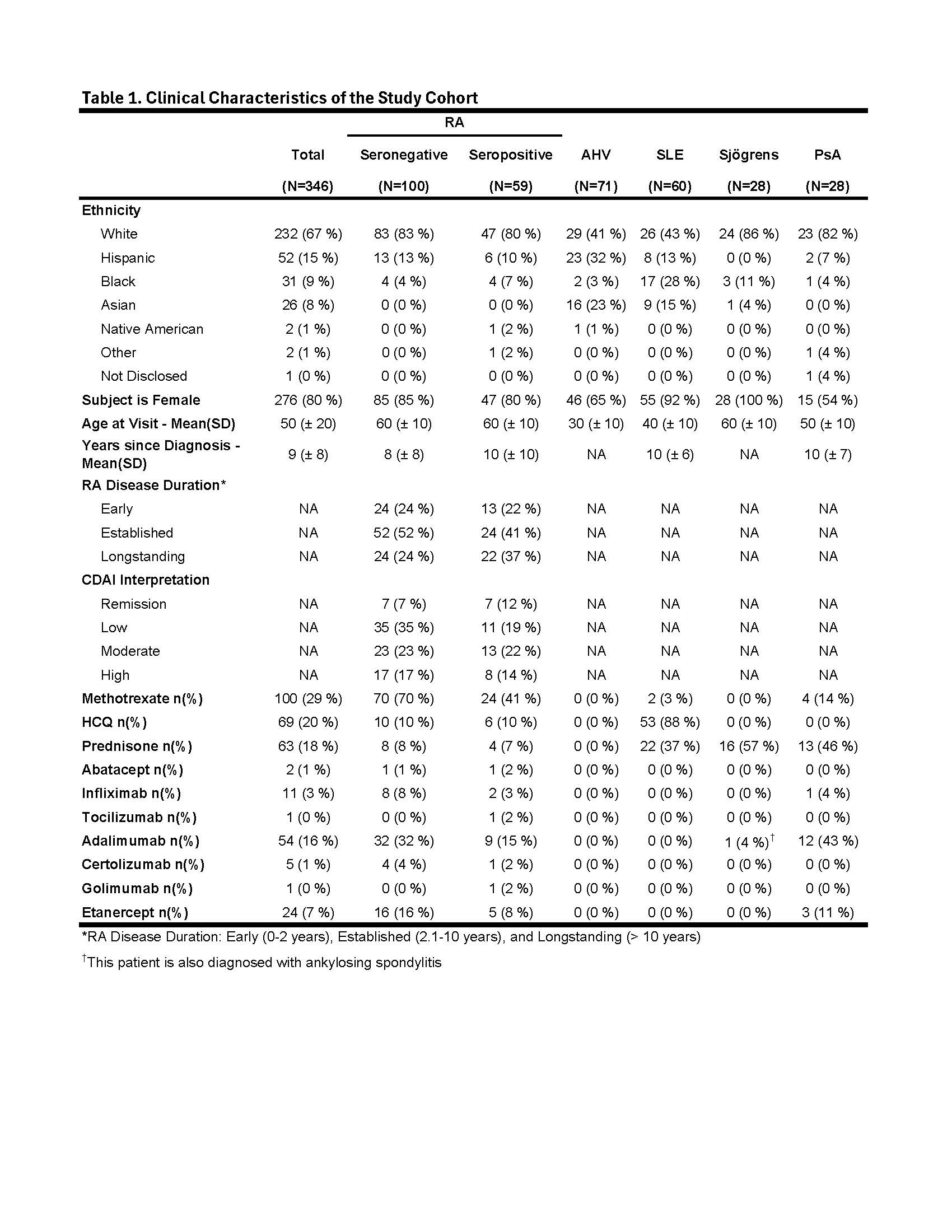
Methods: A cohort of 346 subjects, including 159 RA meeting 2010 ACR classification criteria, 71 apparently healthy volunteers (AHV), 60 SLE meeting the 1997 ACR criteria, 28 clinically diagnosed Sjögrens Syndrome and 28 clinically diagnosed PsA subjects were consented for Ab testing. Enzyme-linked immunoassay (ELIA) testing was performed to measure anti-CCP2 IgG, RF (IgA and IgM) and anti-RA33 (IgA, IgG and IgM) [research use only, RUO; Phadia, Thermo Fisher]. Anti-PAD4 (RUO, IgA & IgM) and anti-CarP IgG Ab (RUO) were measured by ELISA (provided by Werfen as RUO under a research grant). Cutoffs for anti-CCP, RF and Anti-CarP were based on manufacturer’s specifications or as previously established. Anti-RA33 and Anti-PAD4 Ab cutoffs for each isotype were set above the 95th percentile for AHVs. RA subjects testing negative for anti-CCP and RF IgM and IgA were considered SN-RA for the purposes of analysis. Chi-square analyses were performed to compare the frequency of Ab among RA subsets. ROC analysis was performed to compare conventional RA Abs to a combination of conventional and SN-RA markers.
Results: The SN-RA cohort (N = 100) was majority white (83%), female (85%) with a mean (SD) age of 57.4 (± 12.8) years (Table 1). Cumulatively, 42% of the SN-RA group were positive for one or more biomarker with sensitivities for RA of 16%, 11% and 25% for anti-RA33 IgA/IgG/IgM, anti-CarP IgG and anti-PAD4 IgA/IgM, respectively (Fig. 1A). Seropositive RA (SP-RA) subjects (N = 59) were similarly majority white (80%), female (80%) with a mean (SD) age of 56.4 (± 12.9) years. Collectively, 70% of SP-RA subjects were positive for one or more biomarker with sensitivity for RA of 30%, 23% and 43% for anti-RA33, anti-CarP and anti-PAD4, respectively (Fig. 1B). The frequency of mono-specific anti-PAD4 (IgA or IgG) Ab was similar (8% vs. 9%) to the frequency of double positive anti-PAD4 (IgA and IgG) SN-RA (Fig. 1C). Contrasting with the SN-RA group, anti-PAD4 IgA alone was significantly less frequent than anti-PAD4 IgG and IgA double positive in SP-RA (3% vs. 13%, p < 0.05) (Fig. 1D). Among other autoimmune diseases, anti-RA33, anti-CarP and anti-PAD4 Ab were present in 10-30% of subjects, similar to the frequency of RF IgA and IgM (12-17%) in SLE (Fig. 2).
Conclusion: Anti-RA33, anti-CarP and anti-PAD4 Ab identify over 40% of the SN-RA population, with each biomarker having limited overlap among distinct subsets. Previous studies indicate that anti-CarP and anti-PAD4 are associated with more severe RA, while anti-RA33 correlates with milder disease. This combination of biomarkers may provide clinically meaningful sensitivity for SN-RA and complementary prognostic insights in the early assessment of inflammatory arthritis.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Concoff A, Warsi T, Taghavi S, Kumar S, Patalinghug A, Schleif C, Partain B, Ahearn J, Manzi S, Mahler M, Joy V, O'Malley T. Maximizing Diagnostic Sensitivity: Combined Anti-RA33, Anti-CarP, and Anti-PAD4 Autoantibodies in Seronegative Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/maximizing-diagnostic-sensitivity-combined-anti-ra33-anti-carp-and-anti-pad4-autoantibodies-in-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/maximizing-diagnostic-sensitivity-combined-anti-ra33-anti-carp-and-anti-pad4-autoantibodies-in-seronegative-rheumatoid-arthritis/