Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-3:50PM
Background/Purpose: During treatment with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) such as the anti-PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab, 2-4% of cancer patients develop inflammatory arthritis as an immune-related adverse event (IRAE). These IRAEs show striking similarities with inflammatory arthritis and are linked with immune activation. However, the underlying immunological mechanisms are not well characterized.
Methods: We included synovial fluid mononuclear cells (SFMCs, n=31) and peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs, n=6) from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and peripheral spondyloarthritis and PBMCs from healthy controls (n=6).Pembrolizumab-treated cells were analyzed using flowcytometry and pro-inflammatory multiplex assays. The mitigation of the effects of pembrolizumab treatment was compared for the disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) adalimumab, tocilizumab, tofacitinib, and baricitinib.
Results: Pembrolizumab significantly increased MCP-1 production by arthritis SFMCs (P=0.0031) but not by PBMCs from patients or healthy controls (P=0.77 and P=0.43). In SFMCs, pembrolizumab increased the production of TNFα(P=0.049), IFNγ (P=0.047), and IL-12p70 (P=0.031), but did not change the production of IL-6 (P=0.98). The SFMCs treated with pembrolizumab showed an increased frequency of intermediate monocytes (P=0.044) and increased the MCP-1 production only within the intermediate monocyte subset (P=0.028) (Figure 1). Lastly, adalimumab, baricitinib, and tofacitinib treatment were able to attenuate the pembrolizumab-induced MCP-1 production (P=0.0004, P=0.033, and P=0.025, respectively) while this was not seen with tocilizumab treatment (P=0.75) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: We have established an in vitro model to study the immunological reactions caused by pembrolizumab. In this model, pembrolizumab specifically activated intermediate monocytes and induced TNFα, IFNγ, and IL-12p70 production, whereas IL-6 was unchanged.
 Figure 1: MCP-1 production in the monocyte subsets following treatment with pembrolizumab. (A) Representative dotplots of MCP-1 production in classical monocytes. (B) Representative dotplots of MCP-1 production in intermediate monocytes. (C) Upper panel: Frequency of MCP-1+ cells in classical monocytes in each culture. Lower panel: Data were normalized and expressed as ratios. (D) Upper panel: Frequency of MCP-1+ cells in intermediate monocytes in each culture. Lower panel: Data were normalized and expressed as ratios. All data are expressed as median + 95% Confidence interval. * p-value < 0.05, ** p-value < 0.01, *** p-value < 0.001. UT, untreated; Pembro, Pembrolizumab ; CM, Classical monocytes ; IM, intermediate monocytes.
Figure 1: MCP-1 production in the monocyte subsets following treatment with pembrolizumab. (A) Representative dotplots of MCP-1 production in classical monocytes. (B) Representative dotplots of MCP-1 production in intermediate monocytes. (C) Upper panel: Frequency of MCP-1+ cells in classical monocytes in each culture. Lower panel: Data were normalized and expressed as ratios. (D) Upper panel: Frequency of MCP-1+ cells in intermediate monocytes in each culture. Lower panel: Data were normalized and expressed as ratios. All data are expressed as median + 95% Confidence interval. * p-value < 0.05, ** p-value < 0.01, *** p-value < 0.001. UT, untreated; Pembro, Pembrolizumab ; CM, Classical monocytes ; IM, intermediate monocytes.
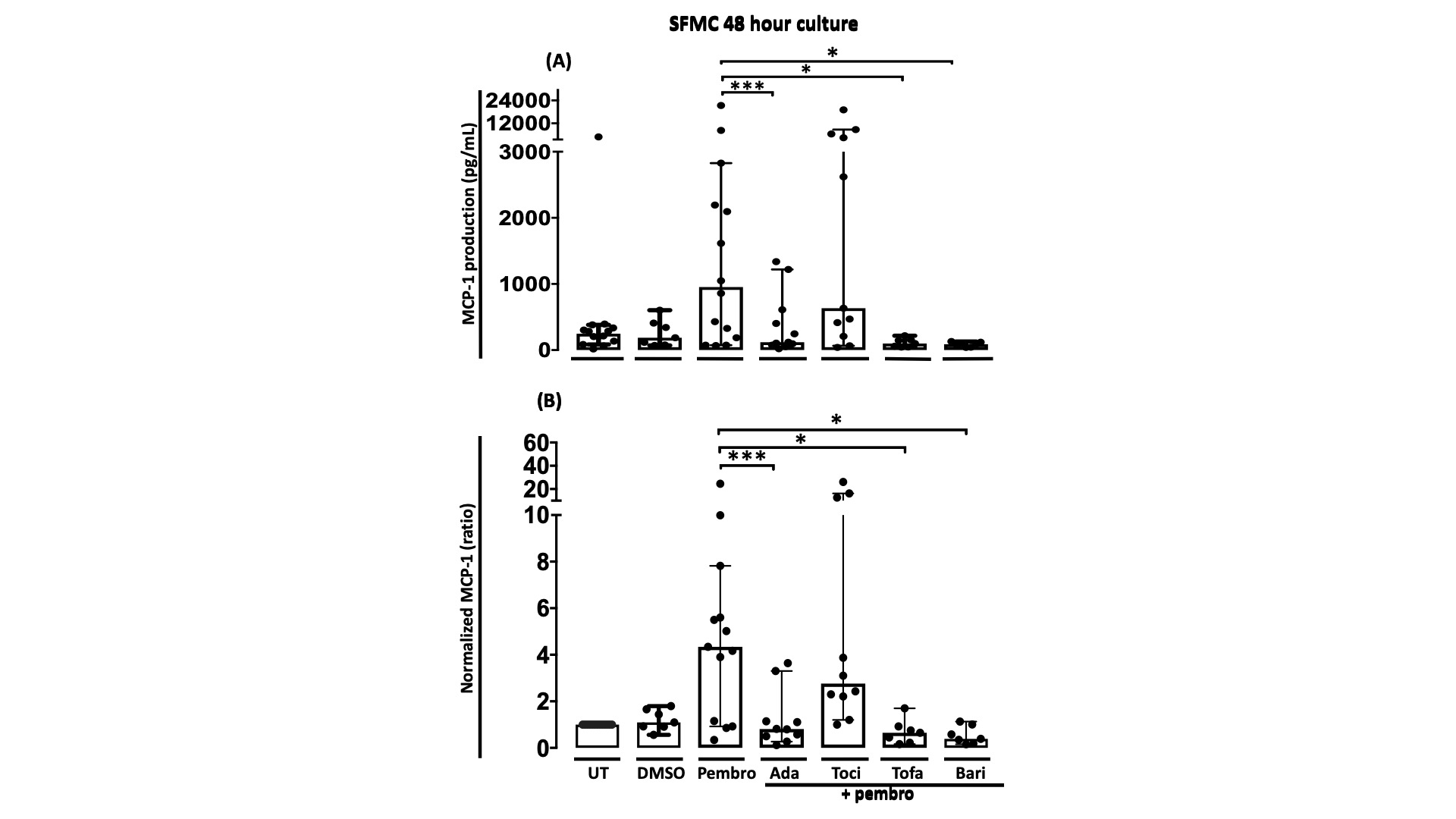 Figure 2: MCP-1 production in SFMC cultures treated with pembrolizumab combined with different DMARDs A) MCP-1 production in SFMCs cultured for 48 h untreated (UT)(n=13) or treated with DMSO (n=7), pembrolizumab (n=13), pembrolizumab + adalimumab (n=10), pembrolizumab + tocilizumab (n=10), pembrolizumab + tofacitinib (n=7) or pembrolizumab + baricitinib(n=7). B) Data were normalized to untreated cultures and expressed as ratios. Data is expressed as median + 95% Confidence interval. * p-value < 0.05, ** p-value < 0.01, *** p-value < 0.001. DMSO, Dimethyl sulfoxide; Pembro, Pembrolizumab; Ada, Adalimumab; Toci, Tocilizumab ; Tofa, Tofacitinib ; Bari, Baricitinib.
Figure 2: MCP-1 production in SFMC cultures treated with pembrolizumab combined with different DMARDs A) MCP-1 production in SFMCs cultured for 48 h untreated (UT)(n=13) or treated with DMSO (n=7), pembrolizumab (n=13), pembrolizumab + adalimumab (n=10), pembrolizumab + tocilizumab (n=10), pembrolizumab + tofacitinib (n=7) or pembrolizumab + baricitinib(n=7). B) Data were normalized to untreated cultures and expressed as ratios. Data is expressed as median + 95% Confidence interval. * p-value < 0.05, ** p-value < 0.01, *** p-value < 0.001. DMSO, Dimethyl sulfoxide; Pembro, Pembrolizumab; Ada, Adalimumab; Toci, Tocilizumab ; Tofa, Tofacitinib ; Bari, Baricitinib.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sørensen A, Andersen M, Juul-Madsen K, Deisting Skejø C, Schmidt H, Vorup-Jensen T, Kragstrup T. In Vitro Characterization of Inflammatory Arthritis Associated with Immune Check Point Inhibition [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-vitro-characterization-of-inflammatory-arthritis-associated-with-immune-check-point-inhibition/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/in-vitro-characterization-of-inflammatory-arthritis-associated-with-immune-check-point-inhibition/
