Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: T Cell Biology & Targets in Autoimmune & Inflammatory Disease Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) is a rare and severe autoimmune disease, characterized by a pauci-immune necrotizing vasculitis leading to inflammation and damage of major organs. ANCAs targeting proteinase-3 (PR3) or myeloperoxidase (MPO), and ANCA-producing B cells play a central role in the pathogenesis of AAV. Autoreactive T cells and their features are less well-studied, but recent studies emphasize their importance in AAV. In this study we aimed to investigate autoreactive T cells and their cytotoxic responses in AAV.
Methods: Single cell RNA and TCR sequencing combined with CITE-seq staining was performed of isolated T cells from healthy controls (HC) (n=4), anti-MPO+ AAV (n=5) and anti-PR3+ AAV (n=4) patients. Secondly, PBMCs of these patients were stimulated in vitro with anti-CD3, Np/pp65, MPO or PR3 autoantigens in combination with anti-CD28 and IL-2 for 72h. After culturing, T cells were analyzed with flow cytometry for activation, proliferation and cytotoxic responses.
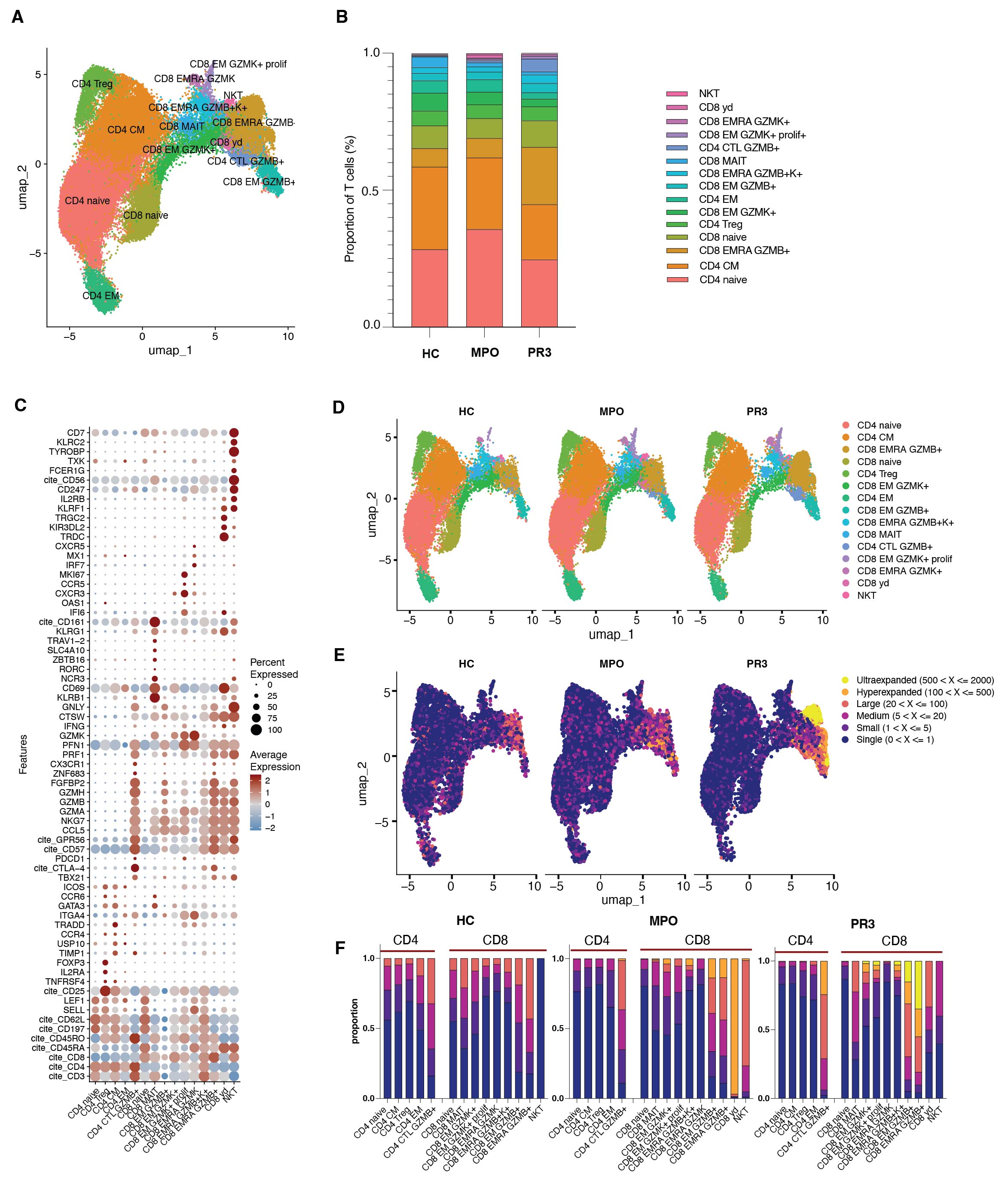
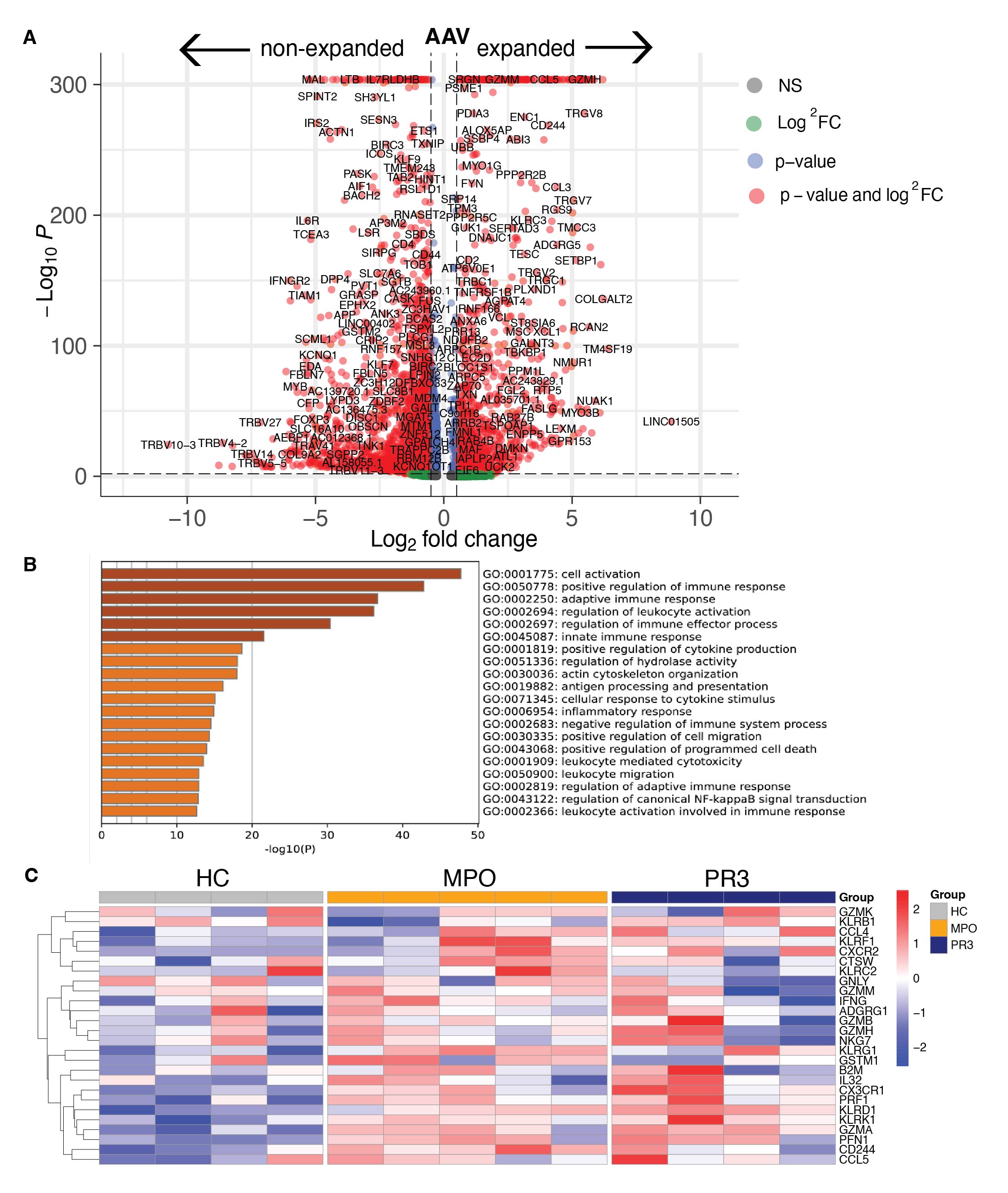
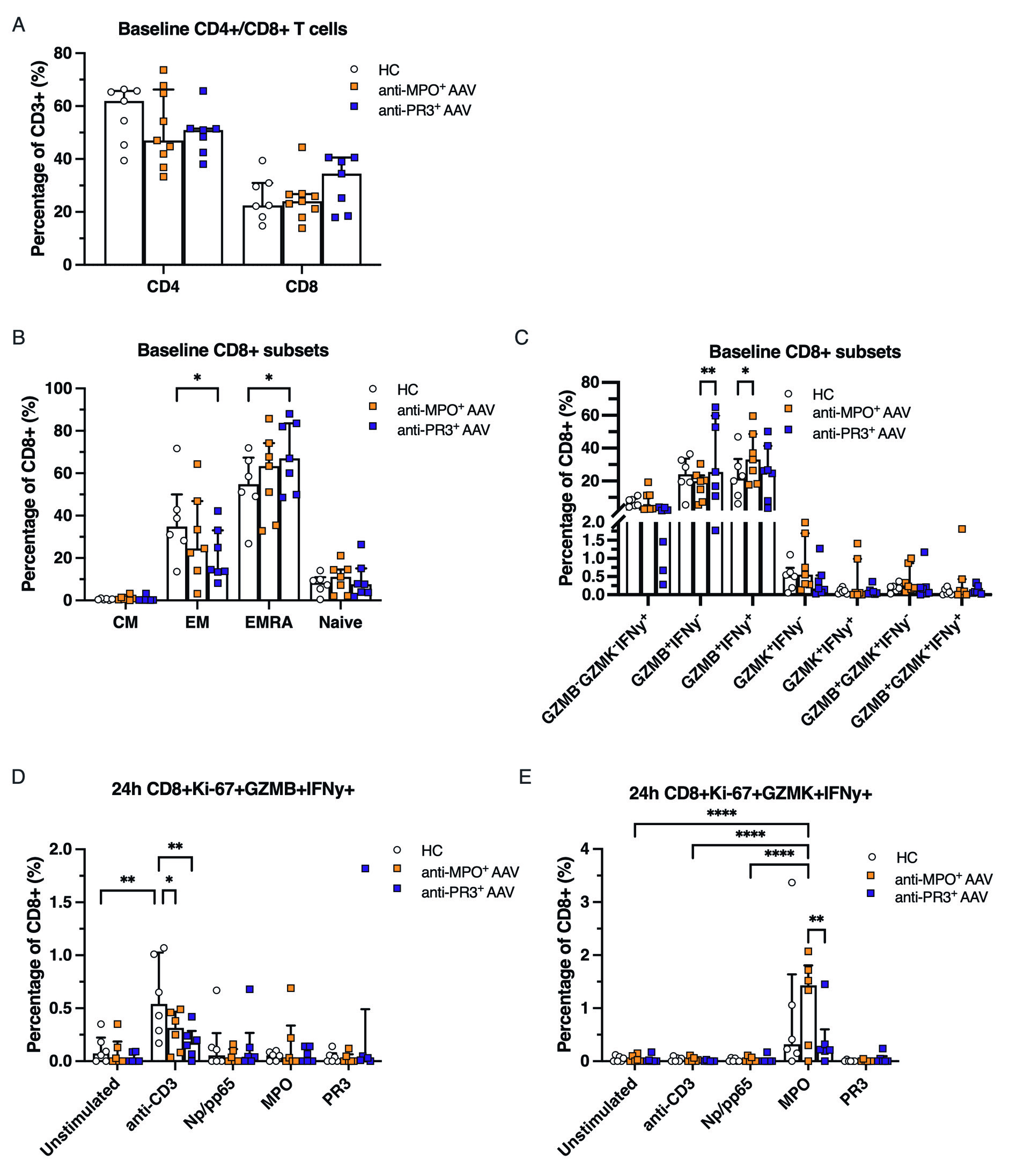
Results: We identified 15 clusters of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells based upon differential gene expression in AAV patients (n=9) and HCs (n=4) (Fig 1A-C). Anti-PR3+ AAV patients exhibited increased effector memory cells re-expressing CD45RA+ (EMRA) GZMB+ CD8+ T cells (20.8%) versus HC (6.7%) (p=0.03) and anti-MPO+ AAV patients (7.2%) (p=0.04) (Fig 1B,D). Both anti-MPO+ and anti-PR3+ AAV patients had large populations of clonally hyperexpanded T cells, which were found mostly in the GZMB+ but also in the GZMK+ CD8+ T cell subsets, which was not observed in HCs (Fig 1E-F). Expanded T cells in AAV patients had increased expression of cytotoxic and tissue homing genes, such as GZMB, NKG7, CST7, CCL5, PRF1, GPR56, CX3CR1 and TBX21 (Fig 2A). Gene ontology (GO) pathway analysis demonstrated that the significantly upregulated genes of expanded T cells in AAV were involved in cell activation and positive regulation of the immune response (Fig 2B). Specifically, CD8 EMRA GZMB+ T cells of AAV patients had significantly increased expression of highlighted cytotoxic and tissue homing genes as compared to HCs (Fig 2C). Secondly, flow cytometry confirmed the increased proportion of CD8 EMRA and GZMB+ CD8+ T cells in anti-PR3 AAV patients (Fig 3A-C), whereas anti-MPO+ AAV patients had increased levels of GZMB+IFNy+ CD8+ T cells as compared to HCs (Fig 3C). 24h of anti-CD3/anti-CD28 stimulation, used as a positive control in the culture assay, induced GZMB+IFNy+ responses in CD8+ T cells in all samples, which was most pronounced in HCs, and not observed after MPO or PR3 stimulation in AAV patients (Fig 3D). On the other hand, MPO specifically induced expansion and proliferation of GZMK+IFNy+ CD8+ T cells in anti-MPO+ AAV patients, in contrast to anti-PR3+ AAV patients and HCs (Fig 3E).
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that clonally expanded cytotoxic CD8+ T cells are present in both anti-MPO+ and anti-PR3+ AAV patients, and we identified a specific autoreactive GZMK+IFNy+ CD8+ T cell subpopulation in anti-MPO+ AAV patients. The identification and characterization of pathogenic autoreactive T cells in AAV could provide novel insights into next-generation therapeutic targets for this autoimmune disease.
patients (n=9) and HCs (n=4). (B) Proportions of different T cell clusters among the groups. C) Bubble heatmap of selected marker genes showing average expression levels and the percentage expression across the annotated clusters. D) UMAP plot of annotated T cells in HC, anti-MPO+ and
anti-PR3+ AAV patients. E) UMAP plots of T cells integrated with TCR clonality. The level of clonal expansions was based upon the frequency of a specific clonotype defined by its unique paired TCRαβ sequence. Each group was indicated by different colors as shown in the legend. (F) The
proportion of the different levels of clonally expanded T cells was shown in each annotated cluster of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells for HC, anti-MPO+ and anti-PR3+ AAV patients.
pathway analysis of significantly upregulated genes of expanded T cells in AAV. C) Heatmap of pseudo bulk average gene expression in each individual patient for selected genes in CD8 EMRA GZMB+ T cells.
The percentage of Ki-67+GZMB+IFNy+ and F) Ki-67+GZMK+IFNy+ expressing CD8+ T cells after 24h of stimulation. Data are represented as median ±IQR. Two-way ANOVA, p* < 0.05, **< 0.01, *** < 0.001 **** <0.0001.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
van Dam L, Younis S, Moon J, Zhang M, Parfasar S, Horomanski A, Sharpe o, van Leeuwen J, Lanz T, van Kooten C, Teng O, Robinson W. Identification of Autoreactive Cytotoxic T Cells in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-autoreactive-cytotoxic-t-cells-in-anca-associated-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/identification-of-autoreactive-cytotoxic-t-cells-in-anca-associated-vasculitis/