Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: Abstracts: SLE – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes I: Omics
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) can lead to severe morbidity and early mortality in SLE patients. While therapeutic options for LN have improved, they are not universally effective and can cause significant adverse effects. Thus, a robust panel of non-invasive biomarkers are needed to optimize and predict treatment response. Using high-throughput proteomics and machine learning, this study generated a prediction model of treatment response based on serum protein expression as part of the Accelerating Medicines Partnership RA/SLE Network.
Methods: Over 5,000 serum proteins were measured in serum of 158 LN patients at the time of diagnostic kidney biopsy (baseline) and 12 weeks post-biopsy using Olink Explore HT. Clinical response was determined at 52 weeks as complete (CR; n=25), partial (PR; n=22), or no response (NR; n=49). Multivariate logistic regression adjusting for age, gender, and genetic ancestry and machine learning algorithm approaches (Extreme Gradient Boosting) were used to generate a robust prediction model of treatment responsiveness.
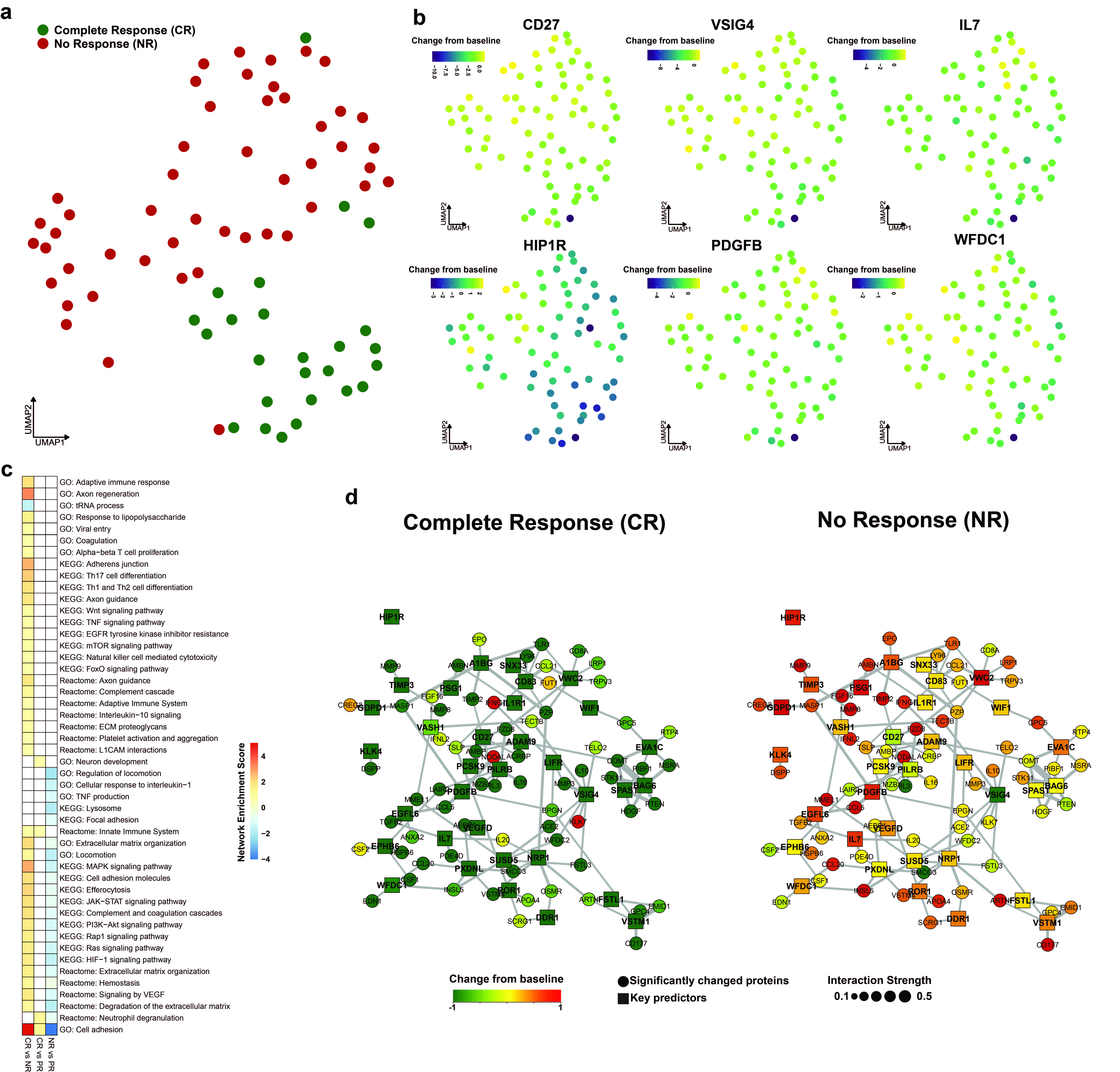
Results: At baseline, patients with NR exhibited 515 (p-value < 0.05; 160 upregulated) dysregulated proteins within the innate immune system and platelet activation and aggregation pathways. In addition, 1227 (p-value < 0.05; 1180 upregulated) proteins involving the TGFb, IL-10, Th1/Th2 differentiation, platelet activation, and leukocyte transendothelial migration pathways at 12 weeks post-biopsy were differentially expressed in patients with NR compared to those with a CR. Proteins involved in T cell proliferation, Th17 cell differentiation, and TNF, Wnt, EGFR, and IL-10 signaling were persistently elevated at week 12 compared to baseline in CR. A model incorporating changes in 34 proteins from baseline to week 12 was more effective at predicting treatment response at 52 weeks (83.8% +/- 0.76%) compared to levels at baseline (67.3% +/- 6.3%) or 12 weeks (70.5% +/- 7.03%) (Figure 1A). In particular, patients with a CR had a significant reduction in CD27, IL-7, VSIG4, HIP1R, PDGFB, and WFDC1 from baseline to 12 weeks post-biopsy (Figure 1B). Gene regulatory network analyses of the top predictors demonstrated significantly down-regulated lymphocyte activation/differentiation (CD27, IL-7, IL-3, IL-16, CD83, and IL-10) and cellular migration pathways (NRP1, IL-16, PDGFB, CSF1, DDR1, FSTL1) in patients with a CR at week 12 (Figure 1C-D).
Conclusion: Early downregulation of specific immune pathways upon treatment precedes future clinical response in LN. Changes in serum protein expression 12 weeks post-biopsy may serve as noninvasive biomarkers of 52-week treatment response in LN patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jones B, Lu R, Fava A, Izmirly P, Anolik J, Putterman C, Wofsy D, Kretzler M, Berthier C, Woodle E, Weisman M, Ishimori M, Accelerating medicines Partnership: RA/SLE Network T, Diamond B, Buyon J, Petri M, James J, Guthridge J. High-Throughput Proteomic Profiling of Longitudinal Serum Samples to Predict Treatment Response in Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-throughput-proteomic-profiling-of-longitudinal-serum-samples-to-predict-treatment-response-in-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/high-throughput-proteomic-profiling-of-longitudinal-serum-samples-to-predict-treatment-response-in-lupus-nephritis/