Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Clinical, radiologic and biomarker data are measurements used in the assessment of juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) disease activity. The development of ultrasound-guided synovial biopsy (USGSB) in children has accelerated synovial histopathology research. Investigate the relationship between clinical features of arthritis, radiologic synovitis, synovial fluid (SF) biomarkers of inflammation, and histologically confirmed synovitis in children with JIA.
Methods: JIA patients requiring a knee joint injection were enrolled. Patients underwent standardized clinical assessment (cJADAS, range 0-30), a musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSUS) examination, and USGSB of the affected knee with collection of synovial fluid (SF). MSUS images were collected and scored by pediatric MSUS experts. MSUS synovitis was scored using a validated semiquantitative MSUS scoring system for the knee joint (MSUS-knee score, range 0-6). Synovial biopsy inflammation was determined by Krenn’s score (KS, which examines for synovial hyperplasia, stromal cellularity/reactivity and inflammatory infiltrate, range 0 to 9, higher scores indicating greater severity. Biomarkers measured in SF included: TNFR1, IL-6, IL-10, MCP-1, ANG-1, ANG-2, MMP-2, MMP-8, CCL18, CCL20, IFNg, IL-17a, IL-2Ra, IL-23, IL-18, resistin, CXCL9, VEGF, TIMP-1 by Luminex, and S100A12, S100A8/A9 by ELISA. Wilcoxon Rank Sum test was used to compare group differences. Spearman correlation (rs) was used to assess the relationship between the studiedvvariables
Results: Thirty-four patients [mean age 10 (SD 5.1)] were enrolled. Their median cJADAS score was 4 (IQR 2-8) while 32% of them had no pain at the affected joint (Table 1). All patients had presence of MSUS synovitis with a median MSUS-knee score of 5 (IQR 4-6). Median KS was 6 (IQR: 4-7). Children receiving conventional and/or biologic disease modifying medications (DMARDs) had similar median KS compared to children not on these treatments [6, (IQR 3-7) and 6 (IQR 5-8), respectively] (p=0.962). Children with polyarticular JIA had a median KS of 5 (IQR 5-6) while the KS for children with oligoarticular was 6 (IQR 4-8) (p=0.725). Children with oligoarticular JIA taking NSAIDs at the time of the USGSB had a significantly lower KS than oligoarticular JIA children not on an NSAID [median 3.5 (IQR 3-4) v 6.5 (IQR 4.2-7.7), respectively] (p=0.033). A significant moderate correlation was found between the MSUS-knee score and the KS rs: 0.45 (0.12 -0.7), with the highest association being between the KS stroma domain and the MSUS-knee score [rs: 0.5 (0.17-0.720] (Table 2). Strong significant correlations (rs>0.8, p< 0.05) were found between SF levels of S100A12, S100A8A9, CCL18, IL-6, MMP-8 and the KS (Table 3). S100A8A9 also had a significant correlation with the MSUS-knee score [rs 0.55 (0.08-0.82)].
Conclusion: This pilot study suggests that the degree of inflammation as measured by the KS does not associate with JIA disease category or DMARDs use but may be modified by concomitant NSAID use The association of the MSUS-knee score and SF biomarkers of inflammation with the KS detected in this study suggest that these measurements may have a role as surrogate markers of histologically confirmed active synovitis.
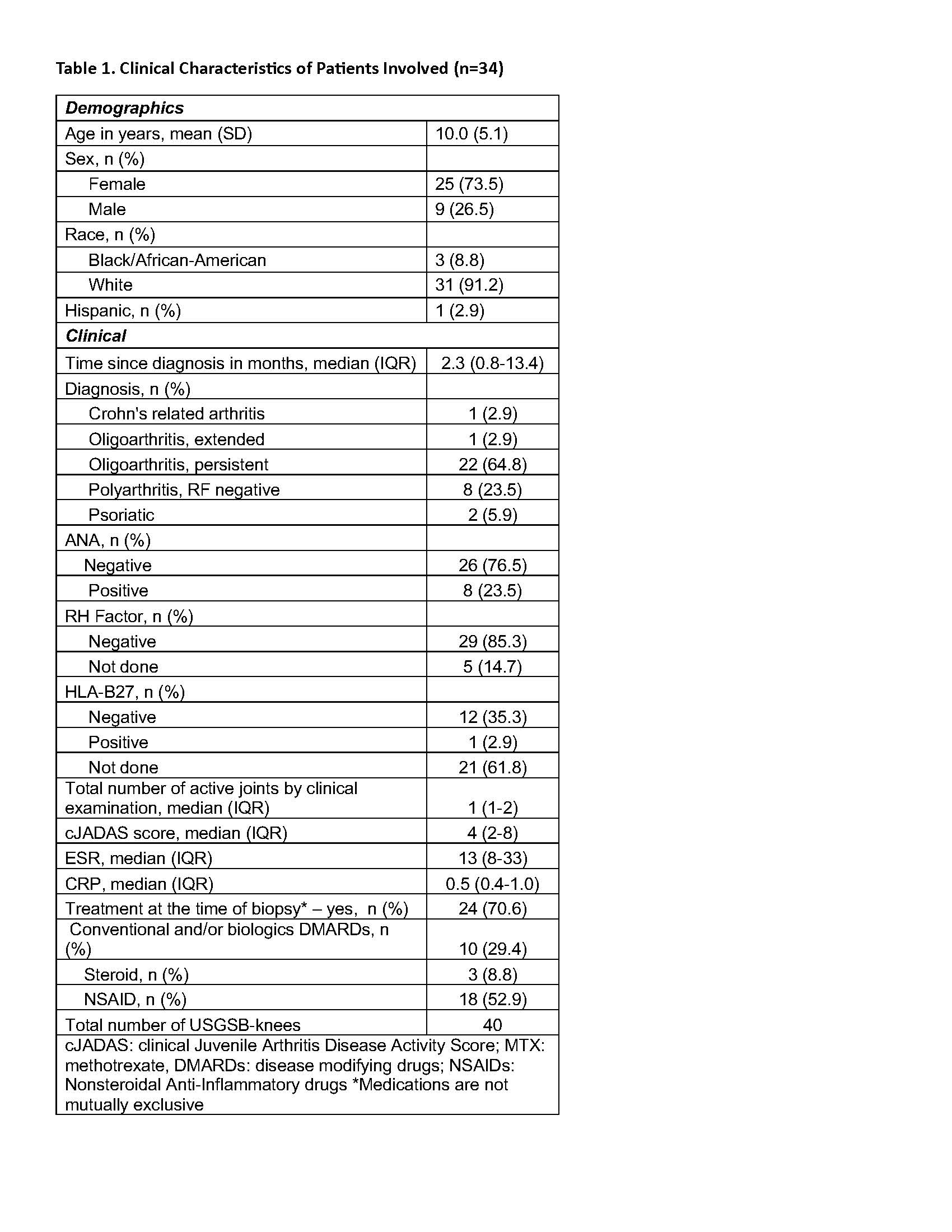 Table 1. Clinical Characteristics of Patients Involved (n=34)
Table 1. Clinical Characteristics of Patients Involved (n=34)
.jpg) Table 2. Relationship between MSUS-knee score and Krenn’s scores (n=34)
Table 2. Relationship between MSUS-knee score and Krenn’s scores (n=34)
.jpg) Table 3. Relationship between Synovial Fluid Biomarkers and Krenn’s scores (n=16)
Table 3. Relationship between Synovial Fluid Biomarkers and Krenn’s scores (n=16)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Vega-Fernandez P, Rogers K, Sproles A, Thornton S, Auld L, Rodriguez-Smith J, Ogbu E, Schmidt K, Vater M, Banschbach K, Schulert G, Grom A, Angeles-Han S, Brunner H, Huggins J, Lovell D, Cassedy A, Baglaenko Y, Ting T, Szabo S. Evaluation of Disease Activity in the Knee Joint Through Clinical, Radiologic, Synovial Fluid and Histopathologic Measurements of Inflammation in Children with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-disease-activity-in-the-knee-joint-through-clinical-radiologic-synovial-fluid-and-histopathologic-measurements-of-inflammation-in-children-with-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/evaluation-of-disease-activity-in-the-knee-joint-through-clinical-radiologic-synovial-fluid-and-histopathologic-measurements-of-inflammation-in-children-with-juvenile-idiopathic-arthritis/
