Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Due to concerns about side effects, combined JAK inhibitors (JAKi) and biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs) have not been recommended for rheumatologic conditions. However, combining them may have benefits in treatment of resistant patients.
The Purpose of this case series is to evaluate the safety and efficacy of combination treatment using JAKi and bDMARD.
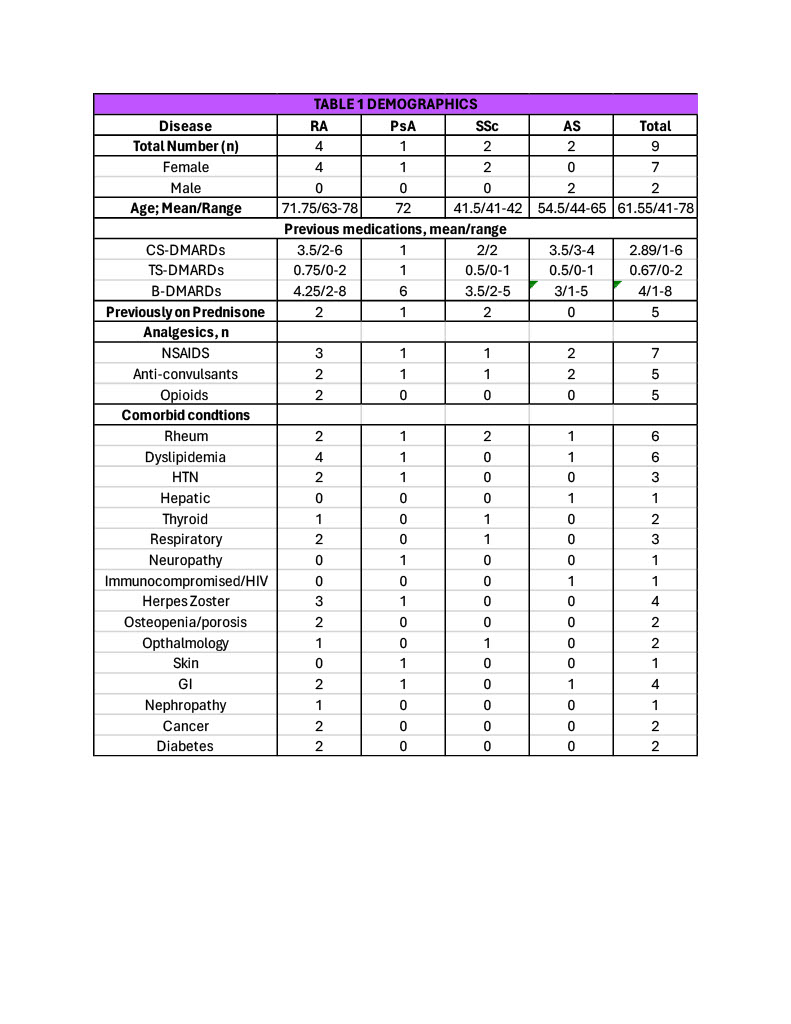
Methods: Clinical efficacy data were extracted from a retrospective case series. The data came from 9 rheumatologic patients, 3 of whom had combination therapy twice (12 total courses of therapy). Changes in patient global and pain scores via Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) scores (Range 0-100, MCID:10.0) were examined at 3,6, 9 and 12-month. Adverse events (AEs), serious adverse events (SAEs- as defined by the FDA) and deaths were recorded.
Results: The patients on the JAKi/bDMARD combination were 7 females and 2 males. Rheumatic diseases included rheumatoid arthritis (RA)(n=5), psoriatic arthritis (PsA)(n=1), scleroderma (SSc)(n=1), and ankylosing spondylitis (AS)(n=2).
Combinations were used for an average of 8 months Demographics are seen in table 1.
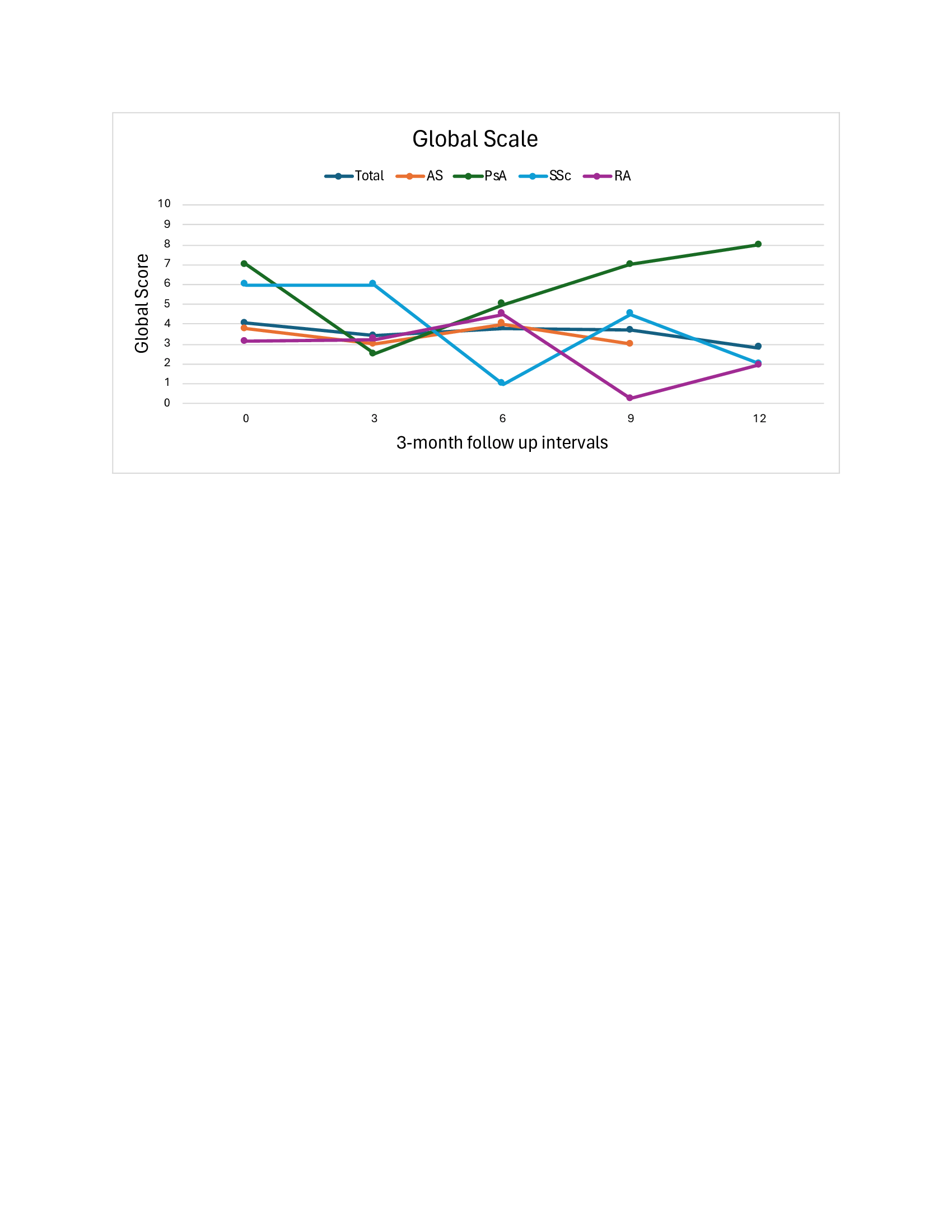
Mean VAS global disease activity score improved from 4.0 to 2.8, (difference: -1.2, clinically significant improvement) (Graph 1). The 5 RA patients improved from 3.1 to 2.0 difference: -1.2, clinically significant improvement). The single PSA patient worsened from 7.0 to 8.0 (difference: +1.0, clinically significant worsening). The 2 AS patients improved from 3.8 to 3.0(difference 0.8; only numerical improvement). The 2 SSC patients improved from 6.0 to 2.0(difference: – 4.0, clinically significant improvement).
The pain scale showed little change per patient.
Table 2 describes the 22 AEs; only one, an infection, required permanent drug discontinuation. There were no SAEs or deaths.
No statistical analysis was done due to the heterogenous patient population and limited study sample size.
As a retrospective, open study, there is selection bias.
Conclusion: Findings from this case series suggest that combination treatment using bDMARDs and JAKi inhibitors may be efficacious, is reasonably safe and may be considered when standard single treatments/monotherapy is ineffective. However, larger-scale, controlled studies are needed to confirm these findings and evaluate the comparative efficacy of combination therapy against single medication treatment
AEs: Adverse Events; SAEs: Serious Adverse Events
RA: Rheumatoid Arthritis; AS: Ankylosing Spondylitis; SSc: Scleroderma; PsA: Psoriatic Arthritis
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Garg B, Antowan J, Furst d. Dual Therapy with a JAKi and bDMARD in Patients with Standard Treatment Resistant Rheumatic Disease: A Case Series [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dual-therapy-with-a-jaki-and-bdmard-in-patients-with-standard-treatment-resistant-rheumatic-disease-a-case-series/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dual-therapy-with-a-jaki-and-bdmard-in-patients-with-standard-treatment-resistant-rheumatic-disease-a-case-series/