Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: The interplay between humoral and cellular response after vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in patients (pts.) with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases (AIRD) remains unknown. To investigate the impact of different immunosuppressive therapies on the development of humoral and cellular immune responses to full 2-dose SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in AIRD pts. with stable low disease activity.
Methods: The immune reactivity to COVID-19 vaccination was investigated in a prospectively recruited AIRD cohort with rheumatoid arthritis, axial spondyloarthritis or psoriatic arthritis which received a therapy with IL-17i, TNFi, JAKi or MTX (alone or in combination). Almost all patients received mRNA-based vaccine, only 4 patients had a heterologous scheme. Anti-spike(S) antibodies(ab.) and sera neutralizing capacity (neutralization dilution 50; ND50) were measured 4 weeks after the first (prime+4w) and 4 weeks after the second vaccination (boost+4w). Vaccine-specific cellular immunity was evaluated by quantifying expression of activation markers on T cells as well as their production of key cytokines, at prime+4w and boost+4w.
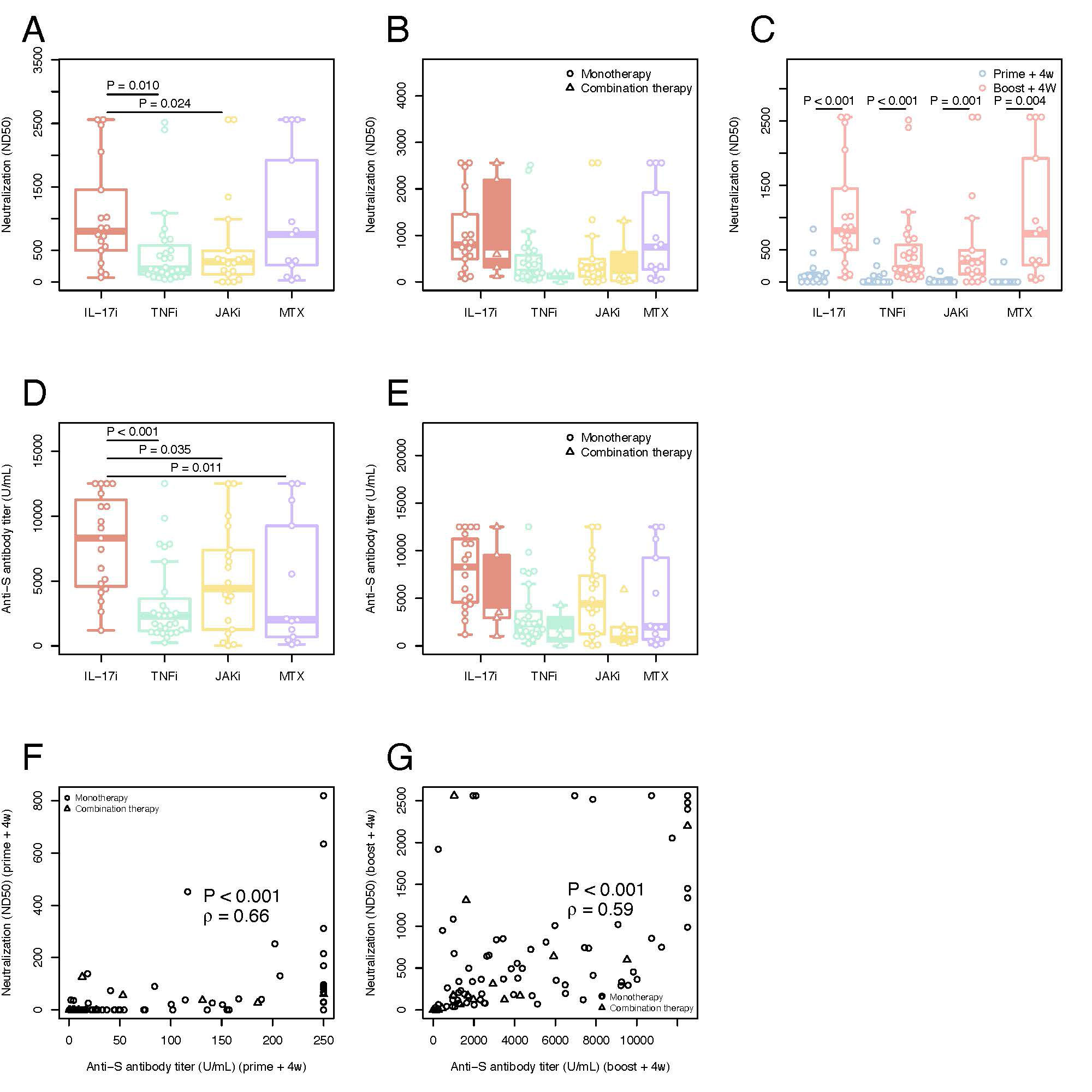
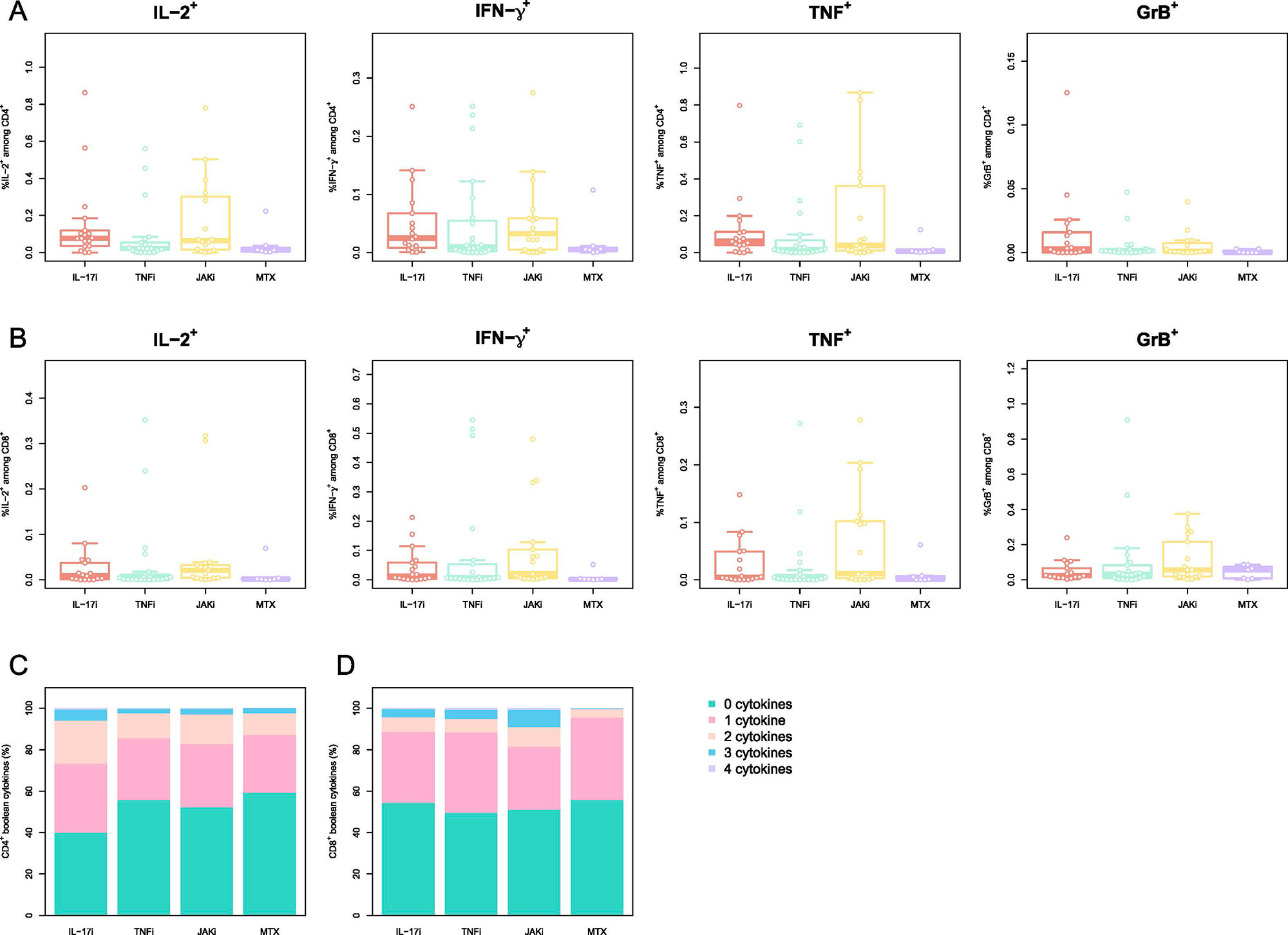
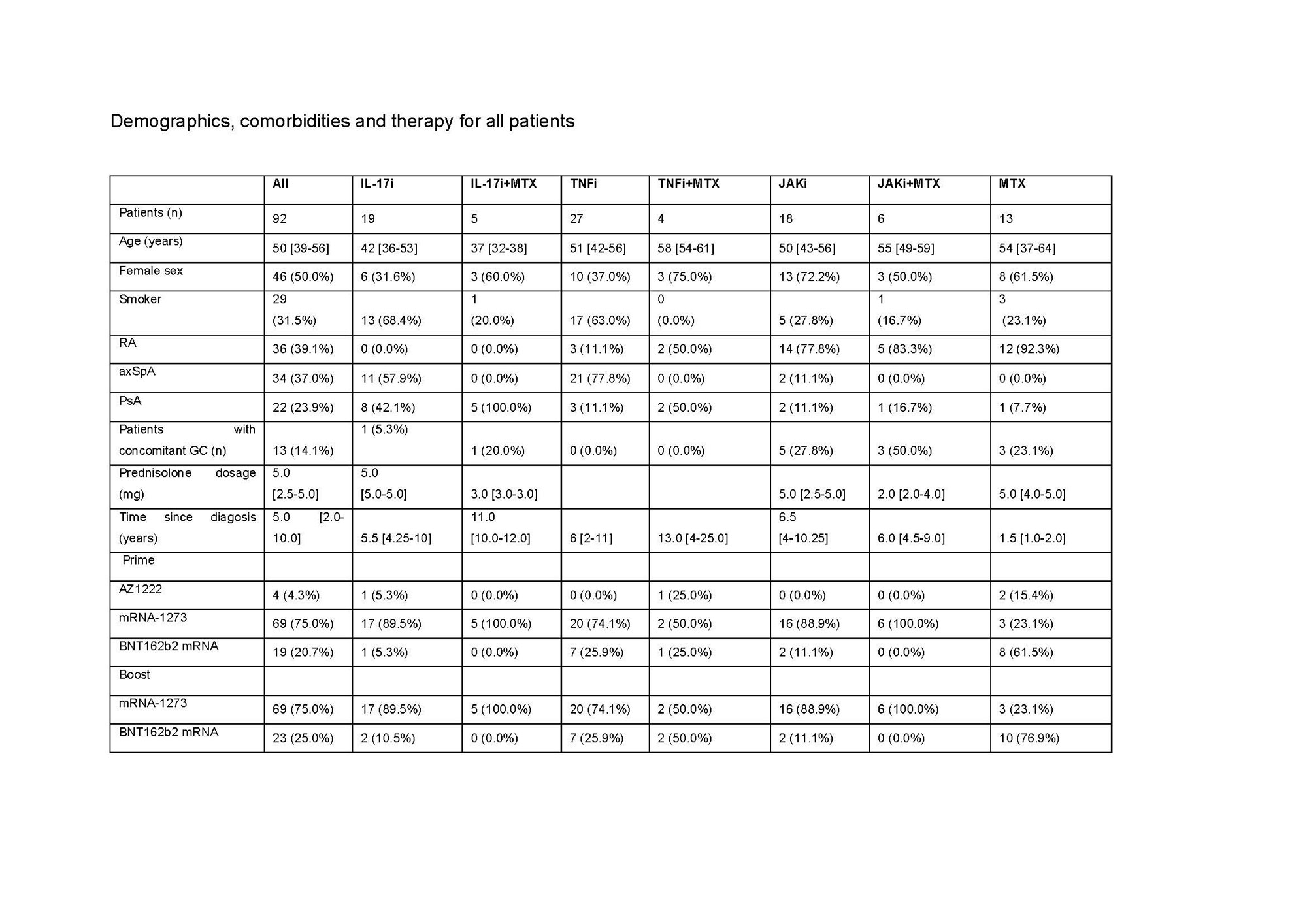
Results: Overall, a total of 92 pts. were included in the final cohort. 31 (33.7%) pts. were on TNFi, 24 (26.1%) on IL-17i, 24 (26.1%) on JAKi, each group encompassing pts. receiving drug inhibitors alone or in combination with MTX.13 (14.1%) were treated with MTX alone. The median time between the vaccination and blood sampling was 31 [IQR: 28-34] days after prime+4w and 28 [IRQ: 28-28] days after boost+4w. Although at prime+4w only 34/90 (37.8%) of pts. presented neutralizing ab., the majority (86/91, 94.5%), developed them at boost+4w. The highest neutralization titer developed the pts. on IL-17i both at prime+4w (74 [IQR: 13-91]) and boost+4w (798 [IQR: 511- 1344]), while no statistically significant differences were found in the neutralization titer at boost+4w for the TNFi, JAKi, and MTX groups: 207 ND50 [IQR: 120-576], 319 [IQR: 133-461] and 749 [IQR: 264-1920], respectively. 81/90 (90.0%) pts. developed IgG ab. against SARS-CoV-2 S-protein at prime+4w and 91/92 (98.9%) at boost+4w. Pts. receiving IL-17i developed higher ab. titers (8295 U/mL [IQR: 4586-11,237]) compared to the other three groups: JAKi (4405 U/mL [IQR: 1436-7265], TNFi (2313 [IQR: 1156-3630] U/mL) and MTX (2010 U/mL [IQR: 693-9254]). Neutralization capacity correlated well with the titer of anti-S ab. at both timepoints. Coadministration of biologic/tsDMARDs and MTX led to lower titers compared to biologic/tsDMARDs monotherapy. All therapies left frequencies of CD154+CD137+ CD4+ T cells and CD137+ CD8+ T cells at prime+4w and boost+4w unchanged. Polyfunctionality and T cell cytokine profiles across therapies did not significantly vary at boost+4w.
Conclusion: Even after insufficient seroconversion for neutralizing capacity and ab. response against SARS-CoV-2 S-proteins between pts. of different mod of action agents, particularly for MTX and JAKi after first vaccination, a second vaccination covered almost all pts. regardless of DMARDs therapy, with better outcomes in those on IL-17i. T cell immunity revealed similar frequencies of activated T cells in all modes of action after the second vaccination.
Neutralization titers (ND50) against SARS-CoV_2 in plasma A) SARS-CoV_2 neutralization antibodies at boost+4w for all four groups of patients on monotherapy B) Comparison between SARS-CoV_2 neutralization antibodies at boost+4w for all four groups of patients on monotherapy (unfilled plots) and combination therapies (filled colored plots) C) Kinetic of SARS-CoV_2 neutralization antibodies for all four groups of patients on monotherapy with IL17i, TNFi, JAKi and MTX. Serological immune responses against SARS-CoV_2 D) Spike-specific IgG titers at boost+4w for all four groups of patients on monotherapy E) Comparison between spike-specific IgG titers at boost+4w for all four groups of patients on monotherapy (unfilled plots) and combination therapies (filled colored plots) F) Correlation of spike-specific IgG titers and SARS-CoV_2 neutralization antibodies at prime+4w G) Correlation of spike-specific IgG titers and SARS-CoV_2 neutralization antibodies at boost+4w. The box plots indicate the 75th, 50th, and 25th quantile, and the whiskers have a maximum length of 1.5 times the interquartile range. Each point represents individual values, small triangles represent the additional patients on combination therapy. The following number of patients are presented: IL17i (n=19 prime+4w and n=18 boost+4w), TNFi (n=27 prime+4w, n=27 boost+4w), JAKi (n=18 prime+4w, n=18 boost+4w) and MTX (n=11 prime+4w, n=13 boost+4w), IL17i/MTX (n=5 boost+4w), TNFi/MTX (n=4 boost+4w), JAKi/MTX (n=6 boost+4w). ND50=50% inhibitory dilution. U/ml=units/mililiter. IL=interleukin. TNF=tumor necrosis factor. JAK= Janus kinase inhibitor. MTX=methotrexate. ρ=Spearman’s correlation coefficient.
PBMCs were stimulated with peptides spanning the SARS-CoV_2 Spike-protein and activated cells were evaluated by multiparametric flow cytometry. Phenotype of CD4+ T cells reactive to SARS-CoV_2 S-protein A) Memory/Naive phenotype of SARS-CoV_2 Spike-reactive CD4+ T cells at boost+4w. Naïve (CD45RA+CCR7+), central memory (CM; CD45RA–CCR7+), effector memory (EM; CD45RA–CCR7–), and EM expressing CD45RA (TEMRA; CD45RA+CCR7–). Phenotype of CD8+ T cells reactive to SARS-CoV_2 S-protein B) Memory/Naive phenotype of SARS-CoV_2 Spike-reactive CD8+ T cells at boost+4w. The cell populations are defined as for A) C-D) Frequency of the cytokines IL_2, IFN-γ, TNF and GrB for SARS-CoV_2 Spike-reactive CD4+ (C) CD8+ (D) T cells at boost+4w. E-F) Boolean combinations of assayed cytokines for CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. The box plots indicate the 75th, 50th, and 25th quantile, and the whiskers have a maximum length of 1.5 times the interquartile range. Each point represents a patient. IL=interleukin. TNF=tumor necrosis factor. JAK= Janus kinase inhibitor. MTX=methotrexate. Gr= granzyme
RA: rheumatoid arthritis, axSpA: axial spondyloathritis, PsA: psoriatic arthritis, GC: glucocorticoid, mg: milligram, IL: interleukin, i: inhibitor, MTX: methotrexate: TNF: tumor necrosis factor, JAK: janus kinase. For quantitative variables, data are provided as median [IQR], while for categorical variables the count (% frequency) is provided
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Andreica I, Blazquez-Navarro A, Sokolar J, Anft M, Kiltz U, Pfaender S, Vidal Blanco E, Westhoff T, Babel N, Stervbo U, Baraliakos X. Different Humoral but Similar Cellular Responses of Patients with Autoimmune Inflammatory Rheumatic Diseases Under Disease-modifying Anti-rheumatic Drugs After COVID-19 Vaccination [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/different-humoral-but-similar-cellular-responses-of-patients-with-autoimmune-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-under-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs-after-covid-19-vaccination/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/different-humoral-but-similar-cellular-responses-of-patients-with-autoimmune-inflammatory-rheumatic-diseases-under-disease-modifying-anti-rheumatic-drugs-after-covid-19-vaccination/