Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (0934–0964) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: We found that TGF-β3 regulates humoral immunity in a context-dependent manner [1]. Recent genome-wide association study reveals that TGF-β3 might be a novel target in African American systemic sclerosis (SSc) patients [2]. Since Tgfb3-/- mice die within 20 hours of birth [3], the physiological roles of TGF-β3 have not clearly elucidated. In this study, we evaluated the immunological and fibrotic roles of TGF-β3 by using mice with conditional Tgfb3 deletion.
[1] Komai T, et al. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1364., [2] Kaundal U, et al. ACR2022, Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9), [3] Kaartinen V, et al. Nat Genet. 1995;11(4):415-21.
Methods: TGF-β3 conditional knockout mice in CD4+ T cells (Tgfb3fl/flCD4Cre) and B cells (Tgfb3fl/flCD19Cre) were created. Histopathology, expression of fibrosis-related genes in lung by qRT-PCR in lungs, and flow cytometric analysis of splenocytes from these mice were conducted. Also, a continuous bleomycin infusion delivered by osmotic minipumps to these mice was conducted as an induced SSc model. To evaluate the effects of overexpression of TGF-β3, either pCAGGS-Mock, pCAGGS-Tgfb3 plasmid vectors were intravenously administered to lupus prone MRL/lpr mice with spontaneous interstitial pneumonia, and lung pathologies were assessed.In vitro, normal human lung fibroblasts (NHLFs) cultured with and without TGF-β3 were evaluated.
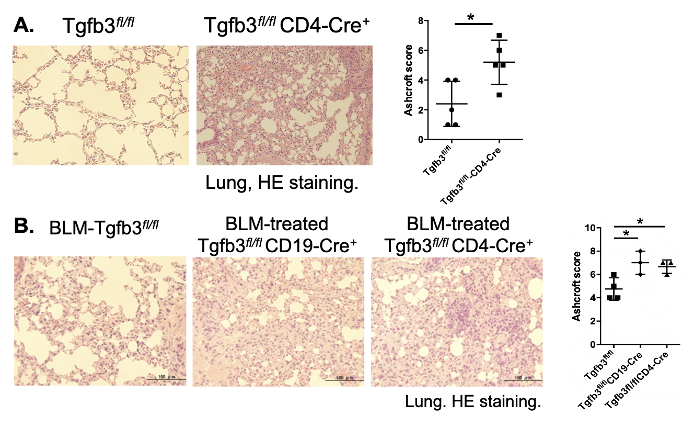
Results: Tgfb3fl/flCD4Cre mice developed inflammatory cell infiltration and fibrosis in lungs spontaneously (Figure 1A), and low-titer anti-dsDNA antibody production and increased marginal zone B cells was observed. The bleomycin-induction exacerbated interstitial pneumonia, and fibrosis-related genes of the lung tissue such as mCol1a1, mCol1a2, mSerpine1, and mSpp1 were up-regulated in both Tgfb3fl/flCD4Cre and Tgfb3fl/flCD19Cre mice in comparison to Tgfb3fl/flmice (Figure 1B). Further, the interstitial pneumonia of MRL/lpr mice was prone to be ameliorated by pCAGGS-Tgfb3 administration. In in vitro experiments, TGF-β3 inhibited the proliferation of NHLFs in a dose-dependent manner.
Conclusion: Our study suggested that TGF-β3 contributes to regulate systemic autoimmune and fibrotic responses. Anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic function of TGF-β3 might lead to future therapeutic target for interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Komai T, Okamura T, Kono M, Yamamoto K, Fujio K. Development of Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features in Conditional Tgfb3 Deletion [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-interstitial-pneumonia-with-autoimmune-features-in-conditional-tgfb3-deletion/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-interstitial-pneumonia-with-autoimmune-features-in-conditional-tgfb3-deletion/