Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Inclusion body myositis (IBM) is a slowly progressive autoimmune skeletal muscle disease for which no effective pharmacological therapy is available. A prominent feature of autoimmunity seen on microscopy is effector cytotoxic CD8+ T cells invading myofibers. Pathophysiologically, a quantitative approach to detection of CD8+ T cell burden in muscle would potentially distinguish IBM from other muscle diseases and provide a biomarker predicting disease progression, stratification for clinical trials, or a surrogate outcome for T cell directed therapies.
89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C is positron emission tomography (PET) tracer with high affinity for the CD8 glycoprotein.
In this pilot study we evaluated the safety, muscle distribution and sensitivity of 89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C, to detect CD8+ T cell inflammation in the skeletal muscle of IBM patients.
Methods: Five patients with IBM from the University of Pennsylvania who met European Neuromuscular Center Criteria (ENMC) for probable IBM and were able to walk at least 10 feet without an assistive device were recruited. Patients on any immunomodulatory therapy or investigational agent were excluded. Screening and formal clinical evaluation by a neuromuscular neurologist (CQ) was performed within 28 days of imaging.
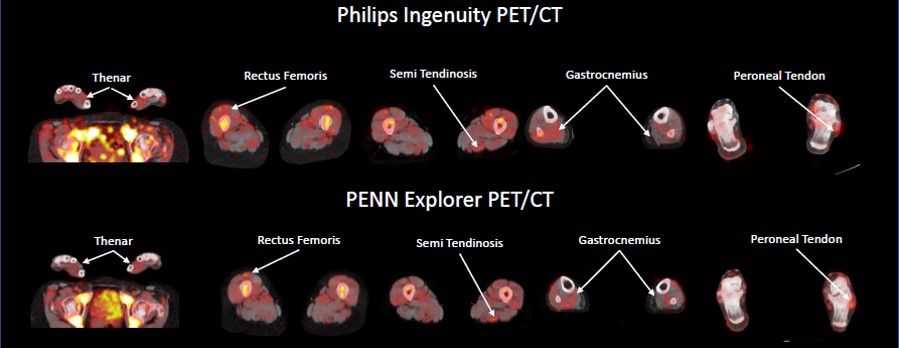
Patients were imaged 24 h after administration of 0.7-1.1 mCI of 89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C on both a standard clinical PET/CT scanner (Ingenuity TF; Philips Healthcare) and the PennPET Explorer, a whole-body scanner with approximately 40 times the sensitivity of a standard PET/CT instrument.
Outcome measures included safety and tolerability and a standard uptake value (SUV)-based quantitative analysis of tracer uptake in various muscle regions. SUV means were compared to a preexisting dataset from an oncology population where available.
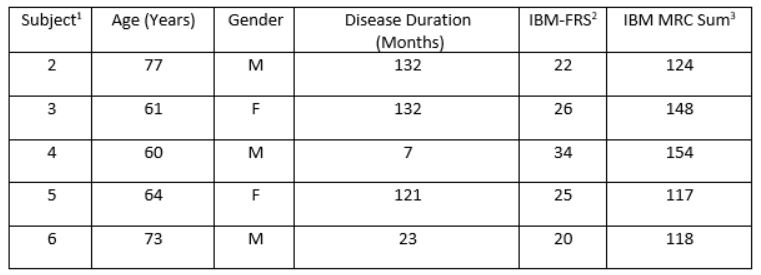
Results: To date all 5 patients have undergone clinical assessment and PET imaging. Four patients have been analyzed. Clinical details of each patient are detailed in Table 1.
89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C was well tolerated. One patient dropped out prior to receiving the tracer due to claustrophobia. A second patient experienced a fall the day after receiving the tracer deemed unrelated to the tracer, but the resulting delayed PET/CT evaluation left time for only PennPET Explorer imaging.
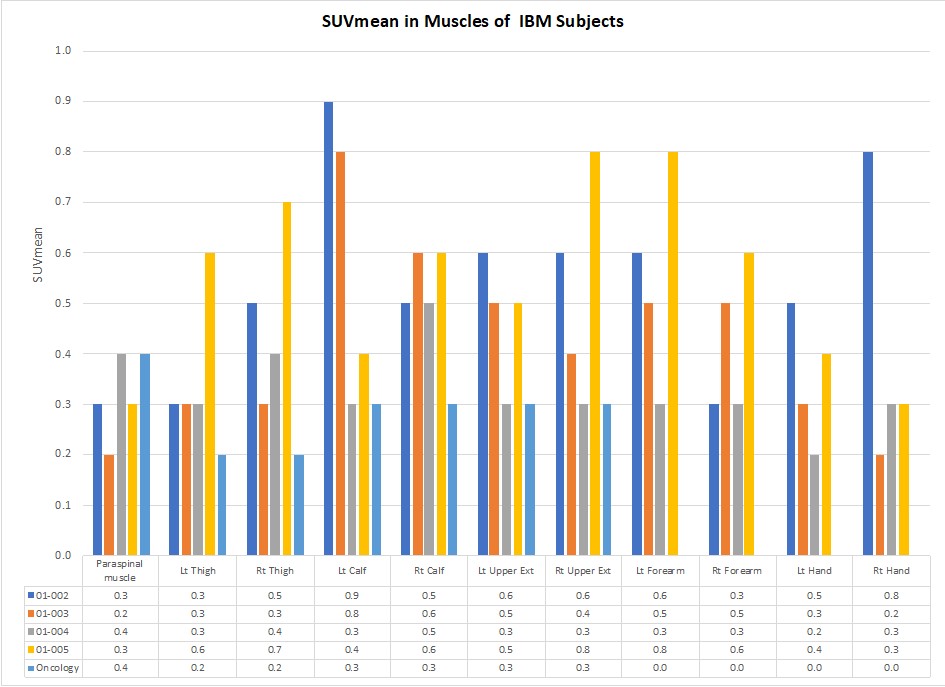
89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C signal was detectable in the muscles of all patients (Figures 1 and 2). In all of the extremities assessed, the average muscle uptake was higher than in our control population, though some individual muscles were similar to control uptake. The highest uptake was seen in the calf (average SUVmean 0.58, SD 0.20), upper extremities (average SUVmean 0.50, SD 0.17), and forearms (average SUVmean 0.49, SD 0.18). The uptake in the paraspinal muscles (average SUVmean 0.30, SD 0.08) was similar to the control population.
Conclusion: 89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C appears safe and well tolerated. This pilot study demonstrated clear uptake of 89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C in the muscles of IBM patients at an intensity greater than the control population. Further studies should examine 89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C uptake in other diseases and correlation with longitudinal changes related to measures of disease progression.
1. Subject 1 was not included as this subject decided against imaging after clinical evaluation
2. IBM-FRS = IBM Functional Rating Scale. The IBM-FRS is a 10 question survey of functional status, including swallowing, arm and leg tasks. Each question is scored 0_4. The maximum score is 40.
3. IBM MRC Sum= A sum of medical research council grading scores, converted to a 10-point scale. This is a non-validated score measuring shoulder abduction, elbow flexion, elbow extension, long finger flexion (digit 2), long finger flexion (digit 4), hip flexion, knee extension, ankle dorsiflexion and ankle plantarflexion bilaterally.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Quinn C, Moulton K, Korn R, Le W, Goel N, Farwell M, Greenberg S. CD8 Positron Emission Tomography (PET/CT) Imaging with 89Zr-Df-IAB22M2C in Patients with Inclusion Body Myositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cd8-positron-emission-tomography-pet-ct-imaging-with-89zr-df-iab22m2c-in-patients-with-inclusion-body-myositis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cd8-positron-emission-tomography-pet-ct-imaging-with-89zr-df-iab22m2c-in-patients-with-inclusion-body-myositis/