Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Abstracts: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes I: Bugs & Drugs (0980–0983)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:30PM-2:45PM
Background/Purpose: The adaptive immune system plays a central role in Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) pathogenesis. Moreover, the composition of the B cell repertoire and its perturbation are known to exist across disease phenotypes (i.e., ACPA positive versus ACPA negative). However, the influence of underlying B-cell repertoire changes in RA according to their response to treatment, and the ability of these to constitute as predictive biomarkers of response to Methotrexate (MTX) are not yet known. The objective of this analysis was to create a nomogram capable of predicting response to MTX at 6 and 12 months based on properties of the baseline B cell repertoire.
Methods: Peripheral blood leukocytes (PBL) from patients from the Scottish Early Rheumatoid Arthritis SERA cohort (1) were included in the analysis and classified into 3 categories according to their response to MTX measured by CDAI or DAS 28 at 6 and 12 months: responders (n=36), non-responders (n=35) and relapsing responders (n=28). BCR sequence repertoires were explored through IGH sequencing via the IGH-LR assay and the Gene Studio S5, sequencing to a target of 1.5M reads per sample. Data were analyzed via Ion Reporter 5.12 and 5.16. A gradient-boosting supervised learning method was used to build a prediction model of MTX response at 6 months and 1 year.
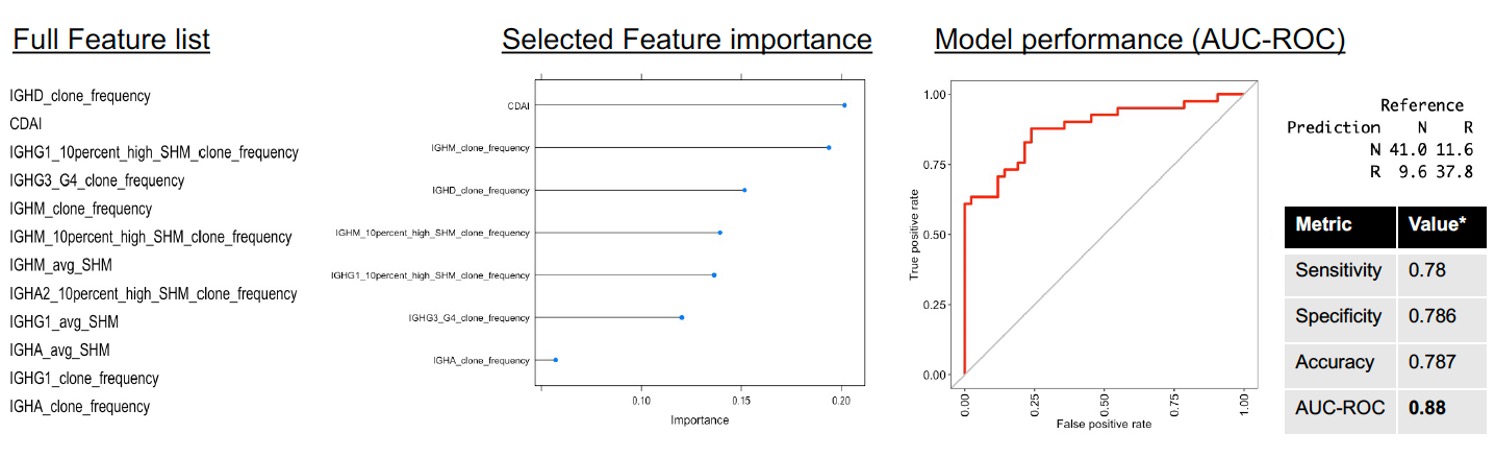
Results: 99 patients, with a mean age of 60.5 (SD 13.72) were included for analysis. Of interest, differences in class-switching and repartition of naïve B cells were observed across all groups. Notably, untreated patients displayed higher levels of IgA, IgE and IgG clones compared to after 12 months of MTX (p=0.003). At baseline, isotypes were more frequently switched towards IgA, IgE and IgG in non-responders than responders (p=0.008). Baseline levels of circulating IgD+ B cells clones were more frequent in responders compared to non-responders (p=0.004) while IgA1+ and IgA2+ clones tended to be more frequently represented in non-responders (p=0.069 and p=0.001 respectively). Over the course of the treatment with MTX, responders and non-responders tended to show an increased frequency of IgM+IgD+ clones whilst a depletion in IgG1+ clones was observed only in responders (p=0.034). In the relapsing responders’ group, no significant depletion at both 6 and 12 months was observed. When analyzing somatic hypermutation (SHM) levels in the BCR variable regions, the levels of SHM were consistently lower in non-responders compared with responders, although the number of SHM tended to increase over time for most isotypes. The top 7 baseline features were selected from a preliminary random forest model: IgM, IgD, IgG3, IgG4 and IgA clone frequency, frequency of IgM and IgG clones with >10% SHM and CDAI. Additional training and optimization of a new gradient boosting model, revealed that the response to MTX in the cohort could be predicted with a sensitivity of 0.78, a specificity of 0.786 and an area under the curve of 0.88 (Figure 1).
Conclusion: This model, based on an innovative machine learning approach in conjunction with a cutting-edge B cell repertoire analysis in RA, constitute the first immunology-based prediction model for response to MTX to our knowledge. This could be further used for personalized therapy in RA.
AUC: area under the curve; SHM: somatic hypermutations.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Najm A, Sarda S, Toro M, Pickle L, Ostresh S, Morton F, Lowman G, Felton A, Goodyear C. B Cells Repertoire Repartition Predicts Response to Methotrexate at 6 and 12 Months in Naïve RA: A Machine Learning Driven Approach [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/b-cells-repertoire-repartition-predicts-response-to-methotrexate-at-6-and-12-months-in-naive-ra-a-machine-learning-driven-approach/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/b-cells-repertoire-repartition-predicts-response-to-methotrexate-at-6-and-12-months-in-naive-ra-a-machine-learning-driven-approach/