Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is characterised by autoimmunity, fibrosis and vasculopathy. There is striking heterogeneity in skin fibrosis that is likely to reflect the balance between pro- and anti-fibrotic pathways underlying spontaneous regression of skin fibrosis in late stage diffuse SSc. We have studied potential serum markers of profibrotic activity in SSc, with a view to understanding their relationship with progression of fibrosis as measured by the modified Rodnan skin score (MRSS) to better define cases likely to respond to fibrosis-targeted therapies.
Methods: We prospectively recruited a cohort of well characterised patients (the BIOPSY cohort) from across the scleroderma spectrum. In total 67 patients had adequate serum and plasma samples to be included in the analysis (21 early diffuse disease (dcSSc) (< 5 years disease duration), 14 established dcSSc, 16 limited SSc (lcSSc), 16 healthy controls (HC)). MRSS was recorded at the time of sample collection. Standard and novel measures of serum or plasma markers were undertaken by immunoassay (20 in total) reflecting extracellular matrix (ECM) turnover or cytokine drivers of fibrosis, and analysed at the same time point to reduce any batch effect.
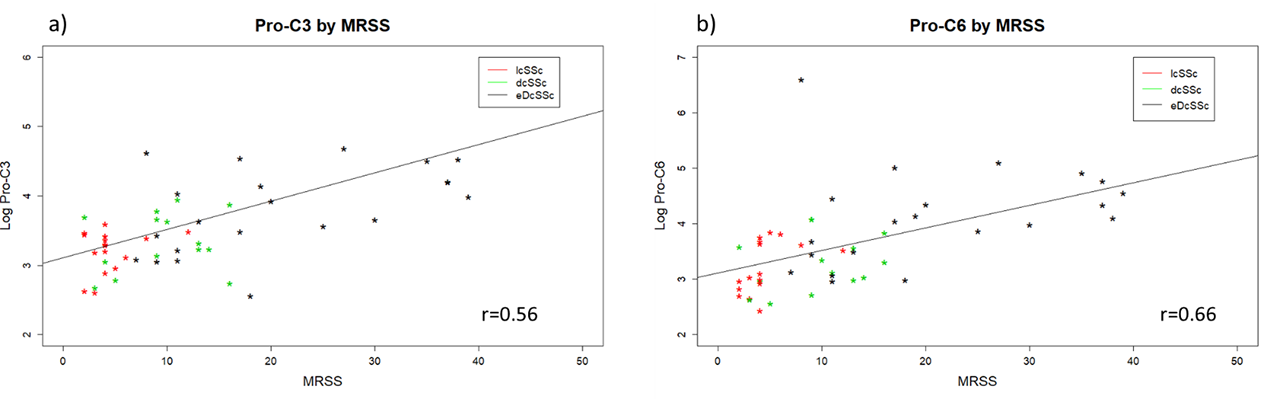
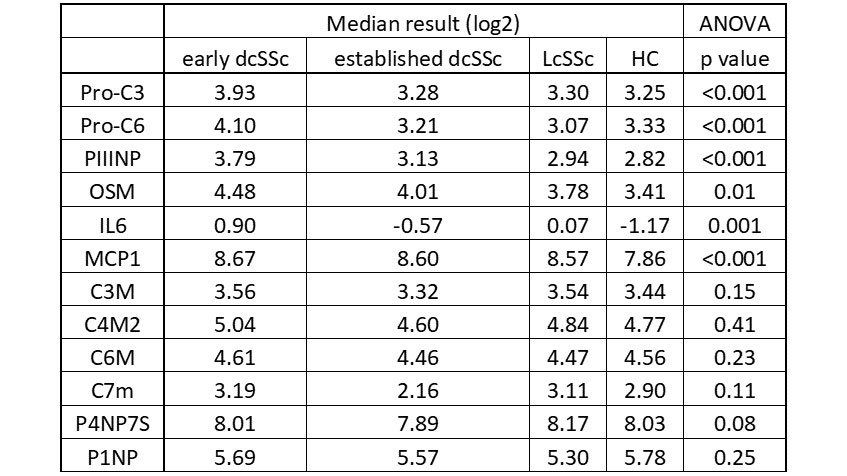
Results: Our results confirmed that 13 analytes showed significant differences in concentration by subgroup using one-way ANOVA. Markers of collagen synthesis were significantly different between the subgroups (Pro-C6, Pro-C3, PIIINP) (Figure 1), while markers of collagen degradation were not significantly altered (C3M, C6M, C4M2, C7M) (Table 1). This difference was most significant between the early dcSSc subgroup compared with the other subgroups (Student t-test with Bonferroni correction). There was significant upregulation of IL-6, MCP-1, and oncostatin M in SSc compared to HC. Consistent with other reports the ELF score, originally validated in liver fibrosis, was significantly higher in the SSc patient cohort. There were significant correlations between several candidate profibrotic serum markers and MRSS: Pro-C3, Pro C6, PIIINP, and IL6 (all p< 0.01) (Figure 2).
Conclusion: Our results show the utility of extended patient cohorts to delineate fundamental biology in SSc. We identify key pro-fibrotic molecular markers upregulated in SSc and correlated these to extent of skin fibrosis. Markers of collagen III and collagen VI synthesis are particularly raised, especially in the early stages of the disease. We did not find any significant difference between SSc subgroups and healthy controls for markers of collagen degradation. These promising cross-sectional data suggest that therapies targeting drivers of fibrosis are most likely to show benefit for skin in early dcSSc. This will be further explored longitudinally in the BIOPSY cohort.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Clark K, Campochiaro C, Nevin K, Csomor E, Galwey N, Morse M, Wisniacki N, Flint S, Ong V, Derrett-Smith E, Denton C. Analysis of Serum Markers Across the Scleroderma Spectrum Shows Subset and Stage Specific Profiles of Fibrogenesis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-serum-markers-across-the-scleroderma-spectrum-shows-subset-and-stage-specific-profiles-of-fibrogenesis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-serum-markers-across-the-scleroderma-spectrum-shows-subset-and-stage-specific-profiles-of-fibrogenesis/