Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS) is characterized by lymphocytic infiltration of the salivary and lacrimal glands, leading to functional loss and gradually causing dry mouth and dry eyes. Recent studies have suggested that mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) transplantation may improve salivary function and reduce lymphocytic infiltration of the salivary glands. This study aimed to confirm the anti-inflammatory effects of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) on pSS pathology and elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
Methods: Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from pSS patients were co-cultured with MSCs under various stimulatory conditions to evaluate the inhibition of cell differentiation and cytokine production. CD4+ T cells and B cells were isolated from the peripheral blood of pSS patients and co-cultured with MSCs stimulated with CpG-ODN or pSS-associated autoantigens. The changes in cell subsets and the suppression of IgG production due to MSC inhibitory effects were evaluated.
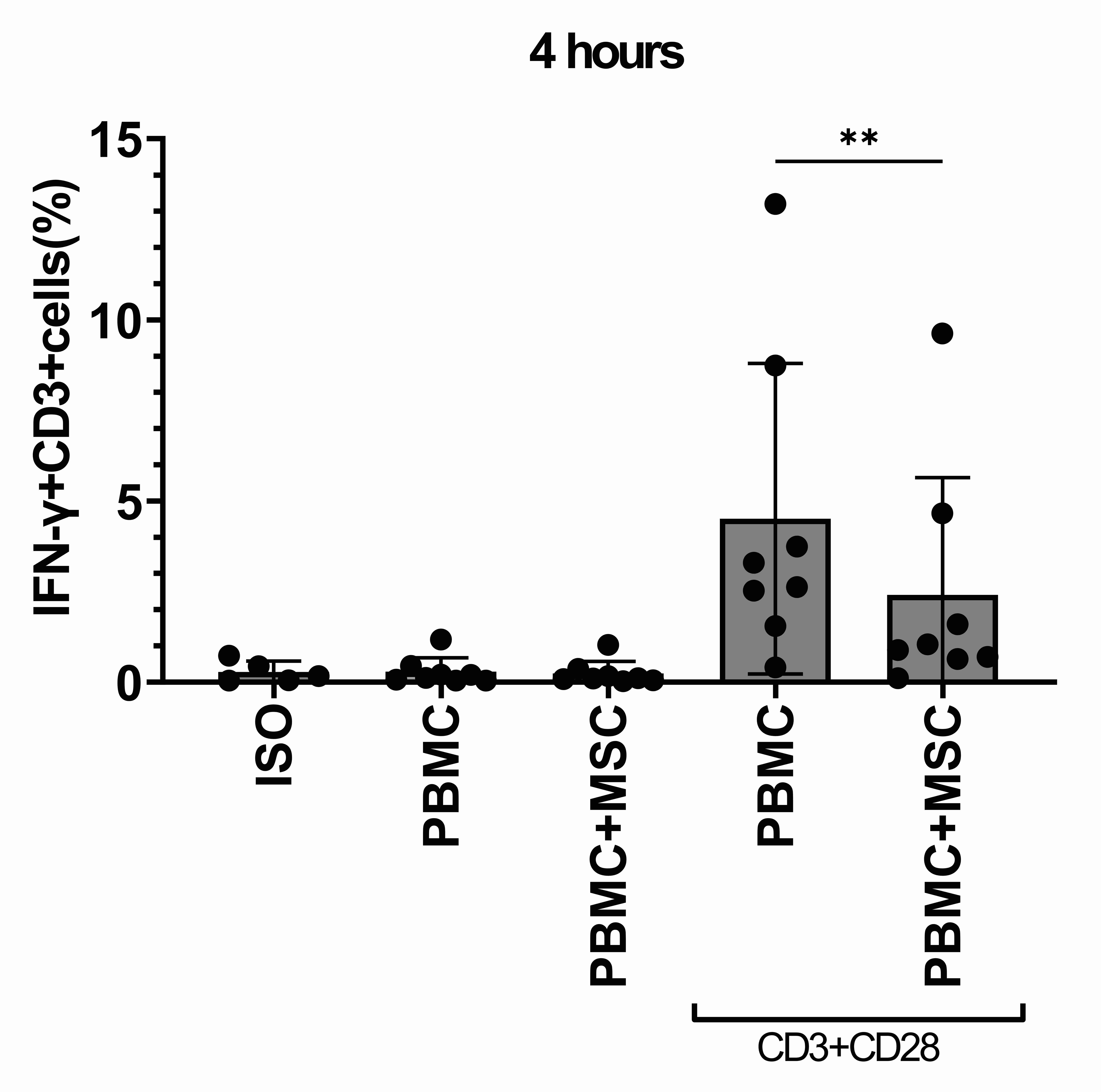
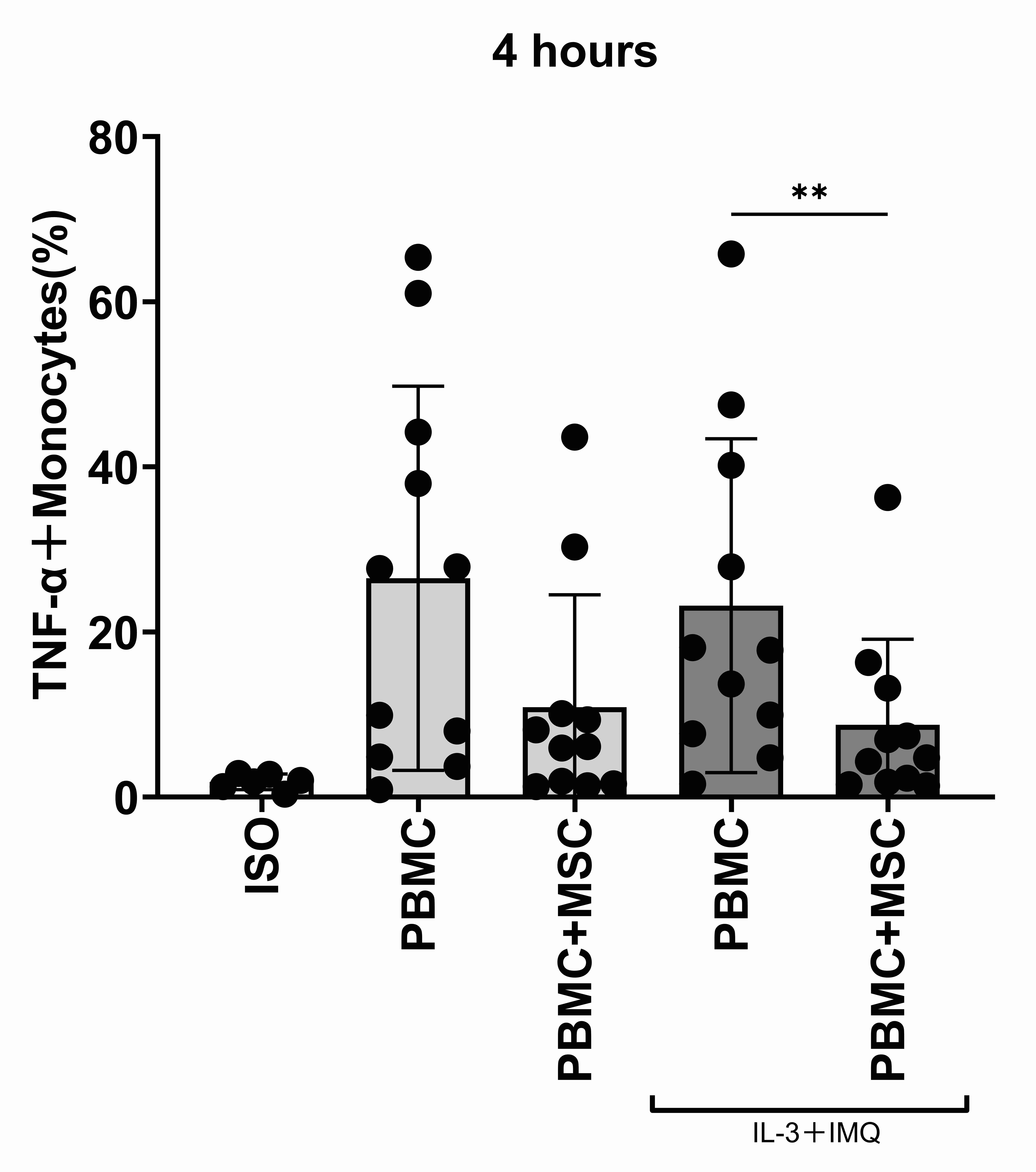
Results: When PBMCs were co-cultured with MSCs in the presence of anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies, the proportion of IFN-γ and IL-4 producing T cells decreased compared to cultures without MSCs. Additionally, when PBMCs were co-cultured with MSCs in the presence of Imiquimod, the proportion of TNF-α producing monocytes decreased compared to cultures without MSCs. Co-culturing CD4+ T cells and B cells from pSS patients with MSCs in the presence of CpG-ODN significantly reduced the proportion of plasma cells compared to B cell monocultures. Furthermore when CD4⁺T cells and B cells were co-cultured in the presence of pSS-associated autoantigen, IgG production was suppressed with MSCs compared to without MSCs.
Conclusion: In the presence of MSCs, TNF-α and IFN-γ production from T cells and monocytes was shown to be suppressed, with reduced differentiation into plasma cells and IgG production to pSS-associated autoantigens. In pSS patients, TNF-α and IFN-γ are known to increase the expression of Fas and FasL on salivary gland epithelial cells, and B cells induce apoptosis of salivary gland epithelial cells via cell-cell contact. The anti-inflammatory effects of MSCs may potentially improve the dry eyes and dry mouth with pSS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hagiwara Y, Murayama G, Kuga T, Nishioka Y, Saito T, Yamaji Y, Miyashita T, Kusaoi M, Yamaji K, Tamura N. Umbilical Cord-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Suppress Sjogren’s Syndrome Pathology [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/umbilical-cord-derived-mesenchymal-stem-cells-suppress-sjogrens-syndrome-pathology/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/umbilical-cord-derived-mesenchymal-stem-cells-suppress-sjogrens-syndrome-pathology/