Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (0934–0964) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
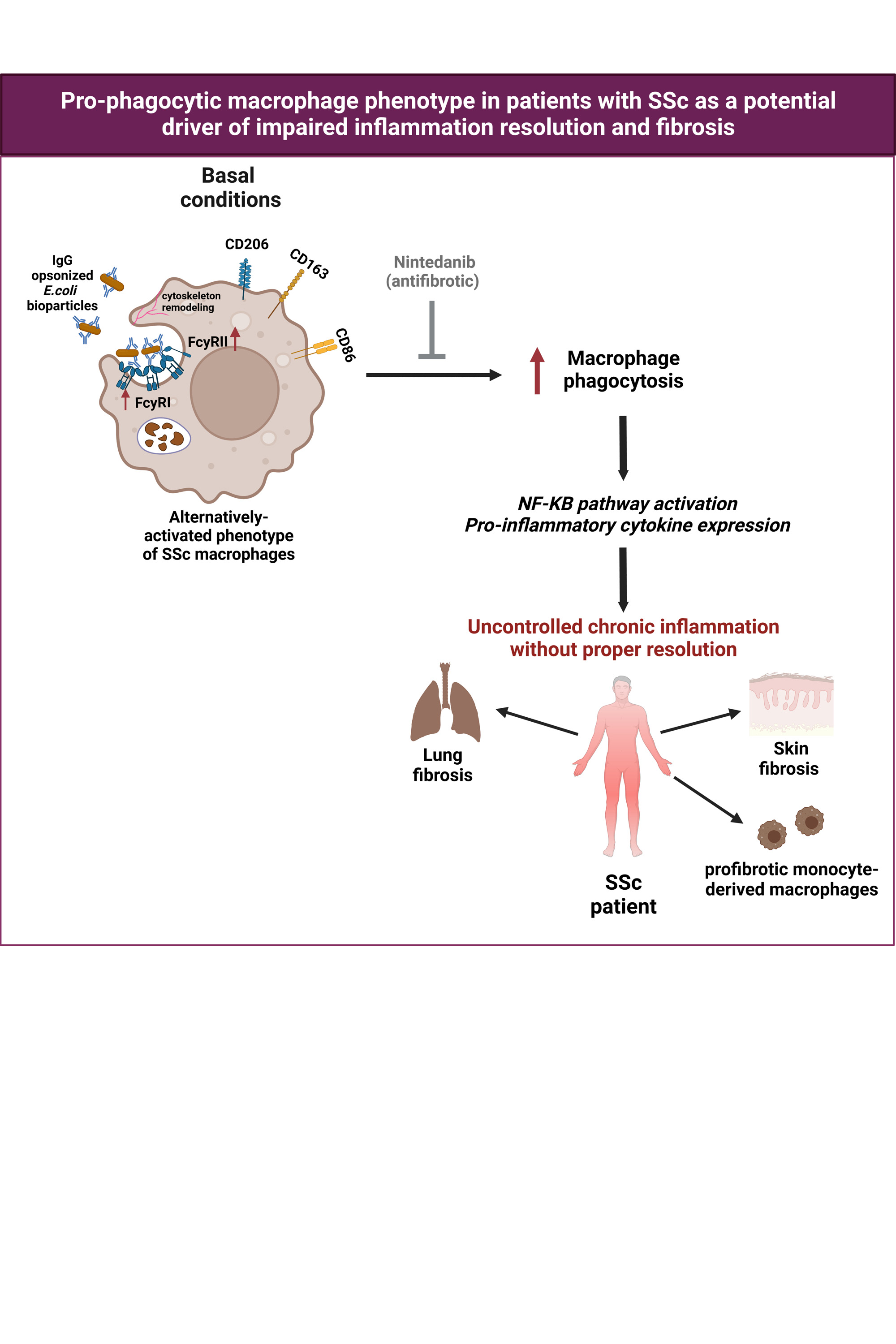
Background/Purpose: Fcy receptors (FcγR) are opsonic phagocytic receptors, requiring tight regulations to prevent uncontrolled activation of pro-inflammatory phagocytosis. SSc macrophages display an alternatively-activated profibrotic phenotype. However, a comprehensive understanding of how this distinct macrophage phenotype can contribute to SSc pathogenesis is missing. We aimed to study if alternatively-activated macrophages from SSc patients exhibit a pro-phagocytic signature.
Methods: Publicly available single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) datasets (GSE138669, GSE212109) on healthy control and SSc patient skin or lung macrophage populations were analyzed using Seurat v4.3.0 package. Human monocyte-derived macrophages (hMDM) were differentiated from CD14+ blood-derived monocytes from healthy controls, SSc, RA, PsA and axSpA patients.For some experiments, M(0) hMDM were pre-treated for 24 hours with 0.1 μM of the antifibrotic drug Nintedanib. Phagocytic activity of M(0) hMDM was measured using pHrodo Red E.coli bioparticles and detected by flow cytometry. Macrophage surface markers were assessed by flow cytometry. NF-κB signalling cascade was studied on the protein level by Western Blot, and IL6 expression was measured using RT-qPCR.
Results: scRNA-seq analysis revealed upregulated FCGR genes and FcyR-mediated pathways in skin macrophages from 12 dcSSc patients and in lung macrophages from 5 SSc patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD) (p.adj.≤0.05; log2FC≥0.5). We identified FCGR3Ahi macrophages in dcSSc patient skin and FCN1hi macrophages in the lungs of SSc-ILD patients as the main phagocytic populations. Functional in vitro studies confirmed enhanced phagocytic activity in alternatively-activated M(0) SSc hMDM (n=57) compared to healthy control cells (n=36, p< 0.0001). Phagocytic activity was observed in M(0) hMDM from pre-early SSc (n=14, p=0.0021), lcSSc (n=38, p=0.0006) and dcSSc (n=5, p=0.0581) patients, and was therefore independent of the disease subtype. Phagocytic activity positively correlated with FcγRI (n=14, Pearson r=0.663, p=0.006) and FcγRII (n=14, Pearson r=0.5178, p=0.0478) expression. Subsequently, engulfment of pHrodo Red E.coli bioparticles led to NF-κB pathway activation followed by increased IL6 expression in SSc M(0) hMDM (n=7) compared to healthy controls (n=5, p=0.0278). Pre-treatment of M(0) SSc hMDM with Nintedanib led to a reduction in phagocytic activity compared to untreated M(0) SSc hMDM (n=7, p=0.0066). In addition, we found that the pro-phagocytic phenotype of SSc M(0) hMDM is also present in other rheumatic diseases, including RA (n=10, p=0.0363) and PsA (n=11, p=0.0235), but not axSpA (n=9, p=0.4867) patients.
Conclusion: Our findings proposed enhanced FcγR expression as a novel biomarker to identify pro-phagocytic macrophages in SSc patients, which can trigger pro-inflammatory responses. Uncontrolled activation of pro-phagocytic macrophages could contribute to the aberrant resolution of inflammation followed by fibrosis in SSc patients (Figure 1). Furthermore, targeting pro-phagocytic macrophages may be an interesting approach for rheumatic diseases beyond SSc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hukara A, Bonazza G, Tabib T, Micheroli R, Jordan S, Bürki K, Schlitz Schönbächler S, Ciurea A, Distler O, Lafyatis R, Blyszczuk P, Kania G. Fcγ Receptors Define Pro-Phagocytic Macrophages and Trigger Pro-Inflammatory Responses in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fc%ce%b3-receptors-define-pro-phagocytic-macrophages-and-trigger-pro-inflammatory-responses-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/fc%ce%b3-receptors-define-pro-phagocytic-macrophages-and-trigger-pro-inflammatory-responses-in-patients-with-systemic-sclerosis/