Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I (0387–0413)
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The Assessment of Systemic sclerosis-associated RAynaud’s Phenomenon (ASRAP) questionnaire is a novel patient-reported outcome (PRO) instrument devised to assess the severity and impact of SSc-RP. We report a data driven approach to item reduction of the preliminary 39-item questionnaire.
Methods: The international multicentre ASRAP validation study enrolled SSc patients with RP from English speaking UK (n=3) and US (n=4) SSc centres during 2 consecutive winters (2019-2021). All participants completed a 39-item ASRAP questionnaire. Pooled data was used to assess dimensionality, before splitting the cohort to facilitate exploratory and confirmatory factor analyses (CFA). Items with low factor loadings < 0.5 and/or low item discrimination parameter estimates (α< 1.5) were considered for removal. Local dependency (LD) marginal Chi square analyses identified redundant items. Goodness-of-fitness testing examined the extent to which observed data fitted the item response model. Finally, differential item functioning (DIF) explored extent to which each item may measuredifferent concepts according to geographic enrolment (UK versus US sites). At each step, items were retained if content validity considered them essential.
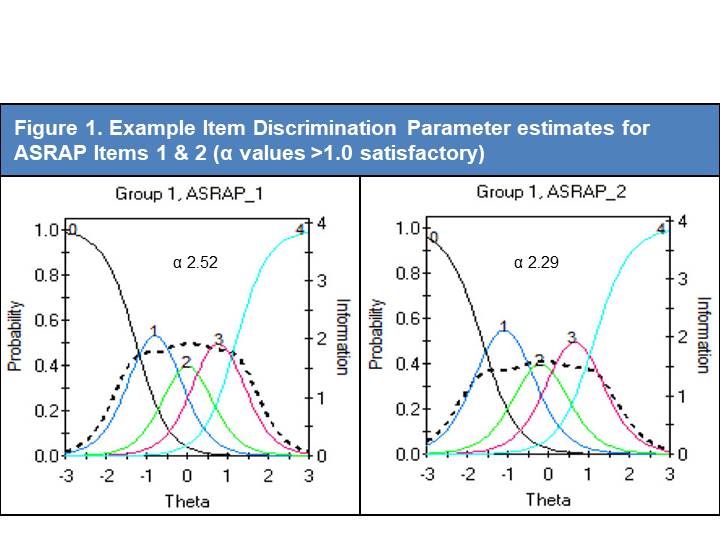
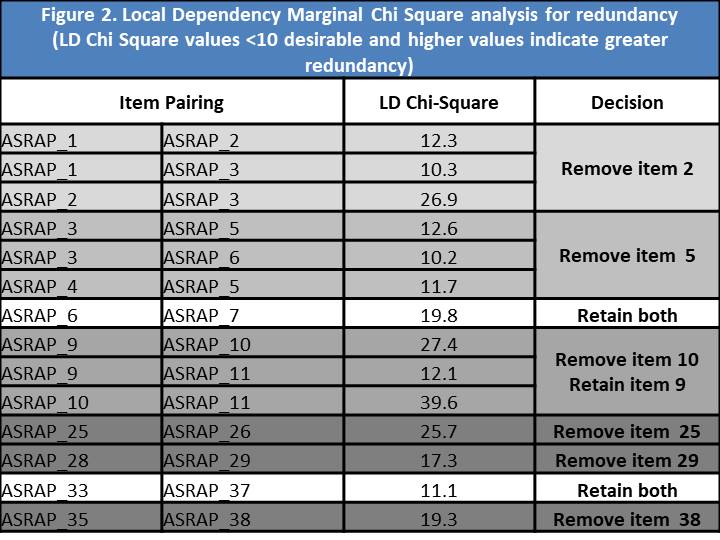
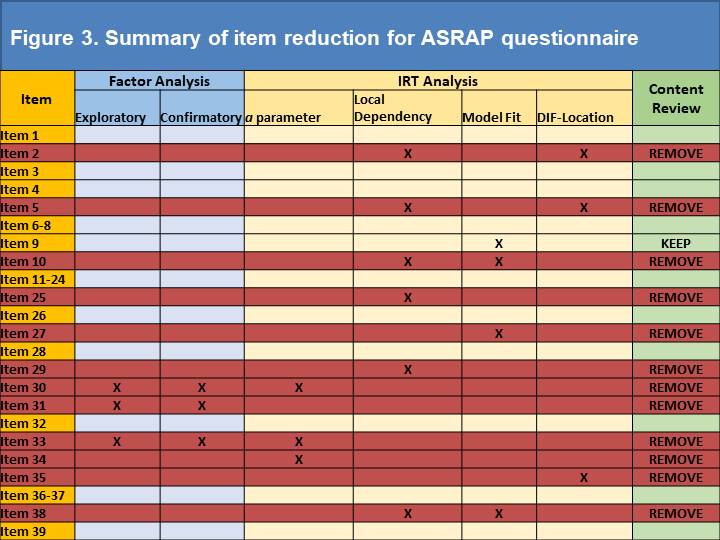
Results: A total of 438 SSc subjects were enrolled at UK (n=238) and US (n=200) sites, with adequate data for analysis on 421 subjects. Eigenvalues for uni- and bi-dimensional options were 21.577 and 3.08 respectively. A single factor solution provided the best-fitting model with factor loadings for the majority of factors ~0.8. Three items were removed owing to lower factor loadings (0.415-0.443). CFA revealed a Root Mean Square Error of Approximation of 0.114, a Standardized Root Mean Square Residual of 0.083 and a Confirmatory Factor Index of 0.917; each indicating excellent fit. Four low scoring Item Discrimination Parameter estimates (Figure 1) were identified (alpha scores of 1.04-1.25), leading to removal of one item (the remainder having already been removed). Only 14 potentially redundant pairings were identified using LD marginal chi square ( >10 indicates redundancy), which led to the removal of a further 6 items (Figure 2). Model fit analyses identified 3 problematic items; one of which was removed, one retained due to content validity and the other already removed). Finally, DIF identified 3 items which differed due to geographic location (2 already removed) and led to removal of an item (Figure 3).
Conclusion: We report a data driven approach (focussed on item response theory) to removing problematic or redundant items from the provisional ASRAP item bank. This has facilitated item reduction to a 27-item PRO instrument that will undergo psychometric testing and other tests of reliability and construct validity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pauling J, Yu L, Denton C, Frech T, Herrick A, Hummers L, Saketkoo L, Shah A, Khanna D, Domsic R. Item Reduction for the Assessment of Systemic Sclerosis-associated RAynaud’s Phenomenon (ASRAP) Questionnaire Using Data from the International Multicentre ASRAP Validation Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/item-reduction-for-the-assessment-of-systemic-sclerosis-associated-raynauds-phenomenon-asrap-questionnaire-using-data-from-the-international-multicentre-asrap-validation-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/item-reduction-for-the-assessment-of-systemic-sclerosis-associated-raynauds-phenomenon-asrap-questionnaire-using-data-from-the-international-multicentre-asrap-validation-study/