Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Hallmark autoantibody reactivities predict different patterns of skin involvement and risk of internal organ involvement. We have asked whether whole skin gene expression may explain these differences.
Methods: Genome-wide bulk RNA sequencing was performed on SSc patients with specific antibodies were included (anti-RNApol III (ARA) (n=6), anti-topoisomerase (ATA) (n=6) and anticentromere (ACA) (n=9)) as well as healthy controls (n=16). Analysis was carried out in Rstudio. Corrected t-test, and ANOVA tests were used for multiple group comparison. Significance for paired comparisons was ≥1.5-fold change with adjusted p-value < 0.05. For ANOVA comparisons, p value of < 0.05, and adjusted p-value of < 0.3 was considered significant. Gene set enrichment was obtained using gProfiler.
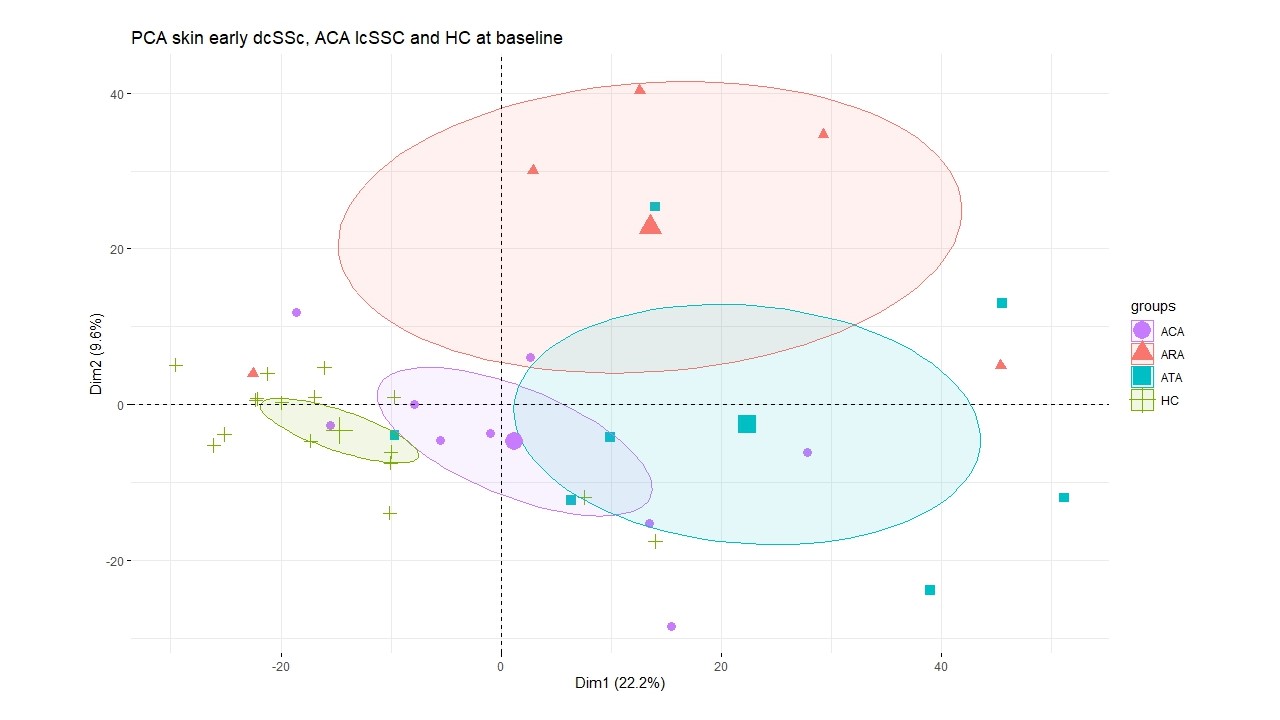
Results: Principal component analysis (PCA) analysis separated autoantibody subgroups (Fig 1). There were 288 significantly differentially expressed genes between SSc and HC, of which 231 were significantly elevated in SSc, including COMP (FC 3.71), SFRP4 (FC 2.64), THBS4 (Log FC 2.66). Pathway analysis revealed significant over expression of extracellular matrix (ECM) pathways, immune response activation, and regulation of complement cascade.
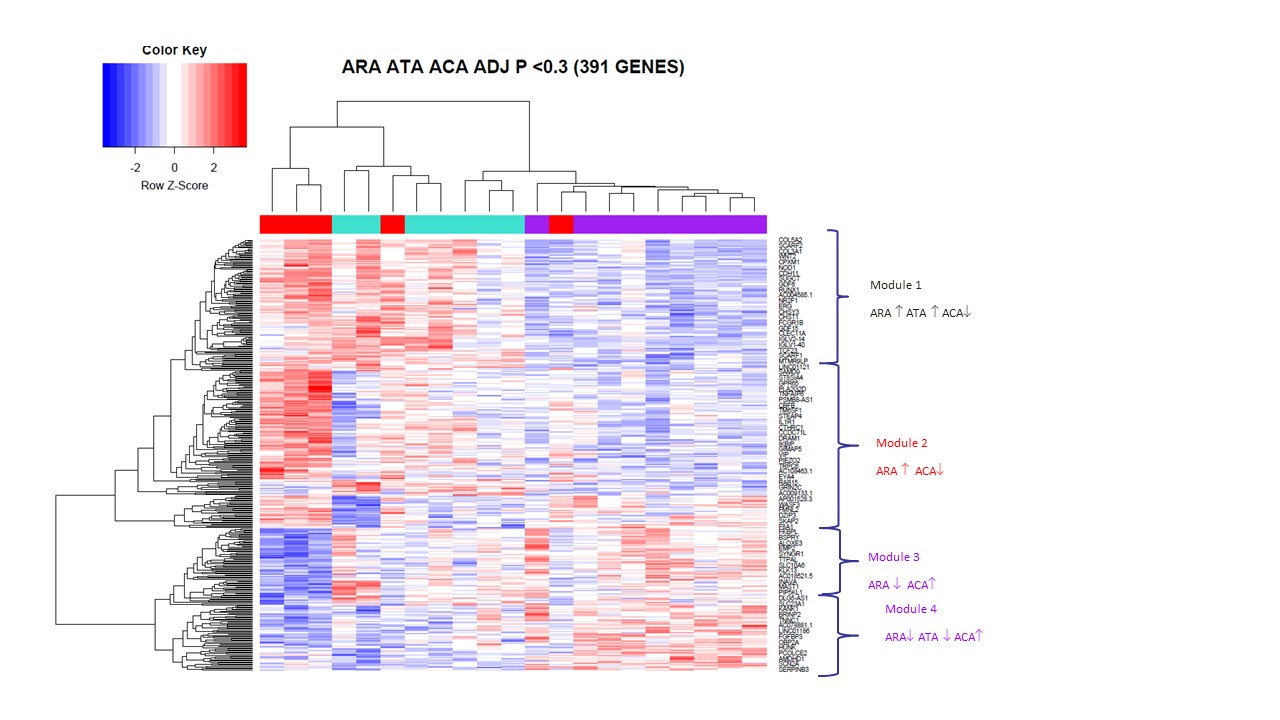
391 genes were significantly differentially expressed between ARA+, ATA+ and ACA+. Unsupervised hierarchical clustering grouped patients by antibody (Fig 2). Four gene expression modules separated ANA subgroups. Module 1 was overexpressed in all dcSSc compared with ACA+ patients. These included COL3A1, WNT2, ADAMTS12, and gene set enrichment revealed predominantly pathways associated with ECM, collagen fibril organization and adaptive immune response. Module 2 was upregulated in ARA+ patients but downregulated in ATA+ and ACA+ patients. This included genes MS4A1, CXCL13, CXCL8. Module 3 was downregulated in ARA+ and upregulated in ATA+ and ACA+ patients. This subgroup included HOTAIR, MYO10, SERPINB9P1. Module 4 was upregulated in ACA+ but downregulated in ARA+ and ATA+. These genes included WIF1, FGFBP1, SPAC17, and CADM3, with upregulation of heparin binding pathway, tissue development and multicellular organismal process.
Conclusion: There were notable differences based on autoantibody not appreciated by disease subset. The absence of cardiovascular genes modules differentiated autoantibody subgroups in consistent with a unifying vasculopathy signature across disease subtypes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Clark K, Campochiaro C, Yee P, Derrett-Smith E, Ong V, Denton C. Whole Skin Gene Expression Analysis Identifies Discrete Modules That Differentiate Antinuclear Antibody Subsets in Systemic Sclerosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/whole-skin-gene-expression-analysis-identifies-discrete-modules-that-differentiate-antinuclear-antibody-subsets-in-systemic-sclerosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/whole-skin-gene-expression-analysis-identifies-discrete-modules-that-differentiate-antinuclear-antibody-subsets-in-systemic-sclerosis/