Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a common multisystem inflammatory condition, affecting approximately 1% of the world population. The mechanisms underlying RA are still incompletely defined and current therapies, such as TNF-alpha inhibition, are mainly applied to mitigate the abnormal inflammation with limited success. RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) in the synovium release cytokines that drive inflammation and attract immune cells, particularly monocytes, to the synovium microenvironment. These monocytes can further polarize to inflammatory macrophages, exacerbate the tissue inflammation and contribute to joint destruction. Herein, we engineered an organotypic, perfusable ‘Synovium-on-a-Chip’ to recapitulate the in vivo pathophysiology of RA synovial microenvironments and to dissect the RA FLS and monocyte associated inflammatory mechanisms that contribute to RA.
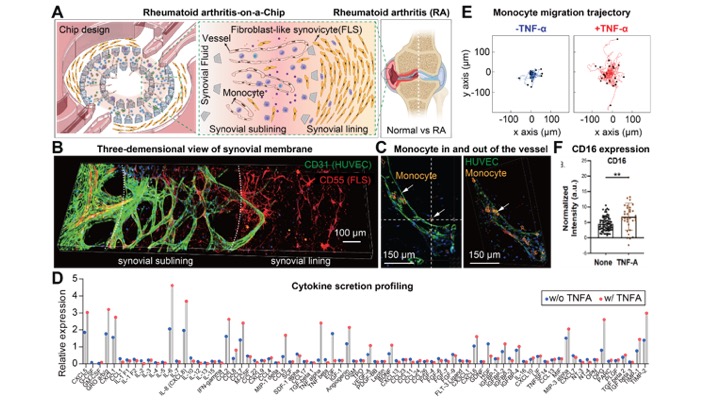
Methods: The microfluidic Synovium-on-a-Chip was constructed using a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)-based soft lithography technique. The chip contains two areas (Fig. 1A). The inner ring was infused with endothelial cells to form a 3D vascularized sublining layer. The outer ring was inoculated with RA FLS which aligned to form a synovial lining layer in a fibrin hydrogel (Fig. 1B-D). Monocytes were isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells and then loaded into the 3D vasculature (Fig. 1C). We analyzed cellular architecture and motility, gene expression, and cytokine secretion. Flow cytometry was used to assess cells after culture.
Results: We found that RA FLS released several cytokines, such as IL-6, CCL5, and CCL8, which facilitate the monocyte recruitment and drive inflammation in the RA niche (Fig. 1D). We confirmed that TNF-α (a major pathogenic cytokine in RA) induced inflammatory cytokine production and enhanced monocyte migration in the inflammatory environment (Fig. 1E). We also observed RA FLS and TNF-α treatment enhanced intermediate/non-classical CD16+ monocyte emergence (Fig. 1F).
Conclusion: We engineered a biomimetic ‘Synovium-on-a-Chip’ system that reconstitutes in vivo RA pathophysiology and dissected interactions between RA FLS and peripheral blood monocytes and their associated inflammatory milieu involved in RA. To our knowledge, ours is the first vascularized device used in biomimetic synovial culture and testing.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wampler Muskardin T, Ma C, Ma B, Van Buren K, Niewold T, Chen W. Vascularized ‘Synovium-on-a-Chip’ – A Novel and Adaptable Model for Dissecting Inflammatory Biology Underlying Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vascularized-synovium-on-a-chip-a-novel-and-adaptable-model-for-dissecting-inflammatory-biology-underlying-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/vascularized-synovium-on-a-chip-a-novel-and-adaptable-model-for-dissecting-inflammatory-biology-underlying-rheumatoid-arthritis/