Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (1945–1972) Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) can cause significant impairment in physical function. Sit to Stand (STS) and Timed Up and Go (TUG) are quick and operator-independent measures of physical function. We evaluated the psychometric properties (reliability, validity, and responsiveness) of these compared to established core set measures (CSMs) of disease activity and outcome. We also assessed the feasibility of patients self-performing these tests at home remotely.
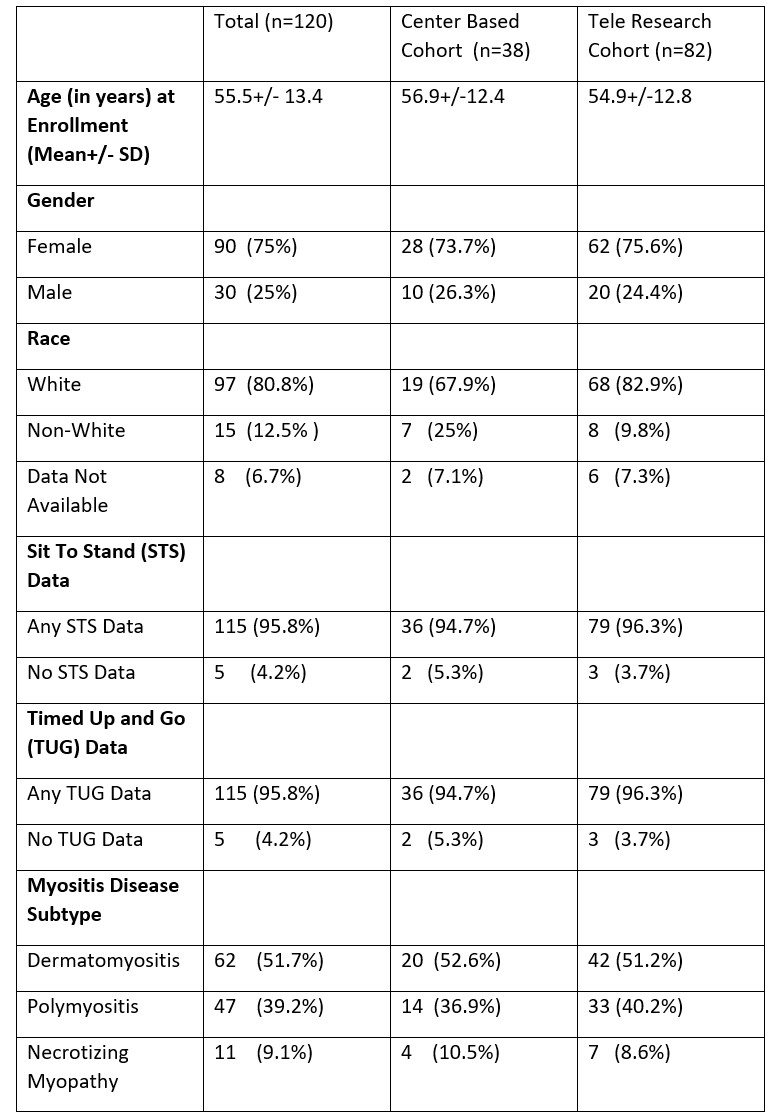
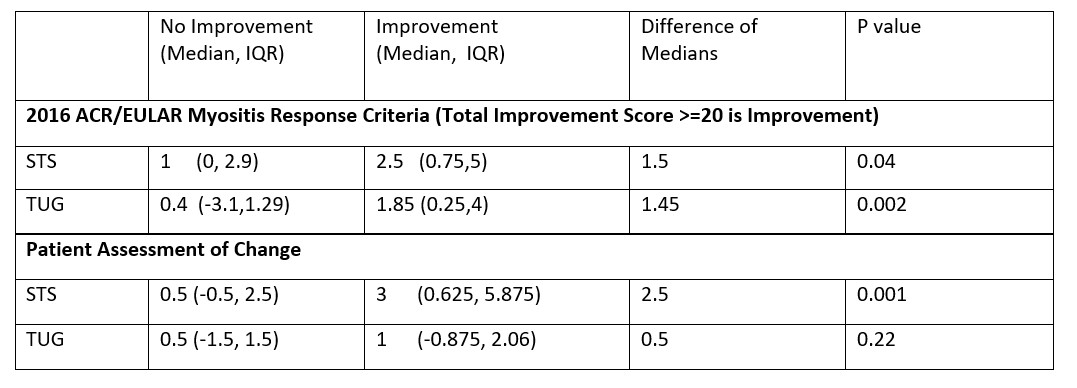
Methods: Data from a 6-month prospective observational study on IIM: Myositis Patient Centered Tele-Research Study (My PACER) was analyzed. There were 2 cohorts, a Tele-Research Cohort (TRC; remote enrollment from anywhere in US) and a Center Based Cohort (CBC; in person enrollment from myositis centers). Patient reported assessments and functional assessments (STS and TUG) were collected monthly over 6-months. STS is the number of times a patient can stand from a seated position and sit back down in 30 seconds. TUG is the time needed to rise from a chair, walk 3 meters, return to the chair and sit down. For the CBC, patients were trained in person by the coordinator, whereas for TRC training was provided by pre-recorded video instructions and patients self-performed the tests remotely. These tests were done twice at each visit, with the average of the two used in analysis. In addition, myositis core set measures (CSMs) were assessed by myositis experts at baseline and 6 month follow up (done in person for CBC patients and remotely through telemedicine visits and medical records for TRC patients). We examined test-retest reliability using Spearman correlation. To assess validity, we compared STS and TUG against all CSMs and other disease activity measures at baseline. We assessed responsiveness by assessing differences of median changes in STS and TUG in different categories of improvement according to various outcome measures and compared them using the Mann Whitney Test.
Results: 120 patients (75% female,80.8% Caucasian, mean age of55.5+/- 13.43 years,39.2 % PM, 51.7% DM, 9.1% Necrotizing Myopathy [NM]) participated in the study. There was strong test-retest reliability between baseline and month 1 for STS (r=0.8) and TUG (r=0.87); p< 0.01.Reliability was high regardless of method of recruitment and training for STS, however, TUG showed higher reliability in patients recruited and trained remotely (TRC) as compared to locally (CBC). Reliability was maintained across clinical disease subtypes (DM, PM and NM). At baseline STS and TUG showed very strong correlation with each other (r=-0.75) as well as with all CSMs except Extra-Muscular Global and CK. Strong correlations were seen with Muscle Disease Activity and a validated PRO of physical function (PROMIS-PF 20).At 6 months, STS and TUG were significantly better among patients who improved according to 2016 EULAR/ACR myositis response criteria (Total Improvement Score) compared to those who didn’t.
Conclusion: STS and TUG showed good reliability including when self-performed by patients remotely using video instructions, with excellent construct validity and responsiveness. STS and TUG are feasible functional assessment in myositis that can be performed in clinic or remotely.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chandra T, Lomanto Silva R, keret s, Sharma A, Moghadam-Kia S, Ascherman D, V. Oddis C, Aggarwal R. Valid and Reliable Physical Function Tests in Idiopathic Inflammatory Myositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/valid-and-reliable-physical-function-tests-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myositis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/valid-and-reliable-physical-function-tests-in-idiopathic-inflammatory-myositis/