Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Hyperuricemia (HUC) has been shown to have an impact in the left atrium and left ventricle remodeling leading to the development of heart failure (HF).
Experimental studies have shown that the increase of HUC results in cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, myocardial oxidative stress, interstitial fibrosis, and impaired diastolic relaxation. Ultimately, patients with HUC may also develop heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Methods: We conducted a cross-sectional study to determine the correlation between serum uric acid levels and the severity of HFpEF, after receiving the Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval (IF2467628). HUC was defined as a mean serum uric acid level equal to or more than 7.0 mg/dL. 161 patients with a diagnosis of HUC were screened by chart review between January 2016 to December 2018 following these inclusion criteria: 1) reported HUC at least one year before the echocardiogram (TTE) was performed, 2) echocardiographic parameters to classify the severity of diastolic dysfunction.
Fisher’s exact test was used for qualitative variables and Pearson chi-square test for quantitative variables. Multiple regression analysis, including potential confounders factors (age, gender, race, use of uric acid lowering agents, use of Losartan, low-dose Aspirin, diuretic agent, use of more than 3 blood pressure-lowering agents, history of comorbid conditions related to diastolic dysfunction (HTN, resistant HTN, Afib, DM, obesity, CKD), presence of Gout and mean ejection fraction) was performed. Calculation of coefficient ratios and their 95% confidence interval for the association between mean uric acid level and grade of severity of diastolic dysfunction was performed. P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. STATA (IC-15.1; Stata Corp) was used for the statistical analysis.
Results: Out of the 161 patients, 56 patients met our inclusion criteria of which 78.6 % had a mean uric acid level above 7 mg/dL. For normal left ventricle function and Grade I diastolic dysfunction group, the mean age was 65.8 (±13.6) years and mean uric acid level was 8.06 (±0.29) mg/dL, as compared to 60.1 (±20.8) years and mean uric acid of 9.36 (±1.09) mg/dL for Grade II and III diastolic dysfunction group. 47.5% of patients with normal and impaired relaxation were on a uric acid lowering agent versus 62.5% of patients in the group with higher grade diastolic dysfunction. 85% of the low-grade diastolic dysfunction group had a co-existing diagnosis of Gout versus 93.7% of the group with grade II and III diastolic dysfunction. The difference of mean uric acid level between Grade III diastolic dysfunction and normal diastolic function was of 4.99 mg/dL (p< 0.001), 3.86 mg/dL (p= 0.009) for Grade I and 3.83 mg/dL (p= 0.020) for Grade II diastolic dysfunction. Our results (Table 4) showed that the risk of severe diastolic dysfunction increases by 0.053 (95%-CI 0.001-0.106; p= 0.047) for every unit of increase in mean of uric acid level.
Conclusion: There is a directly proportional correlation between the level of uric acid and the severity of diastolic dysfunction. The group with higher diastolic dysfunction had a higher prevalence of Gout independent of confounding variables.
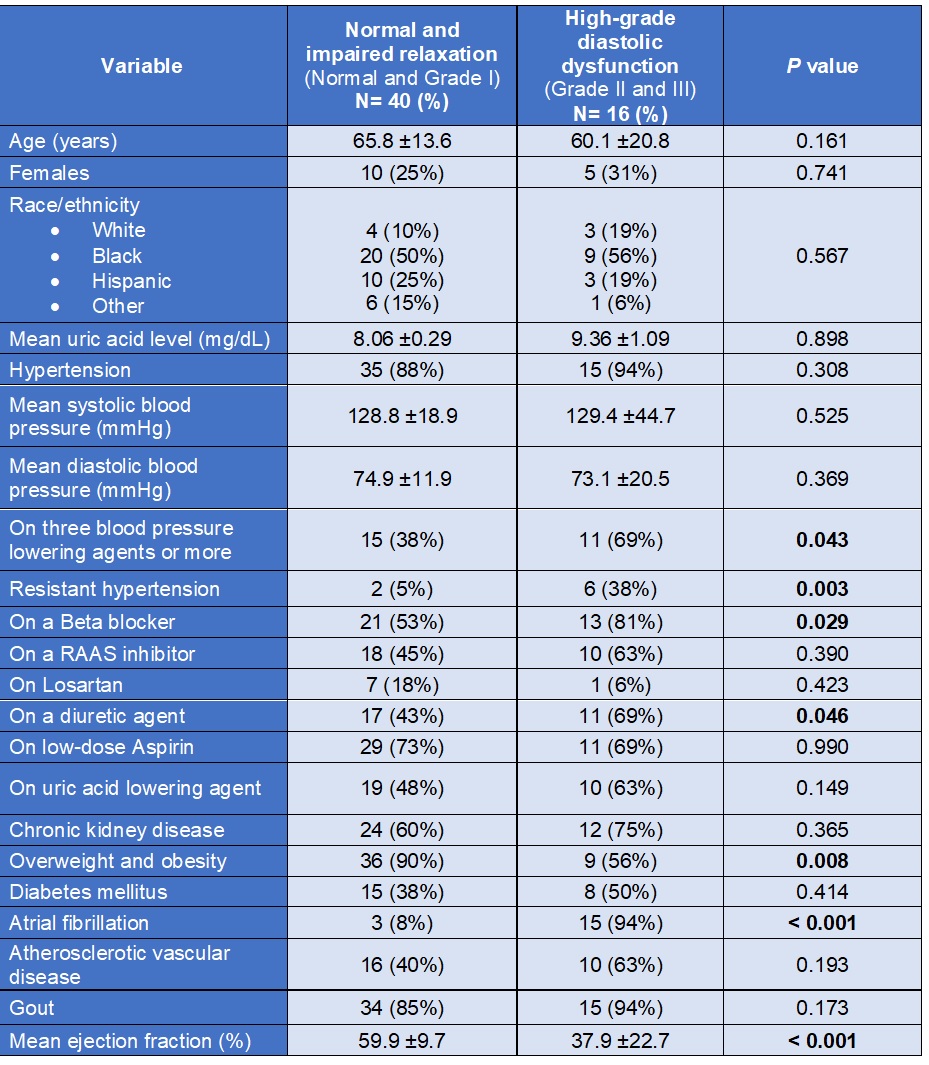 Table 1. Baseline Characteristics
Table 1. Baseline Characteristics
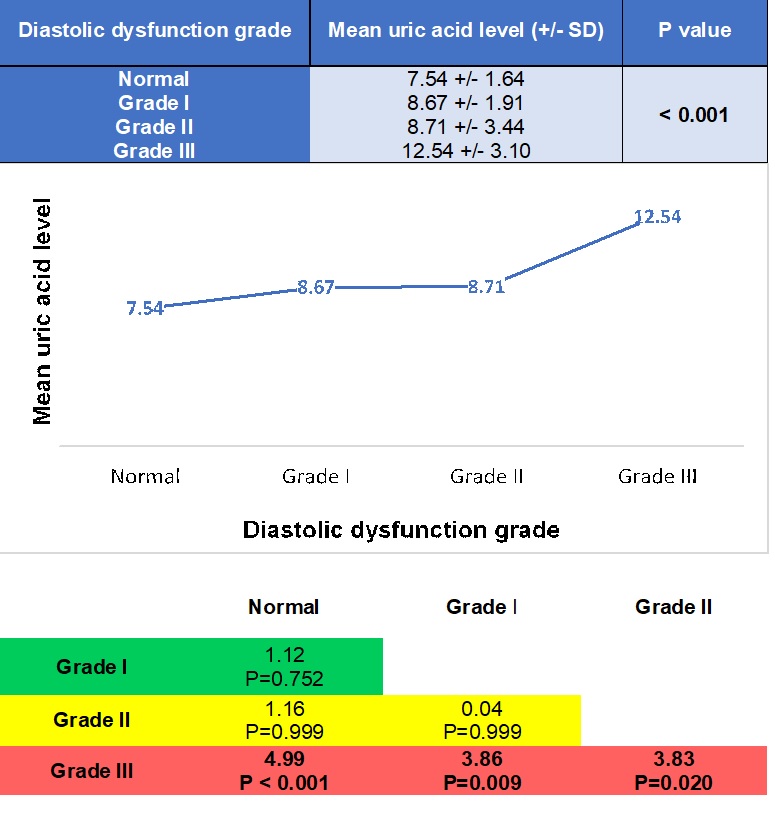 Table 2. Mean uric acid level across diastolic dysfunction grades
Table 2. Mean uric acid level across diastolic dysfunction grades
 Table 3. Correlation between mean uric acid level and the severity of HFpEF
Table 3. Correlation between mean uric acid level and the severity of HFpEF
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Arevalo A, Munoz A, Haddadin F, Sud K, Contreras G, Murray S, Ali Y, Argulian E. Uric Acid Level Is Associated with Severity of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/uric-acid-level-is-associated-with-severity-of-heart-failure-with-preserved-ejection-fraction/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/uric-acid-level-is-associated-with-severity-of-heart-failure-with-preserved-ejection-fraction/
