Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 6:00PM-7:00PM
Background/Purpose: Increasing attention has been recently paid to the development of parent- and child-centered composite DAS for the assessment of health status of children with rheumatic diseases. We aimed to develop and test an entirely parent-centered composite DAS for JDM, named parent Juvenile DermatoMyositis Activity Index (parJDMAI). Two versions of the score were evaluated.
Methods: Both parJDMAI1 and parJDMAI2 include the following items: 1) parent assessment of skin disease activity (Parent Skin Scale) on a 0-5 scale, by giving 1 point to the presence of each of: i) rash on eyelids, ii) nose/cheeks, iii) knuckles, iv) trunk/arms, v) skin ulceration; 2) parent assessment of muscle disease activity (Parent Muscle Scale) on a 0-5 scale, by giving 1 point to the presence of each of: i) fatigue/discomfort, ii) muscle weakness, iii) muscle pain, iv) voice change, v) difficulty swallowing; 3) parent assessment of childs fatigue on a 0-10 visual analog scale (VAS) (0 =no fatigue; 10 = maximum fatigue). As fourth item, the parJDMAI1 includes the parent global assessment of childs wellbeing on a 0-10 VAS (0 = best; 10 = worst), whereas the parJDMAI2 includes the parent global assessment of disease activity on a 0-10 VAS (0 = no activity; 10 = maximum activity). To give the 4 components of the tools the same weight, the scores of the Parent Skin and Muscle Scales were doubled. Thus, the total score of both instruments ranges from 0 to 40. Initial validation was conducted on a multicentric prospective sample of 213 patientsfollowed in standard clinical care (number of visits = 577), and on a monocentric sample including 50 patients, all assessed at baseline and 32 also assessed after a median of 3.9 months (number of visits = 82). Validation analyses included calculation of the correlations between individual parJDMAI items and physician-centered JDM outcome measures, and between the total score of parJDMAI1 and parJDMAI2 with that of the global composite DASs for JDM named JDMAI1 and JDMAI2. Because both JDMAI1 and JDMAI2 include the parent global assessment of childs wellbeing, which is also part of parJDMAI1, we also tested the correlations of parJDMAI1 with reduced versions of JDMAI1 and JDMAI2, that included only the 3 physician-centered items. Spearman correlations were defined as low, moderate or high when rS was 0.4, ≥ 0.4 and ≤ 0.7, or 0.7, respectively.
Results: Correlations between individual components of parJDMAI1 and parJDMAI2 and physician-centered JDM outcome measures were low-to-moderate in the multicentric sample, but moderate in the monocentric sample. Likewise, correlations between the scores of parJDMAI1 and parJDMAI2 and that of original and reduced versions of JDMAI1 and JDMAI2 were strong in the monocentric sample, but moderate in the multicentric sample.
Conclusion: The new parent-centered composite DASs revealed satisfactory measurement properties. That correlations with physician-centered outcome measures and original and reduced JDMAI versions were higher in the monocentric sample than in the multicentric cohort indicates that the proposed tools should be further tested in different clinical and cultural environments before their widespread use can be recommended.
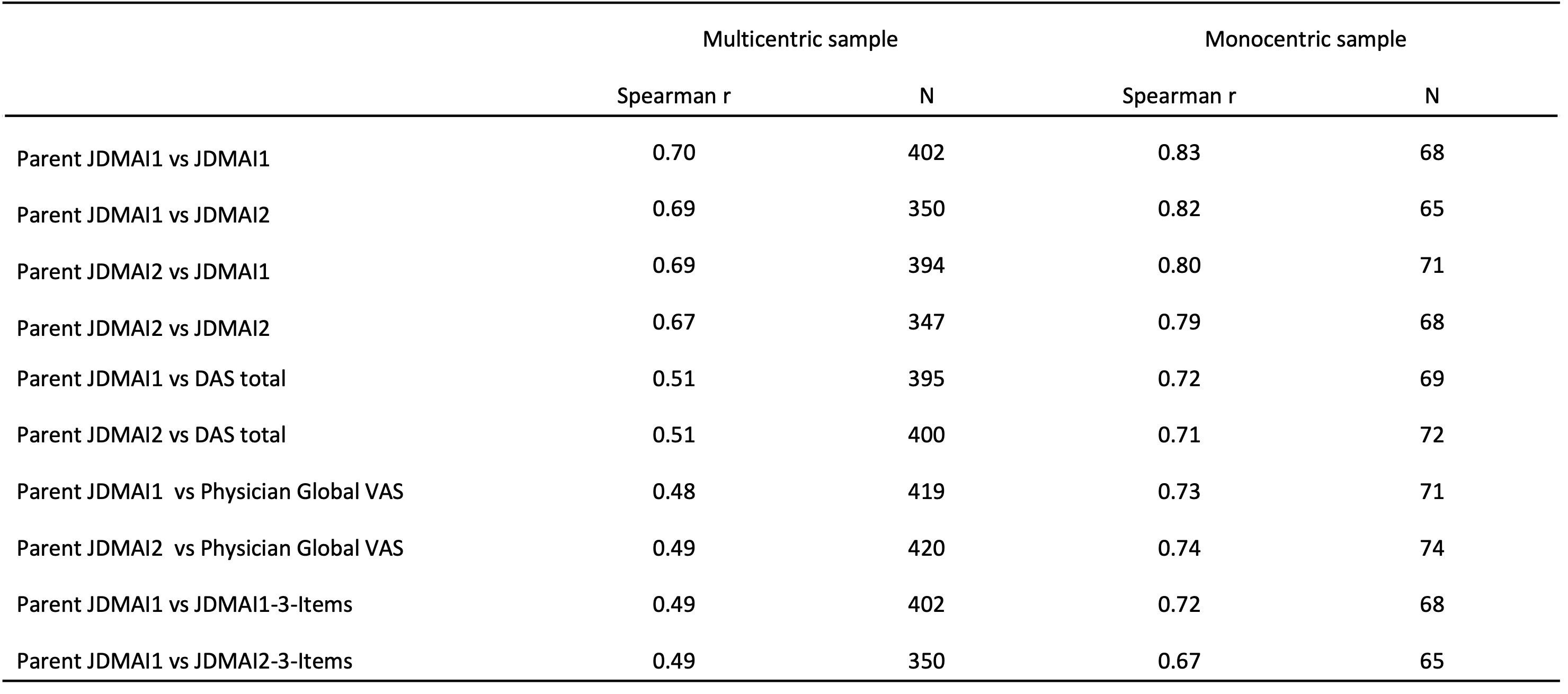 Spearman correlation between parJDMAI1 and parJDMAI2 and other JDM outcome measures.
Spearman correlation between parJDMAI1 and parJDMAI2 and other JDM outcome measures.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rosina S, Rebollo-Giménez A, Tarantola L, Naddei R, Consolaro A, Pistorio A, Ravelli A. Towards the Development of Composite Parent-Centered Disease Activity Scores for Juvenile Dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 4). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/towards-the-development-of-composite-parent-centered-disease-activity-scores-for-juvenile-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to 2023 Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/towards-the-development-of-composite-parent-centered-disease-activity-scores-for-juvenile-dermatomyositis/
