Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Neutrophils are key initiators and promoters of autoimmunity, including SLE, via the elaboration of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs). We tested the efficacy of the biolipid mimetic, NAP1051 that has transcellular activity in the inflammatory process. NAP1051 is a lipid-based agonist of FPR2/ALXR that inhibits neutrophil migration and promotes macrophage mediated efferocytosis in SLE-prone NZM 2328 mice.
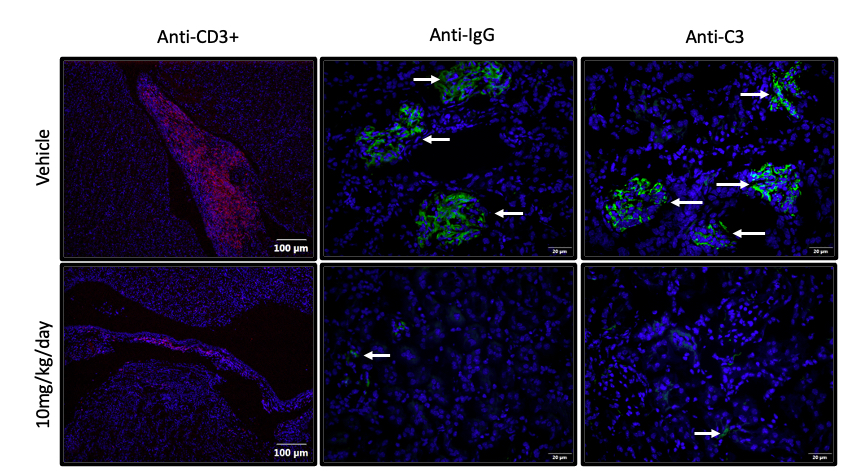
Methods: Female NZM mice 4-5 months of age (when serologic autoimmune and renal glomerulonephritis have developed) were gavaged with graded doses of NAP1051 (2.5, 5.0, 10 mg/kg/day and vehicle; n=5 per group) for 28 consecutive days and monitored for proteinuria. At study termination, blood chemistry, CBC, and immune profiles were determined. Kidneys were harvested for expression of inflammatory cytokines and markers of NETosis. The kidneys were also assessed by H&E staining and T-cell infiltration, IgG and C3 complex depositions by immunofluorescence staining.
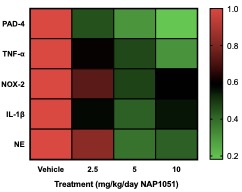
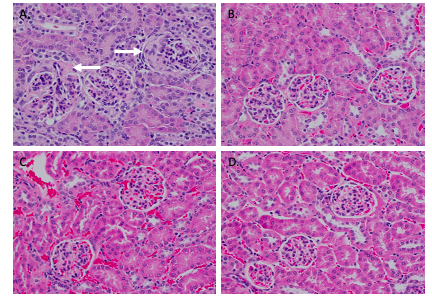
Results: NAP1051 dramatically attenuated nephritis in a dose-dependent manner, as evidenced by reduced proteinuria, serum BUN levels, expression of inflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, TNF- α), and expression of biomarkers of NETosis (NOX-2, PAD4 and NE) in the kidney (Figure 1). Infiltrating T-cells and glomerular deposition of C3 and IgG in the kidney were also greatly reduced by NAP1051 treatment (Figure 2). Perhaps most strikingly, vehicle-treated mice developed glomerular crescents, consistent with rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis, whereas glomerular pathology was completely absent at the higher doses of NAP1051 (Figure 3). Importantly, there were no biochemical or histological signs of drug-related toxicities at any tested dose. Serological testing showed no changes in anti-dsDNA and anti-IgG levels between treatment groups.
Conclusion: NAP1051 demonstrated dose-dependent efficacy clinically and pathologically in NZM mice. NAP1051 prevented chronic glomerulonephritis, damage to the kidney tissues and reduced the expression of inflammatory markers without signs of toxicity. Interestingly, NAP1051 reduced T-cell infiltration into the kidney without affecting circulating autoantibody levels, suggesting that this compound exerts its therapeutic effect in a manner that is independent of autoantibody production. NAP1051 was also able to reduce NETosis biomarker expression in a dosage-dependent manner, suggesting that it is able to reduce PAD4 and neutrophil elastase expression. Taken together, NAP1051 exerts its activity through modulating NETosis for the treatment of SLE. Additional studies are currently underway to confirm these initial results and, if confirmed, would set the stage for evaluation in human SLE.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dave P, Dong T, Mead A, Asante I, Ebright B, Zhou E, Li R, Petasis N, Stohl W, Louie S. Therapeutic Efficacy of a Biomimetic ALXR Agonist in Murine Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-efficacy-of-a-biomimetic-alxr-agonist-in-murine-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-efficacy-of-a-biomimetic-alxr-agonist-in-murine-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-sle/