Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: Abstracts: Sjögren’s Disease – Basic & Clinical Science (1680–1685)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:15PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Performance of the recently developed composite responder index STAR is highly awaited. We conduscted this study to evaluate the performance of STAR in previously completed clinical trials shared within the NECESSITY consortium.
Methods: Data from 9 trials used for STAR development (Abatacept (ASAP-III), leflunomide+hydroxychloroquine (REPURP-SS) and rituximab (TEARS and TRACTISS), the iscalimab and ianalumab phase 2 trials, Baminercept, hydroxychloroquine (JOQUER), tocilizumab (ETAP)) and two other independent clinical trials (GSK (NCT02631538), Belimumab + Rituximab, Belimumab, Rituximab versus placebo and BMS Abatacept (NCT02915159). Trials were classified, by an expert panel, as positive, negative or “in between”, in regards to primary and key secondary endpoints. The STAR candidate, and its 14 alternate binary option (including the recently developed CRESS) responses were calculated retrospectively at the timing of the primary endpoint of the corresponding trial.To better appraise sensitivity to change of the STAR options, meta-analyses of the 11 RCTs were run for each option, separately for positive and “in between” trials together, where positive results were expected, and negative trials, where no difference between groups was expected. Meta-analyses were run using the Mantel-Haenszel method with Paule-Mandel estimator for τ2, Q-profile method for confidence interval of τ2and τ and continuity correction of 0.5 in studies with zero cell frequencies. Treatment effect was expressed as an odds ratio (OR): 1 or below indicates the absence of any effect, above 1 favors the experimental treatment. Consequently, a STAR option that is sensitive and specific to change should have a treatment effect close to the null effect for the negative trials, and as far from the null effect for the positive trials.
Results: Of the 11 trials, 7 were classified as positive by the expert panel. Among these positive trials, when using STAR candidate and the 14 alternate binary options, OR ranged from 2.85 to 3.75, and the number of trials actually positive (ie, having significant between arm difference with the STAR option) ranged from 2 to 4 (figure 1 in red). Among the 4 negative trials, when using the STAR candidate and the 14 alternate binary options, OR ranged from 0.69 to 2.11. OR was statistically significant (in favor of an effect of the treatment) in 3 STAR alternate option, which wrongly detect a difference in trial were no efficacy was observed (figure 1 in blue). The STAR candidate displays an OR of 3.01 (1.85 – 4.91) in positive trials and 1.30 (0.82 – 2.05) in negative trials and detects significant differences in 4 of the 7 positive trials (figure 2). The CRESS displays an OR of 3.12 (1.60 – 6.07) in positive trials and 2.11 (1.32 – 3.37) in negative trials and detects significant differences in 4 of the 7 positive trials, and one of the negative trials.
Conclusion: In this analysis based on 11 trials, the STAR appears to detect treatment response accurately, with a high sensitivity to change for treatments showing a beneficial effect. Additionally, it exhibits specificity to change by not falsely detecting improvement in negative trials.
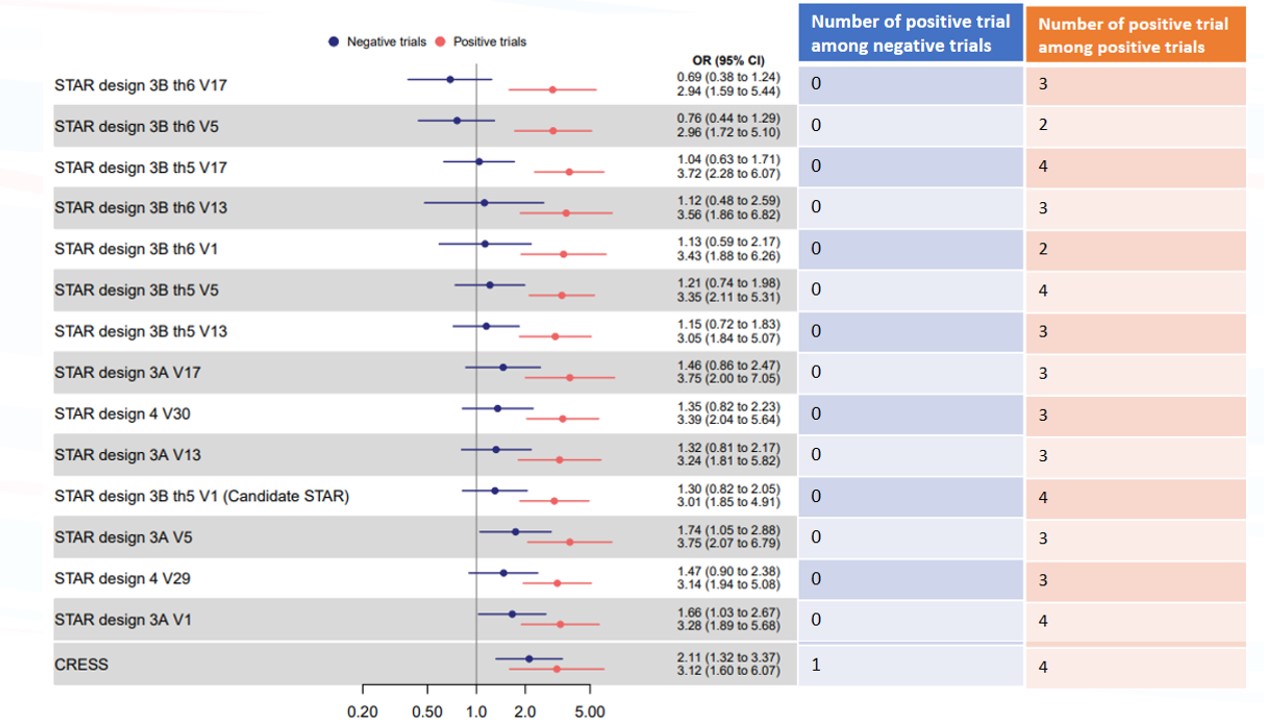 Summary of results of the meta-analyses of negative and positive trials, using as endpoint, the STAR candidate and alternate binary options
Summary of results of the meta-analyses of negative and positive trials, using as endpoint, the STAR candidate and alternate binary options
.jpg) Meta-analyses of the 4 negative and 7 positive trials using the STAR candidate as endpoint
Meta-analyses of the 4 negative and 7 positive trials using the STAR candidate as endpoint
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Seror R, Baron G, Perrodeau E, Piatrova A, Bootsma H, Bowman S, GOTTENBERG J, Cornec D, Bombardieri m, Arends S, Fisher B, Hueber W, Sreih A, Christodoulou A, van Maurik A, van Roon J, Devauchelle V, Gergely P, Mariette X, Porcher R. The Sjögren’s Tool for Assessing Response (STAR) demonstrates its ability to accurately detect treatment efficacy in 11 recent RCTs in Sjögren’s disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-sjogrens-tool-for-assessing-response-star-demonstrates-its-ability-to-accurately-detect-treatment-efficacy-in-11-recent-rcts-in-sjogrens-disease/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-sjogrens-tool-for-assessing-response-star-demonstrates-its-ability-to-accurately-detect-treatment-efficacy-in-11-recent-rcts-in-sjogrens-disease/
