Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: SLE – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: LN confers poor prognosis, and there is a lack of effective non-invasive tests to assess disease activity and treatment response. We previously showed that a set of six urinary biomarkers (NGAL, KIM-1, MCP-1, adiponectin, hemopexin, ceruloplasmin) is sensitive and specific in adult patients with active LN, using renal biopsy as reference. In pediatric patients, Renal Activity Index for Lupus (RAIL) is effective in distinguishing inactive vs active LN and can differentiate LN treatment responders from non-responders. We hypothesized that the same would be true in adult patients.
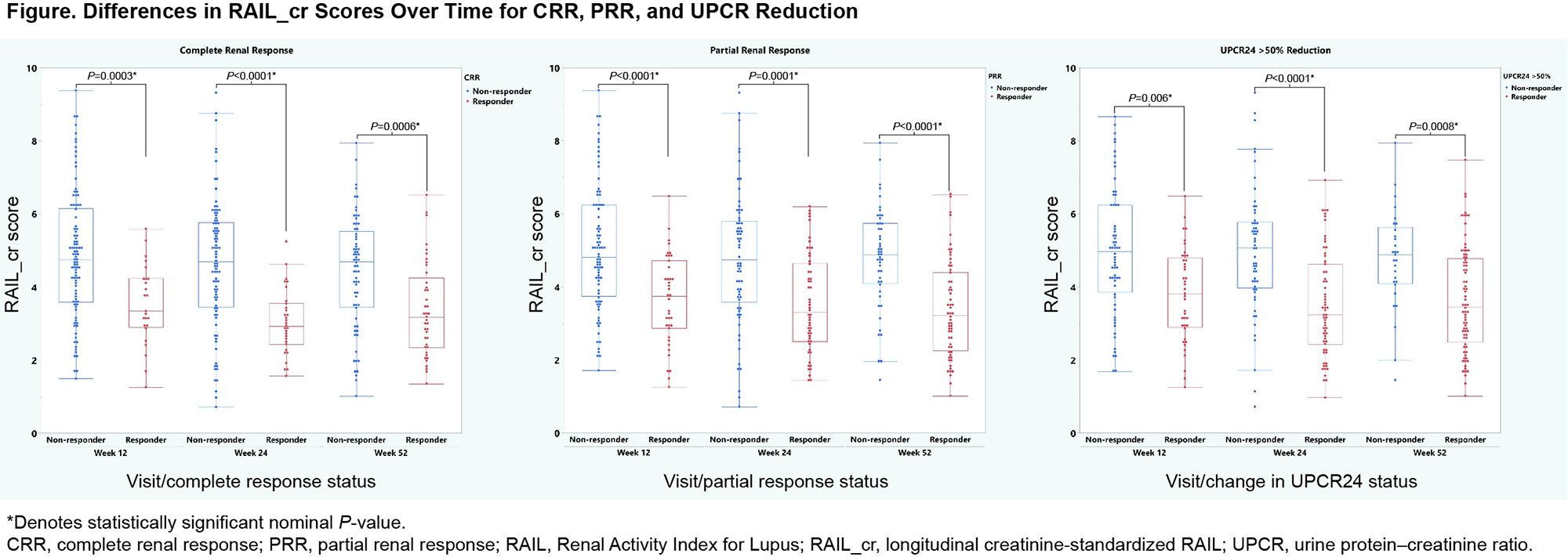
Methods: Urine samples were obtained at baseline, Week 12, 24, and 48 from 131 biopsy-proven active Class III and IV adult patients with LN participating in a phase 2 trial (NCT02547922). Urine samples were also taken at baseline from a subset of 59 patients with renal BILAG scores C, D, or E from a phase 3 trial with active non-renal SLE (NCT02446912); RAIL biomarkers were assayed using single-plex assays. All patients fulfilled ≥4 of the 11 ACR SLE 1997 classification criteria. Clinical characteristics comparisons and Wilcoxon rank sum tests comparing urinary biomarkers between studies were performed, and RAIL scores were calculated. Receiver operator characteristic (ROC) analyses were conducted assessing the ability of RAIL scores to distinguish patients with renal activity and involvement. In the LN trial, longitudinal creatinine-standardized RAIL (RAIL_cr) scores were compared between non-responders and patients with complete renal response (CRR), partial renal response (PRR), and urine protein–creatinine ratio (UPCR) decrease ≥50% (UPCR50). CRR was defined as 24 h UPCR ≤0.7 mg/mg, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or a decrease ≥20%, no treatment discontinuation, and no restricted medication use. For PRR, improvement in 24 h UPCR to < 1.0 mg/mg (if baseline UPCR ≤3 mg/mg) and to ≤3.0 mg/mg (if baseline UPCR >3 mg/mg) and >50% improvement was required.
Results: Among 131 LN patients, 43% were white, and 83% were female with a median age of 34 years. At baseline, median (interquartile range) proteinuria (mg/dL), eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2), and RAIL_cr scores were 2.62 (1.53–4), 91.8 (63.1–125), and 5.59 (4.31–6.47), respectively. In the SLE study (n=59), 76% were white and 93% were female with a median age of 36 years. Median non-renal SLEDAI-2K score was 12. RAIL biomarker concentrations and median RAIL_cr scores were higher in the LN group than the SLE group (P< 0.001). ROC analyses, including RAIL score, showed an area under the curve of 0.8 with an odds ratio of log-transformed RAIL 2.03. In the LN trial at Weeks 12/24/52, there were 25/31/41 patients with CRR, 39/54/60 with PRR, and 40/73/77 with UPCR50, respectively. RAIL_cr scores significantly differentiated responders at Weeks 12, 24, and 48 using a Wilcoxon rank sum test (Figure).
Conclusion: RAIL_cr identifies adult SLE patients with active renal disease. Longitudinal RAIL_cr scores differentiate responders and non-responders to LN treatment. RAIL_cr has novel clinical utility as a non-invasive biomarker signature to monitor treatment response over time.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Brunner H, Lindholm C, Cody E, Devarajan P, Huang B, Sinibaldi D, Ramaswamy M, Knagenhjelm J, Qiu T, Jones F, Brohawn P, Tummala R, White W. The Renal Activity Index for Lupus (RAIL) Identifies Active Renal Disease in SLE Patients and Its Longitudinal Score Associates with Renal Responses in Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-renal-activity-index-for-lupus-rail-identifies-active-renal-disease-in-sle-patients-and-its-longitudinal-score-associates-with-renal-responses-in-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-renal-activity-index-for-lupus-rail-identifies-active-renal-disease-in-sle-patients-and-its-longitudinal-score-associates-with-renal-responses-in-lupus-nephritis/