Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0609–0672) Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster I: Research
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Pulmonary involvement is major causes of mortality in patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc). The breath-holding test (BHT), rapid bedside test, is a useful surrogate marker of pulmonary capacity in SSc patients. This study aimed to develop a machine learning (ML) model to predict pulmonary parameters, using real-time data of oxygen saturation (SpO2) and pulse rates obtained during the BHT in SSc patients.
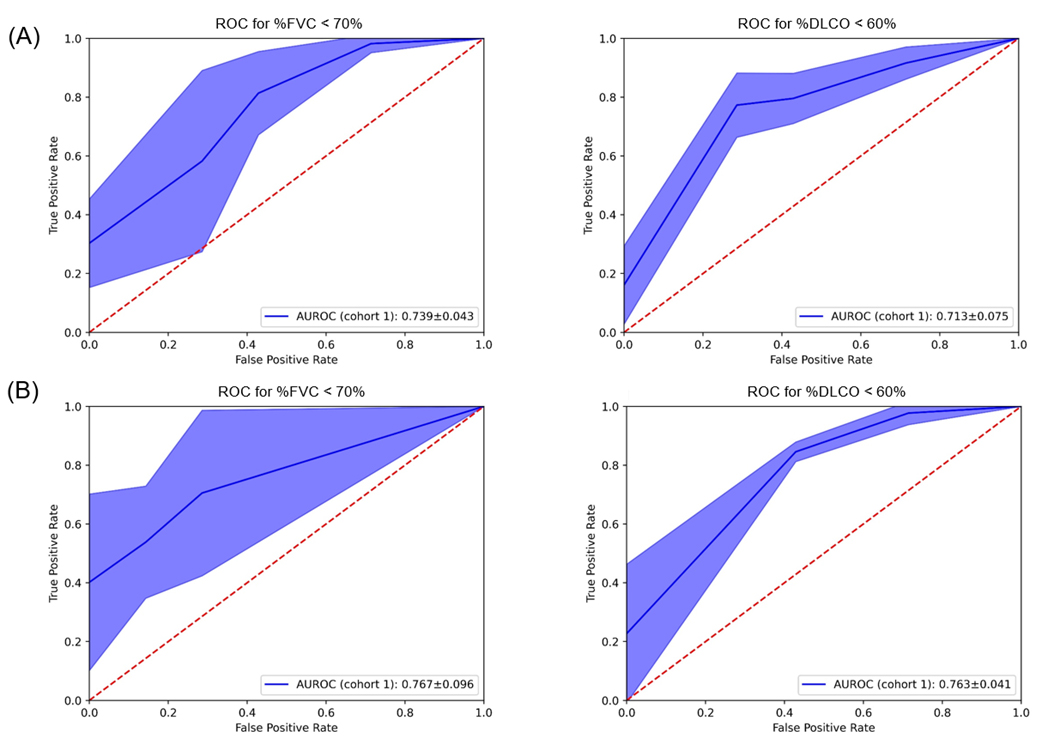
Methods: Two prospective SSc cohorts were recruited for the study. Cohort 1 (n = 72) was for training a ML model and collected from August 2020 to February 2021, while Cohort 2 (n = 84) was for external validation of the established model and collected from April 2022 to September 2022. Real-time values of SpO2 and pulse rates were obtained during the BHTs and 6-min walking tests (6MWT) in Cohort 1, while the same data were collected during BHT in Cohort 2. The random forest classifier was applied to predict pulmonary functions (Forced vital capacity, FVC; diffusion capacity of carbon monoxide, DLCO), using data on SpO2 and pulse rates. In addition, demographic information such as age, gender, and body mass index, modified Rodnan skin score was also concatenated to the input feature. The validity of the ML model was evaluated using the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve and the Area Under the ROC Curve (AUROC).
Results: A total of 72 subjects were enrolled in Cohort 1 and 84 subjects in Cohort 2, respectively. There was an overlap of 36 subjects between Cohort 1 and 2. In 4-fold cross-validation evaluation from Cohort 1, the ML algorithm using data from BHT showed AUROC of 0.739 ± 0.043 for %FVC < 70%, and 0.713 ± 0.075 for %DLCO < 60%, respectively (Figure 1A). A model using only SpO2 during BHT values showed a comparable AUROC to predict FVC and DLCO (AUROC for %FVC; 0.767 ± 0.096, and %DLCO; 0.763 ± 0.041, respectively) (Figure 1B). The ML model using data from 6MWT showed similar performance compared with BHT (AUROC for %FVC; 0.780 ± 0.040 and %DLCO; 0.754 ± 0.099, respectively). Cohort 2, an external validation cohort, showed similar AUROC (For %FVC, 0.686; for %DLCO, 0.669).
Conclusion: Our ML models showed the potential to discriminate decreased pulmonary function in SSc patients using data from SpO2 and pulse rates during the BHT and 6MWT. Our results suggest that BHT, when combined with SpO2 monitoring, can be useful to detect impaired lung capacity in SSc patient in whom a pulmonary function test is difficult to perform. (NCT04484948)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yeo J, Lim M, Kim J, Jung J, Lee S, Lee E. The Effectiveness of Breath-holding Test to Predict Pulmonary Function in Systemic Sclerosis Patients Using Machine Learning Model [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effectiveness-of-breath-holding-test-to-predict-pulmonary-function-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients-using-machine-learning-model/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-effectiveness-of-breath-holding-test-to-predict-pulmonary-function-in-systemic-sclerosis-patients-using-machine-learning-model/