Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Cell bound complement activation products (CB-CAPs) including erythrocyte-bound C4d (EC4d) and B-lymphocyte C4d (BC4d) demonstrate increased diagnostic accuracy compared to conventional SLE markers (anti-dsDNA, anti-Smith and C3/C4). Clinical studies have validated a multianalyte panel (MAP) algorithm that integrates CB-CAPs with conventional autoantibodies (Ab), demonstrating balanced sensitivity and specificity for SLE. This study tests the clinical validity of CB-CAPs and MAP in a large cohort by evaluating their unique contribution to SLE sensitivity beyond conventional markers.
Methods: A pooled analysis was performed using biomarker data collected from 12 single and multi-center clinical validation trials involving 36 investigators across the U.S. A total of 1034 unique adult SLE subjects meeting the 1997 ACR criteria were analyzed and compared to 1489 controls (apparently healthy volunteers [AHV], N = 458; other autoimmune rheumatic diseases [OARD], including RA, N = 439; primary Sjögrens, N = 166; other rheumatic disease, N = 138; chronic pain disorders, including fibromyalgia, N = 235; chronic localized pain, N = 52). Flow cytometry was performed on erythrocytes and lymphocytes isolated from whole blood samples (EC4d & BC4d). Abs were measured by ELIA and C3/C4 were measured by immunoturbidimetry. Machine learning algorithms were employed to build predictive models for distinguishing SLE from a combined group of OARD and AHV. A Gradient Boosting Classifier model, chosen for superior LogLoss in 10-fold cross-validation, served as the base model (CB-CAPs, conventional Ab and C3/C4). A logistic regression model using MAP scores was developed. Both models underwent 10-fold cross-validation, with a 20% test set used for validation. Biomarker sensitivity for SLE was compared using chi-square analysis.
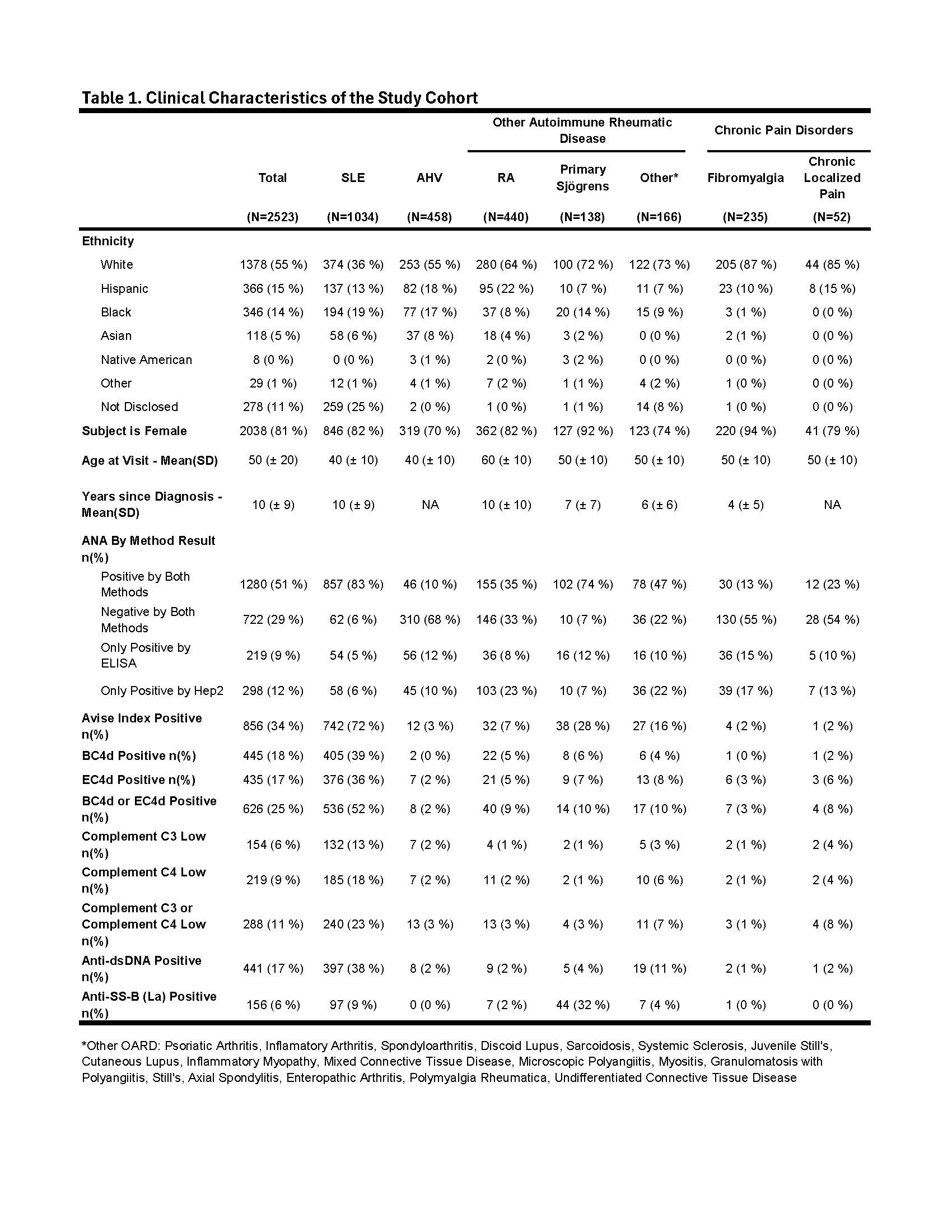
Results: The SLE cohort was majority female (82%), white (36%), mean (SD) age of 40 (± 10) with mean years since diagnosis of 10 (± 9) (Table 1). The combination of EC4d, BC4d, Abs and C3/C4 captured 67% of SLE with EC4d, BC4d, conventional markers contributing 4%, 7% and 17%, respectively, to the overall sensitivity for SLE (Fig.1A). Isolated positive CB-CAPs were more sensitive than isolated low C3/C4 (17% vs. 3%; p < 0.001) (Fig. 1B). The addition of MAP to CB-CAPs and conventional markers captured 76% of SLE (Fig. 1C). MAP was isolated positive in 25% of SLE cases, significantly (p < 0.001) higher than Abs (1%) and C3/C4 (3%), respectively. ROC analysis of MAP and a base model combining CB-CAPs, Abs and C3/C4 yielded similar AUCs on training (88% vs. 86%) and test (90% and 88%), respectively (Fig. 2A). BC4d had the highest relative feature importance (37%), compared to anti-dsDNA (19%) and EC4d (16%), with C3 & C4 at < 10% (Fig. 2B). The base model was highly specific for SLE, except vs. Sjögrens (Fig. 2C & 2D).
Conclusion: Integrating CB-CAPs with conventional markers significantly improves SLE diagnostic accuracy. The combination of MAP, conventional Ab and C3/C4 captured 76% of SLE cases, while MAP alone identified 25% of cases that were missed by conventional markers. This approach enhances diagnostic accuracy, highlighting the vital contribution of CB-CAPs to SLE sensitivity beyond conventional markers.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Concoff A, Warsi T, Taghavi S, Kumar S, Patalinghug A, Schleif C, Partain B, Ahearn J, Liu C, Wilson N, Manzi S, O'Malley T. Systematic Analysis Demonstrates the Added Value of CB-CAPs to SLE Diagnosis in a Large Validation Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systematic-analysis-demonstrates-the-added-value-of-cb-caps-to-sle-diagnosis-in-a-large-validation-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/systematic-analysis-demonstrates-the-added-value-of-cb-caps-to-sle-diagnosis-in-a-large-validation-cohort/