Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1123–1146) Metabolic & Crystal Arthropathies – Basic & Clinical Science Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Synovial fluid analysis is an essential diagnostic tool for evaluating crystalline and infectious arthritis. Traditionally, a leukocyte count threshold of >50,000 cells/µL has been used to help identify septic arthritis while awaiting culture results. However, no large or representative studies have systematically assessed the diagnostic performance of this leukocyte cutoff or characterized leukocyte counts across different causes of inflammatory synovial fluid.
Methods: A de-identified database from Froedtert Hospital and the Medical College of Wisconsin (1.9 million patients) was queried on March 17, 2023. All patients who underwent joint aspiration with synovial fluid analysis prior to March 1, 2023 were included. Structured and unstructured text were used to identify synovial fluid leukocyte count, crystal analysis, gram stain, and culture results. Demographic data were extracted; ICD-9-CM / ICD-10-CM codes were used to identify prevalent autoimmune diseases or crystalline diseases (1 year lookback) and prosthetic joint infections (PJI) (30 days before and after synovial fluid analysis).
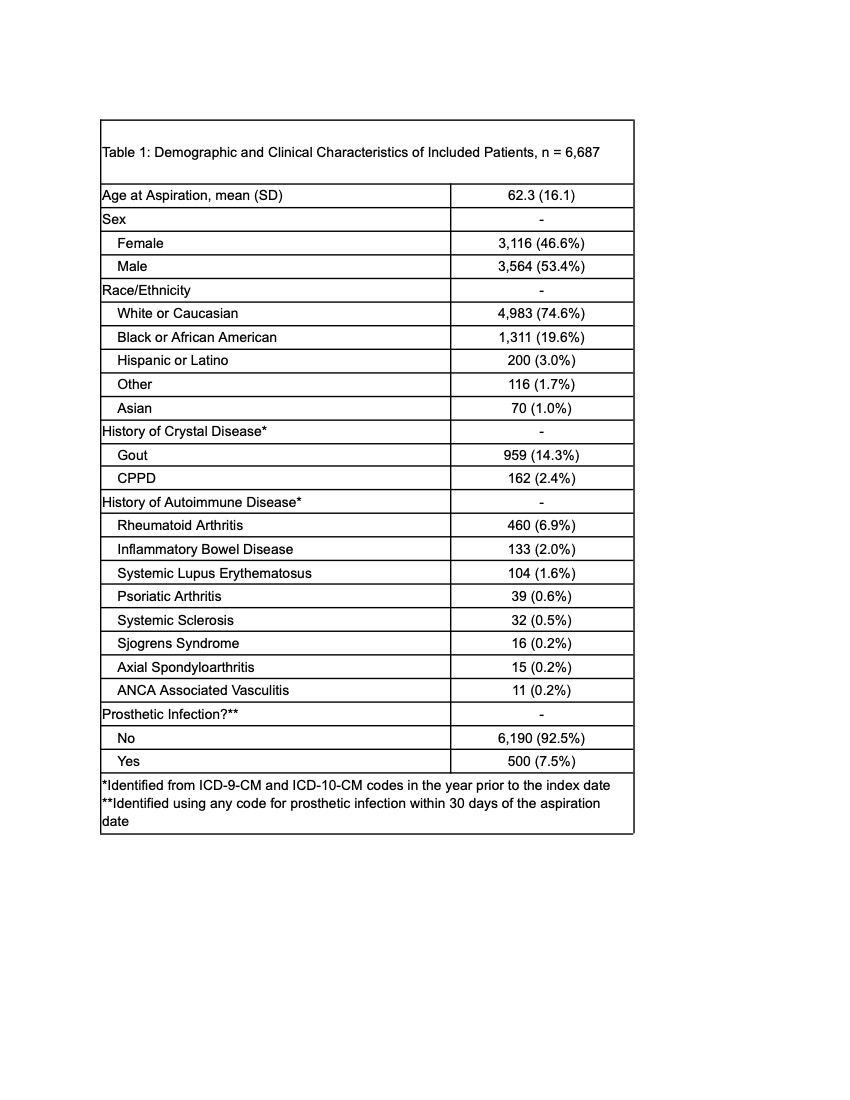
Results: A total of 9,054 synovial fluid analyses from 6,690 patients were identified. The average age at first aspiration was 62.3 years (standard deviation (SD) 16.1 years) and most patients were male (53.4%) and white (74.6%) (Table 1). After categorizing synovial fluid aspiration results in a hierarchical fashion, the highest leukocyte counts occurred among fluid positive for staphylococcus or streptococcus infection (65,568, SD 81892) followed by other positive cultures (41,035, SD 55,259), MSU (20,966, SD 34,186), CPPD (13,202, SD 21,132), rheumatic diseases (12,827, SD 32,234), and negative for crystals or infection (9,822, SD 31,884) (Figure 1). Joints that had an over-representation of a crystal result included the ankle (50.6% MSU), knee (48.2% negative for crystals), shoulder (63.5% CPPD), and toe/foot (69.6% MSU) (Figure 2). A conventional leukocyte count cutoff of 50,000 had a low sensitivity (0.28) and a high specificity (0.95); a higher cutoff of 100,000 had an even lower sensitivity (0.10) and a higher specificity (0.99).
Conclusion: Highly elevated synovial leukocyte cutoffs ( >100,000) had a high specificity for septic arthritis, but even conventional cutoffs ( >50,000) had a low sensitivity for “ruling out” infectious causes for inflammatory joint fluid.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Usmani S, Rana G, Patel S, Kennedy P, Putman M. Synovial Counts, Cultures, and Crystals: An Analysis of 9,000 Aspirations [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synovial-counts-cultures-and-crystals-an-analysis-of-9000-aspirations/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/synovial-counts-cultures-and-crystals-an-analysis-of-9000-aspirations/

.jpg)
.jpg)