Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Previous studies of RA patients have shown changes in NK cell populations (as defined by CD56 expression). The nature of these cellular changes remains controversial. We aim to comprehensively characterize CD56 expression in RA immune cells, including conventional NK cells and other CD56 expressing cells, such as myeloid cells.
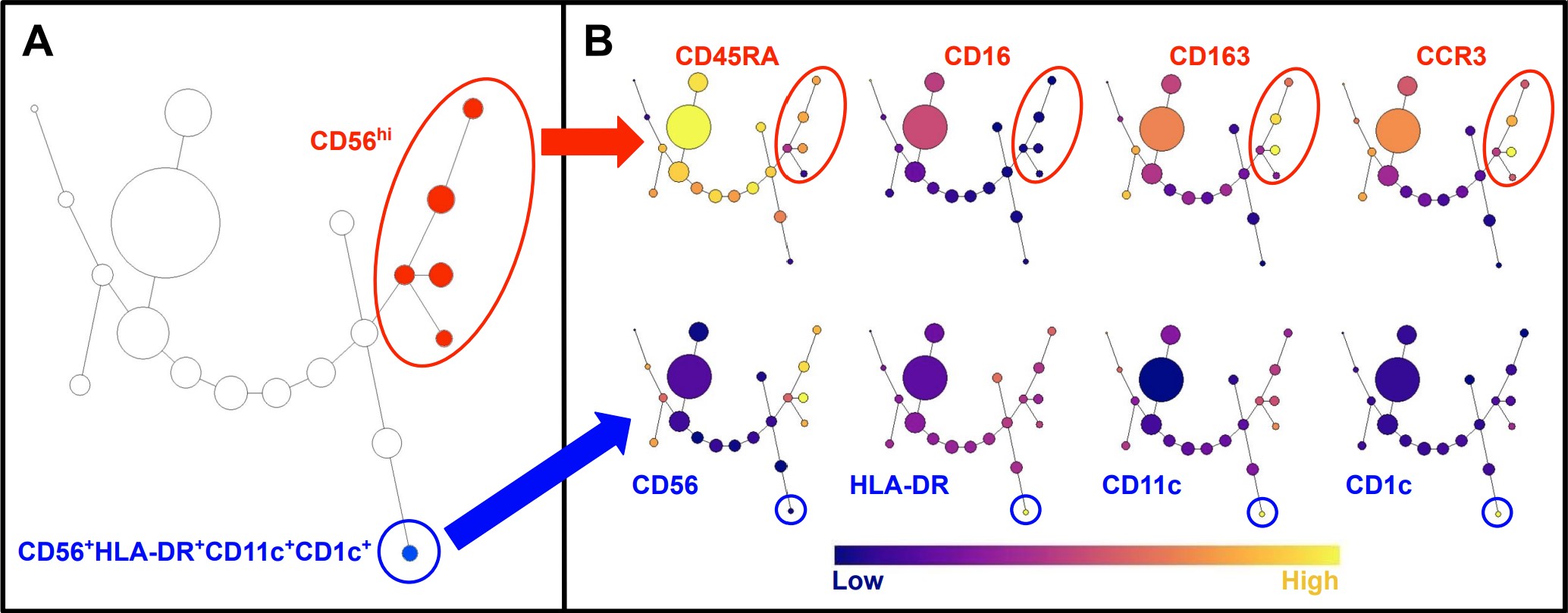
Methods: Using flow cytometry, we studied peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from RA patients satisfying the 2010 ACR classification criteria and matched healthy donors (n = 16 each). To comprehensively characterize potential CD56 changes in RA, we excluded only lymphocytes and monocytes (CD3−CD19−CD14−; Lineage), retaining all other CD56+ cells (including but not limited to conventional NK cells; CD56+Lin−). We measured mean fluorescence intensities (MFI) including CD56, CD16, CD11c, CD1c, CD45RA, CD163, CCR2, CCR3, CCR7, and HLA-DR. We used SPADE (Spanning-tree Progression Analysis of Density-normalized Events) on a patient with severe polyarticular RA to screen for marker combinations defining other potential CD56 expressing populations. Mann-Whitney U testing with a threshold of p < 0.05 was performed to assess for significant differences.
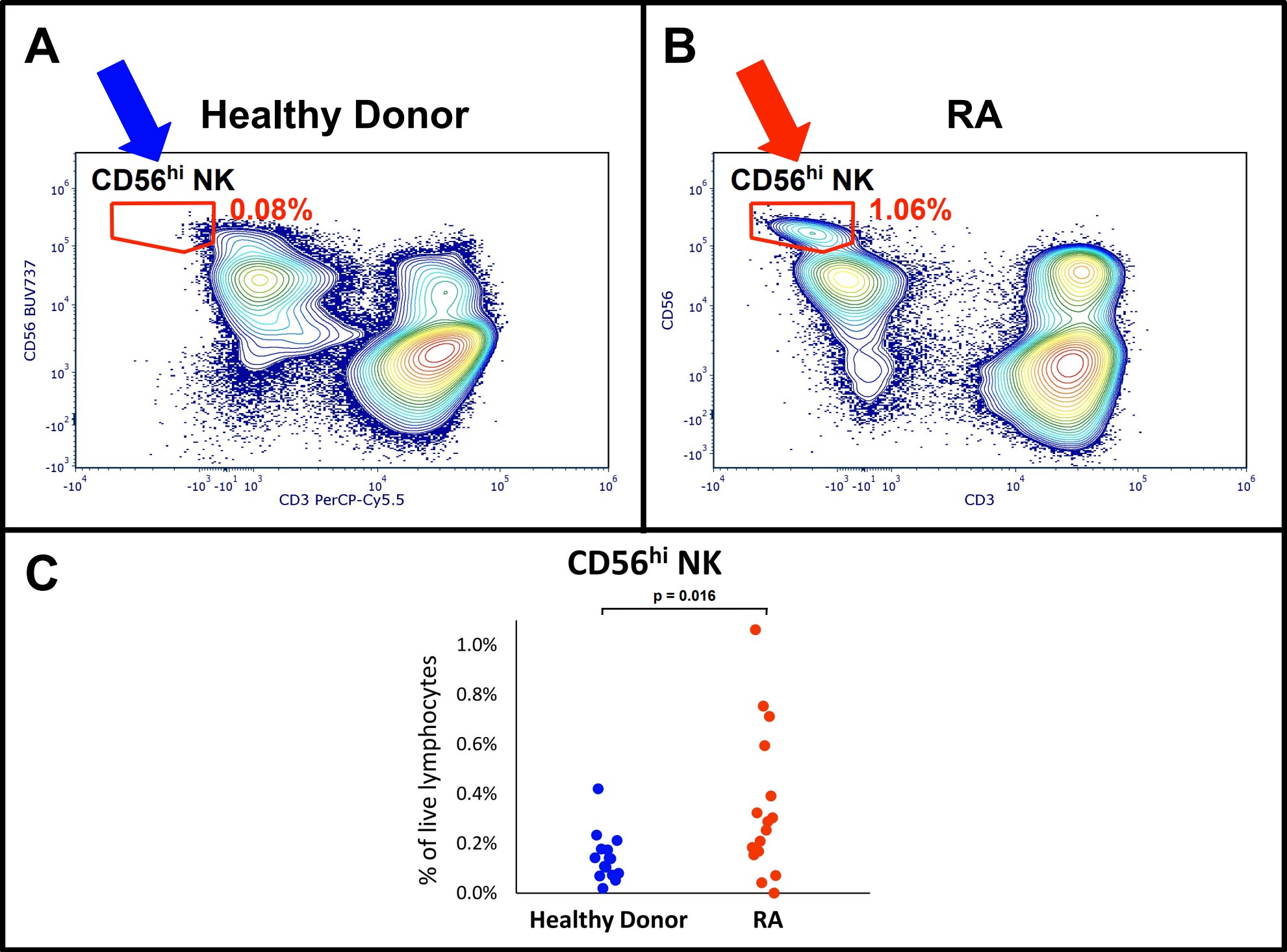
Results: The CD56hi NK subset was increased in RA (0.35% of live lymphocytes in RA, compared to 0.14% in health; p = 0.016) but the phenotype of CD56hi cells did not differ between RA and health (p > 0.05). SPADE clustering of CD56+Lin− showed that CD56hi NK cells were composed of five subpopulations defined by differential MFIs of CD45RA, CD16, CD163, CCR3. A separate cluster showed a CD56+HLA-DR+CD11c+CD1c+ phenotype. Total NK cells (CD56+CD3−) as a percentage of live lymphocytes were not different in RA patients (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: The total NK cell population is shifted towards CD56hi in RA which may contribute to RA pathogenesis through increased cytokine production. Other CD56 changes in RA patients include new phenotypes such as the CD56+HLA-DR+CD11c+CD1c+ population, which phenotypically resembles dendritic cells. These observations warrant further mechanistic study of a potential connection between NK cells and antigen-presenting cells in the pathogenesis of RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Khairallah E, Qudsi H, Ben Gabr J, Perl A, Geier C. Spectral Cytometry Shows Increased CD56hi NK Cells and New HLA-DR+CD56+ Phenotypes in RA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/spectral-cytometry-shows-increased-cd56hi-nk-cells-and-new-hla-drcd56-phenotypes-in-ra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/spectral-cytometry-shows-increased-cd56hi-nk-cells-and-new-hla-drcd56-phenotypes-in-ra/