Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Sodium is stored in tissues such as the skin where it may contribute to development and progression of autoimmune diseases and hypertension through activation of local immune cells. There is little information about tissue sodium in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The purpose of this study was to determine if skin sodium content is: 1) higher in participants with RA than in controls, and 2) associated with blood pressure and disease activity in patients with RA.
Methods: This cross-sectional study included 32 patients with RA and 33 control participants. Lower leg skin sodium content was measured using magnetic resonance imaging. Office and ambulatory 24-hour blood pressure measurements were obtained, and disease activity was assessed by Disease Activity Score-28 for RA with CRP (DAS28-CRP).
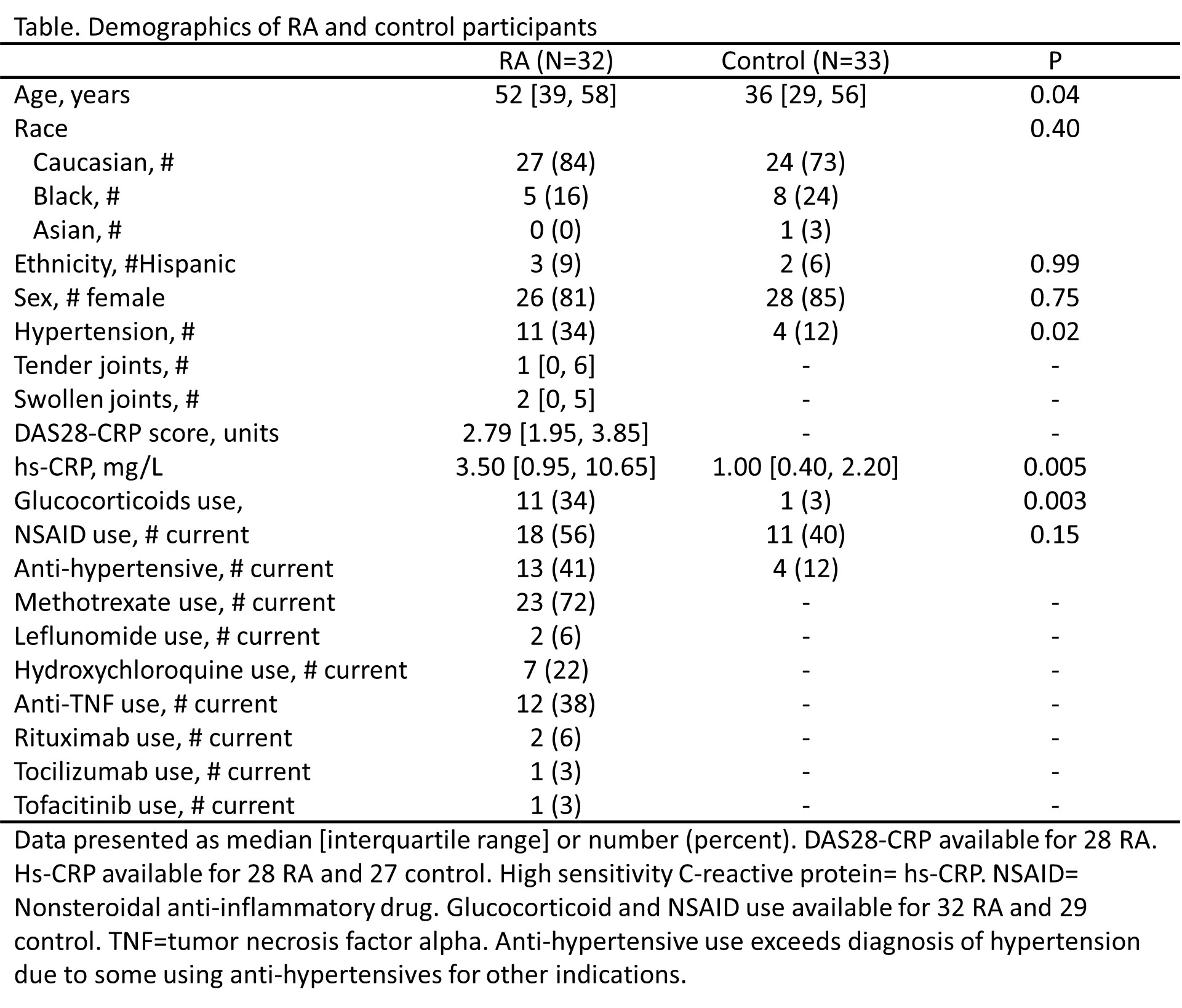
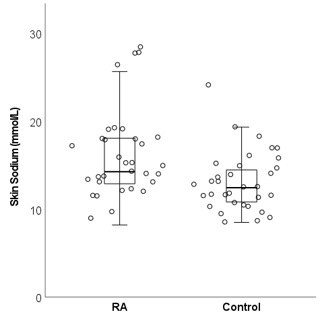
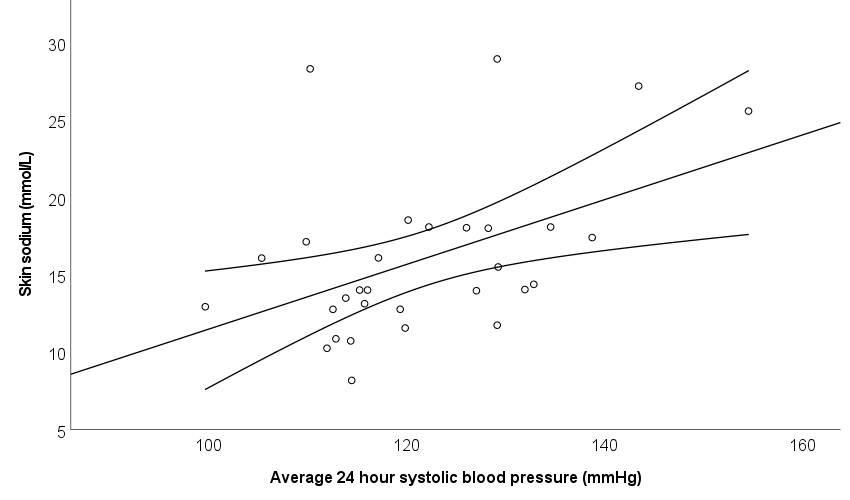
Results: Participant demographics are included in Table. Skin sodium content was higher in patients with RA than in control participants (14.22 [12.82, 18.04] vs 12.41 [10.67, 14.55] mmol/L), p=0.005 (Figure 1). Every 1 mmol/l increase in skin sodium was associated with a 1.05 mmHg (95% CI 0.29, 1.82 mmHg) increase in average 24-hour systolic blood pressure (p=0.009) and remained significant after adjustment for age (p adj = 0.04) (Figure 2); similarly every 1 mmol/l increase in skin sodium was associated with 1.17 mmHg (0.42, 1.92 mmHg) increase in average diurnal systolic blood pressure (p=0.003) and remained significant after adjustment for age (p= 0.02). In contrast, there was no significant correlation between skin sodium and nocturnal blood pressure, DAS28 score or its components.
Conclusion: Skin sodium is increased in patients with RA compared to control participants and is correlated with 24-hour and diurnal systolic blood pressure but not RA disease activity. Future studies testing the impact of dietary salt on blood pressure and disease activity will help elucidate these relationships.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ramirez C, Oeser A, Crescenzi R, Stein C, Ormseth M. Skin Sodium in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Association with Blood Pressure and Disease Activity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/skin-sodium-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-association-with-blood-pressure-and-disease-activity/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/skin-sodium-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-association-with-blood-pressure-and-disease-activity/