Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-3:50PM
Background/Purpose: Vascular endothelial cells that provide the structure for blood vessels have traditionally been perceived as passive, structural units that provide blood flow. We recently discovered that a key step in synovial sublining fibroblast expansion in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is driven by endothelial-derived Notch signaling and that Notch3 blockade attenuates arthritis pathology. This observation suggests that synovial endothelial cells, rather than being passive conduits of blood flow, and orchestrate tissue remodeling through secretion of paracrine growth factors, or angiocrine factors. The goal of this study is 1) to define heterogeneity of synovial endothelial cells and 2) to identify novel angiocrine factors involved in the RA pathogenesis.
Methods: Synovial tissues were obtained from RA or osteoarthritis (OA) patients. For scRNAseq analysis, CD45- stromal cells from were subjected to droplet-based scRNAseq (10X Genomics). For bulk RNA-seq analysis of synovial endothelial cells, disaggregated synovial endothelial cells (CD45- PDPN- CD31+ CD146+) from were FACS-sorted and subjected to SMART-seq2. Confocal microscopy imaging analysis were performed to visualize protein expression of endothelial cell subset-specific markers.
Results:
- Synovial endothelial cell heterogeneity. We identified arterial (PODXL+ NOTCH4+), venous/capillary (DARC+ CD74+), and lymphatic (LYVE1+) endothelial cells as the major endothelial cell types in synovia. We identified distinct effector modules in venous/capillary and arterial endothelial cells. Whereas venous/capillary endothelial cells are characterized by high expression of genes encoding HLA class II molecules (CD74, HLA-DRA), arterial endothelial cells are the dominant cellular source of growth factors (IGF2, PDGFB) and morphogens (DLL4, JAG1).
- Expansion of arterial endothelium in RA synovia. To define transcriptomic changes in RA synovial endothelial cells, we performed deep RNA-seq analysis of CD31+ CD146+ endothelial cells from RA and OA synovia. Differential gene expression analysis revealed striking upregulation of genes involved in cell adhesion (ICAM2, MCAM) and leukocyte recruitment (CXCL12). Interestingly, many endothelial genes upregulated in RA map to the arterial as opposed to venous endothelial cell clusters in our scRNAseq analysis, including NOTCH4 and PODXL, suggesting relative arterialization of endothelial cells in RA synovia (Fig. 1).
- Arterial endothelium as the source of Notch gradient in synovial sublining. Using PODXL as a marker for arterial endothelial cells, we found PODXL+ endothelial cells are located deep in the synovial sublining. Spatial analysis revealed signification correlation between PODXL+ arterial endothelium and NOTCH3+ fibroblasts, suggesting arterial endothelium is the dominant source of Notch gradient driving sublining expansion in RA (Fig 2).
Conclusion: Single cell profiling of synovial endothelial cells revealed previously underappreciated transcriptomic heterogeneity that reflect distinct lineages and functional states. In RA, synovial endothelium transition towards an arterial state characterized by expression of angiocrine factors that contribute to arthritis pathology.
 FIgure 1. ScRNAseq analysis of synovial endothelial cells. A. Venous (blue) and arterial (red) endothelial cells projected in tsNE space. B. Endothelial genes upregulated in RA synovia.
FIgure 1. ScRNAseq analysis of synovial endothelial cells. A. Venous (blue) and arterial (red) endothelial cells projected in tsNE space. B. Endothelial genes upregulated in RA synovia.
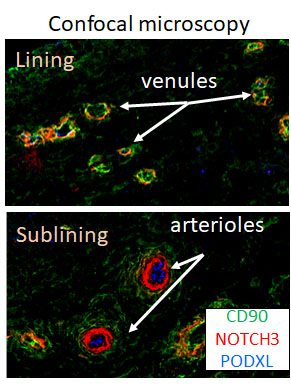 Figure 2. Representative confocal microscopy image of RA synovia endothelium network showing venules near lining and PODXL1+ arterioles in the subliing. Note Notch3 (red)+ cells near arterioles.
Figure 2. Representative confocal microscopy image of RA synovia endothelium network showing venules near lining and PODXL1+ arterioles in the subliing. Note Notch3 (red)+ cells near arterioles.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wei K, Korsunsky I, Marshall J, Watts G, Major T, Zhu Z, Li Y, Buckley C, Raychaudhuri S, Brenner M. Single-cell Profiling of Synovial Stromal Cells Reveals an Angiocrine Endothelium in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-profiling-of-synovial-stromal-cells-reveals-an-angiocrine-endothelium-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-profiling-of-synovial-stromal-cells-reveals-an-angiocrine-endothelium-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/
