Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Spondyloarthritis (SpA) is a group of immune-mediated inflammatory disorders such as ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and psoriatic arthritis (PsA), along with acute anterior uveitis (AAU) which is a common comorbidity of SpA. We aim to determine the fecal and plasma metabolic profiles to elucidate metabolic function underlying disease pathophysiology.
Methods: We performed untargeted metabolic profiling using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) on 103 fecal (19 AS, 18 AAU, 14 AS+AAU, 26 PsA, and 26 healthy controls [HC]) and 114 plasma (21 AS, 21 AAU, 20 AS+AAU, 26 PsA and 38 HC) samples. Metabolic data were analyzed using discriminatory statistical methods to dissect disease-associated metabolic signals and various confounders i.e. BMI and HLA-B27 status., and reported after multiple tests corrections. Fecal and plasma marker of inflammation (calprotectin) and plasma levels of bacterial endotoxin (LPS) were also measured.
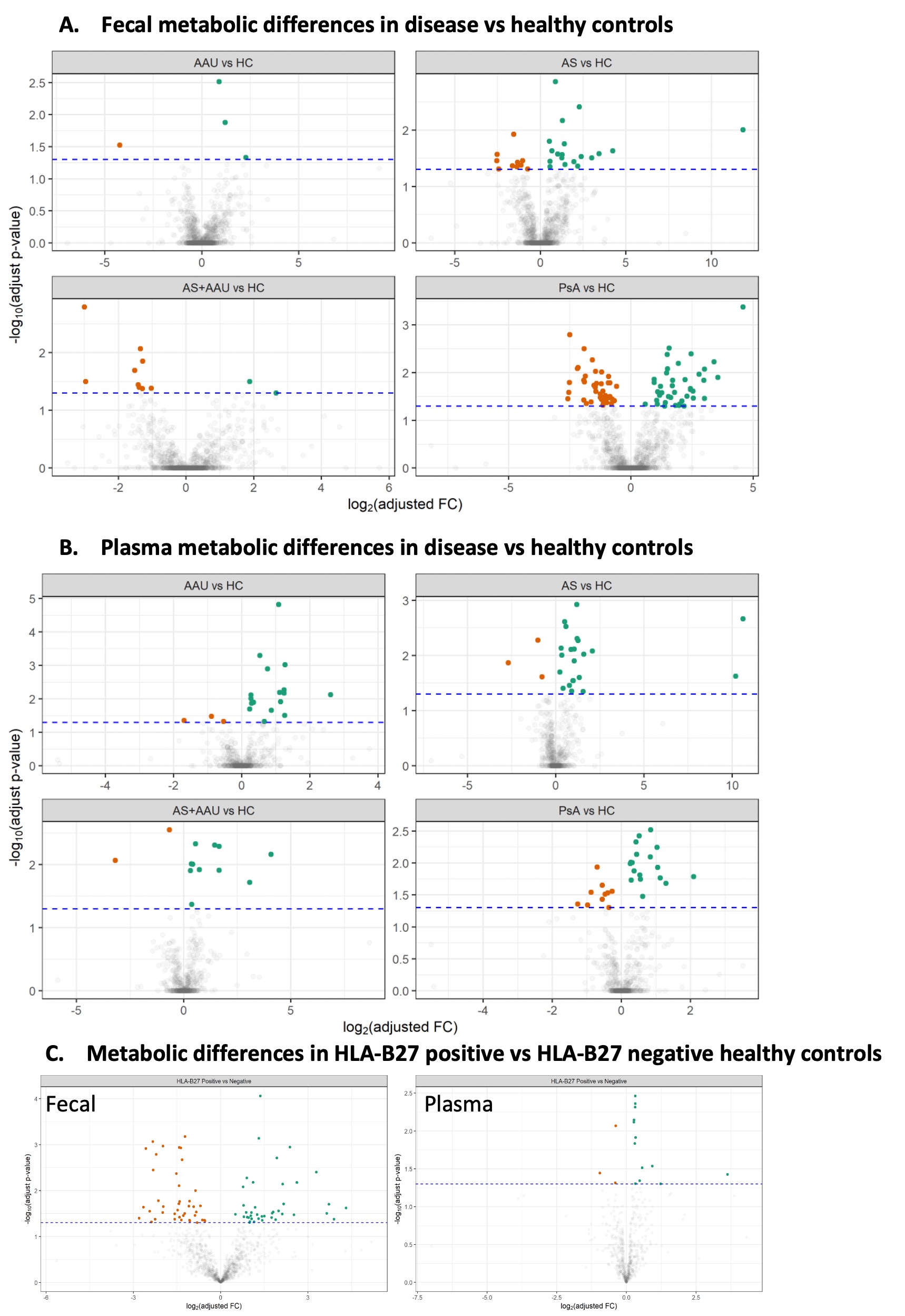
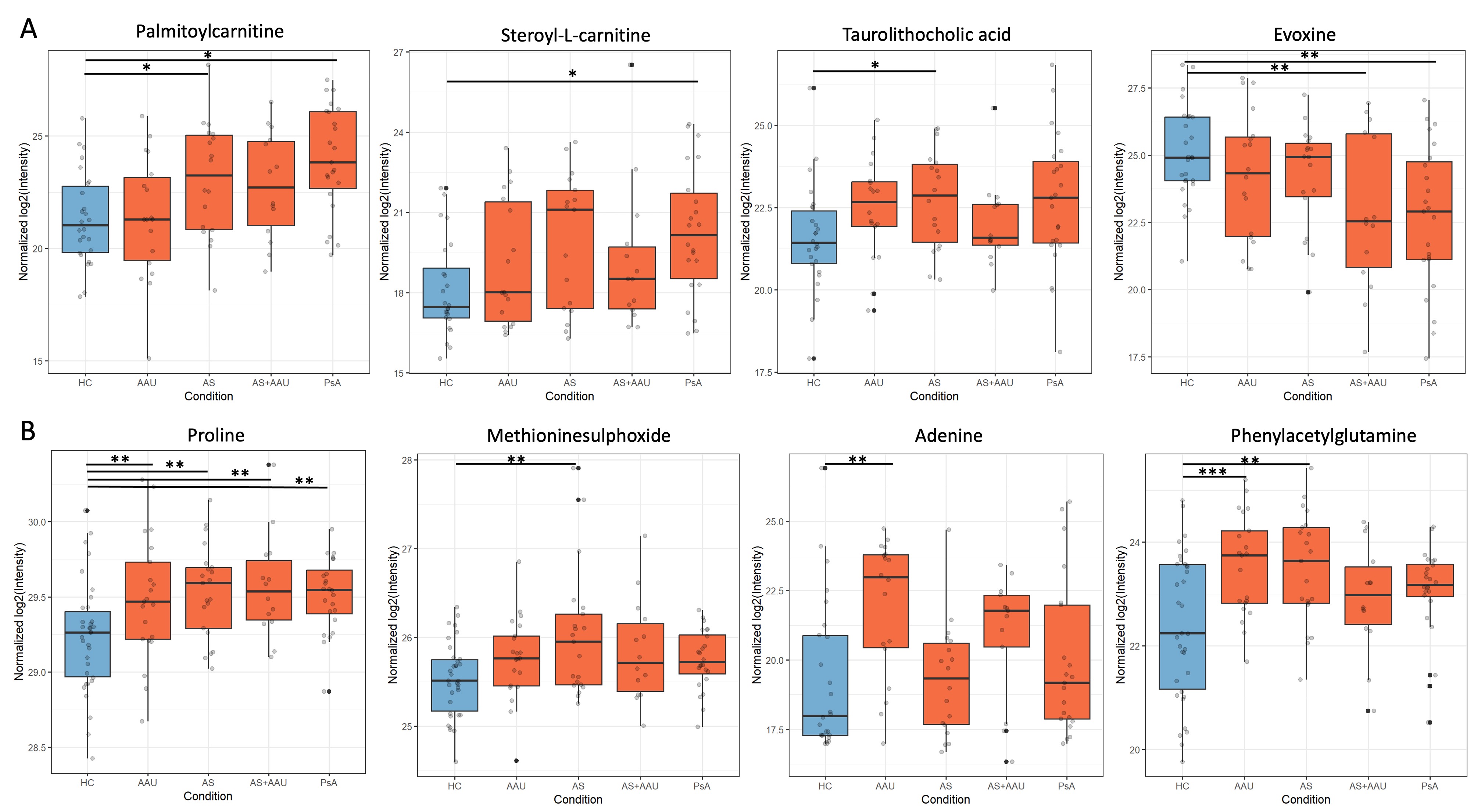
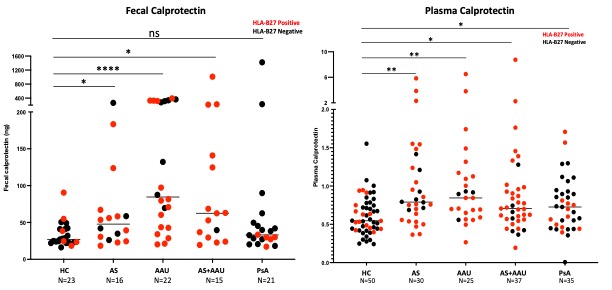
Results: Results: Metabolomic profiling of the fecal and plasma samples revealed shared and unique metabolic signatures in AS, PsA and AAU patients in comparison with HC (Fig. 1). The fecal samples from AS, AS+AAU, and PsA showed a significant increase in multiple inflammatory metabolites such as stearoyl-L-carnitine, palmitoylcarnitine, taurolithocholic acid, and biliverdin in comparison to HC, concomitant with a significant decrease in the levels of various anti-inflammatory metabolites including enterolactone and evoxine in comparison to HCs (Fig 2A). Similarly, the plasma of all patient groups exhibited elevated levels of inflammatory metabolites such as phenylacetylglutamine and 3 indoxy sulphate, methioninesulphoxide, and adenine in comparison to HC (Fig 2B). Comparison between disease groups showed differences in intensities of metabolic perturbations in the carnitine, bile, tryptophan, and other anti-inflammatory markers. In addition, HC carrying HLA-B27 allele exhibit significant metabolic changes in fecal and plasma profiles in comparison with HLA-B27 negative HCs (Fig 1). Furthermore, all patient groups had significantly increased levels of plasma calprotectin, and plasma LPS levels in comparison with HC, while fecal calprotectin in AS, AAU, and AS+AAU were significantly increased in comparison to HC, but in PsA patients, the levels were similar to HCs (Fig. 3). Multi-omics network analysis to determine the association between altered fecal and plasma metabolic profile in all patient groups and its association with gut microbes, inflammatory markers and disease severity are underway.
Conclusion: We discovered both shared and unique fecal and plasma metabolic features associated with AS, PsA, AAU and AS+AAU in comparison with HCs, which has the potential to reveal why certain people develop one disease instead of the other despite their common association with HLA-B27. Future investigations validating the effects of these metabolites may lead to potential mediators of disease pathogenesis and identify novel metabolites as disease biomarkers and therapeutic strategies in SpA and other inflammatory diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Couvillion S, Flores J, Davin S, Ogle K, Fale-Olsen E, Davis J, Many G, Shaut C, Martin T, Suhler E, Deodhar A, Rosenbaum J, Nakayasu E, Gill T. Shared and Unique Fecal and Plasma Metabolic Signatures and Increased Inflammatory Markers in Ankylosing Spondylitis, Psoriatic Arthritis and Acute Anterior Uveitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/shared-and-unique-fecal-and-plasma-metabolic-signatures-and-increased-inflammatory-markers-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-psoriatic-arthritis-and-acute-anterior-uveitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/shared-and-unique-fecal-and-plasma-metabolic-signatures-and-increased-inflammatory-markers-in-ankylosing-spondylitis-psoriatic-arthritis-and-acute-anterior-uveitis/