Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Elderly-onset RA (EORA) and polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) are common rheumatic diseases in the elderly, but their pathogenesis is not yet fully understood. Seronegative EORAneg and PMR have similar clinical characteristics making them difficult to distinguish based on clinical features. The aim of this study was to explore the differences in the serum metabolome using 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) to identify potential biomarkers of PMR vs EORAneg.
Methods: ARTIEL (Arthritis in the Elderly) is a cohort that consists of newly diagnosed arthritis in patients older than 60 years. Blood samples were collected at baseline (pre-treatment), along with physician and patient outcome measures throughout a 12-month period. Patients were compared with controls who were random individuals of the same age and gender. A Bruker Avance 700 MHz spectrometer was used to acquire NMR spectra of serum samples. Chenomx NMR suite 8.5 was used for metabolite identification and quantification. IL6 and TNF levels were determined by ELISA. SPSS v.27 and MetaboAnalyst 4.0 were used for statistical and pathway analysis.
Results: From the 66 patients included, 20 were diagnosed with PMR, with an average age of 76.40±4.99, 15% were males, and an average CRP level of 31.56±28.27 mg/dL; 28 patients were diagnosed of EORAneg patients with an average age of 76.75±6.99, 57% males, and an average CRP level of 41.57±52.14 mg/dL; and 18 controls with an average age of 75.39±6.04, 39% males, and an average CRP level of 4.10±6.78 mg/dL. At diagnosis, EORAneg patients had a mean DAS28ESR of 6.21±1.00. One hundred percent of PMR patients reported shoulder pain, and 90% reported pelvic pain. Fifty-eight polar metabolites were identified. 3-Hydroxybutyrate, acetate, glucose, glycine, lactate, and O-acetylcholine were significantly different between the 3 groups. Of these, 3-hydroxybutyrate, acetate, glucose, and lactate were elevated in EORAneg while glycine and O-acetylcholine were lower in PMR compared to control group (Figure 1). Of interest, TNF and IL-6 correlated with different metabolites in PMR and EORAneg suggesting different inflammatory activated pathways (Figure 2). Finally, a logistic regression analysis identified two metabolites, o-acetylcholine and acetate, that contributed to the separation of PMR from EORAneg with 80% sensibility and 96.4% specificity (Figure 3).
Conclusion: EORAneg and PMR have a different serum metabolomic profile that can be used as biomarker to discriminate between both diseases. Further metabolic profiling studies is needed to properly identify significant metabolites in EORAneg vs PMR, and to better understand elements of inflammation pathobiology in these populations.
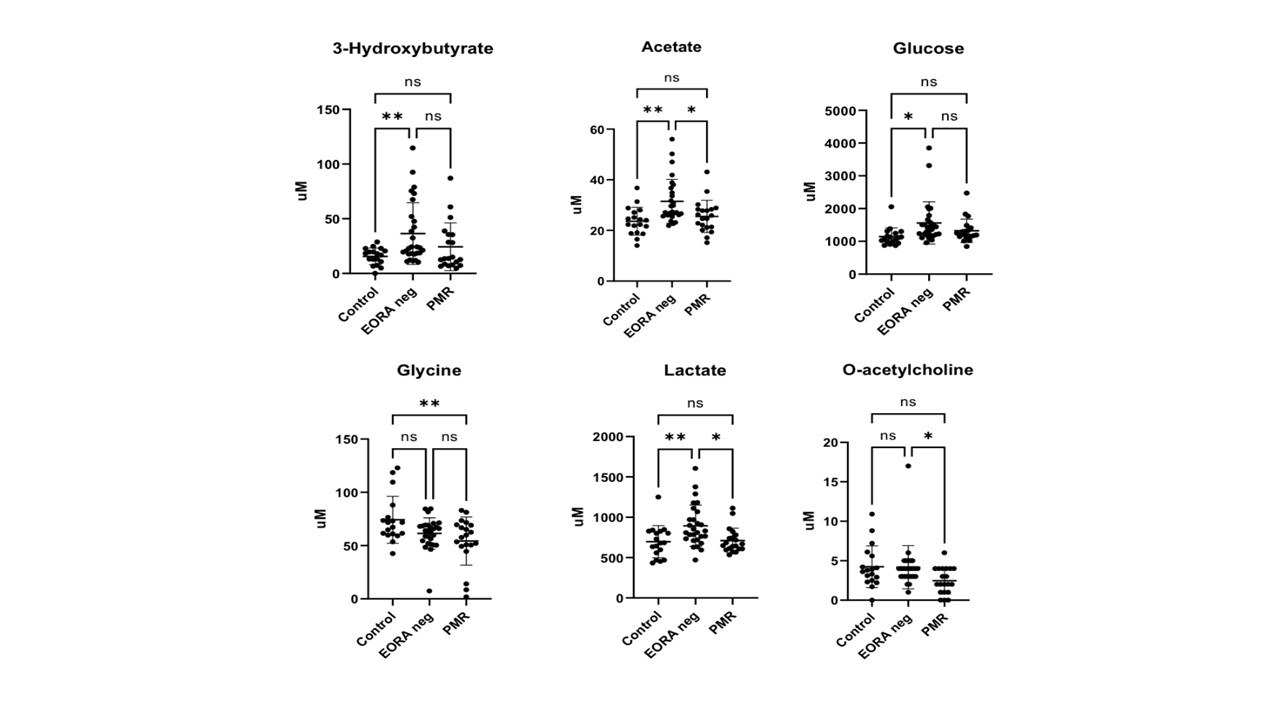 Figure 1. Concentrations of polar metabolites identified with 1H-NMR in control group, elderly-onset seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (EORAneg) and polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) at baseline. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ns= not statistically significant.
Figure 1. Concentrations of polar metabolites identified with 1H-NMR in control group, elderly-onset seronegative rheumatoid arthritis (EORAneg) and polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR) at baseline. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ns= not statistically significant.
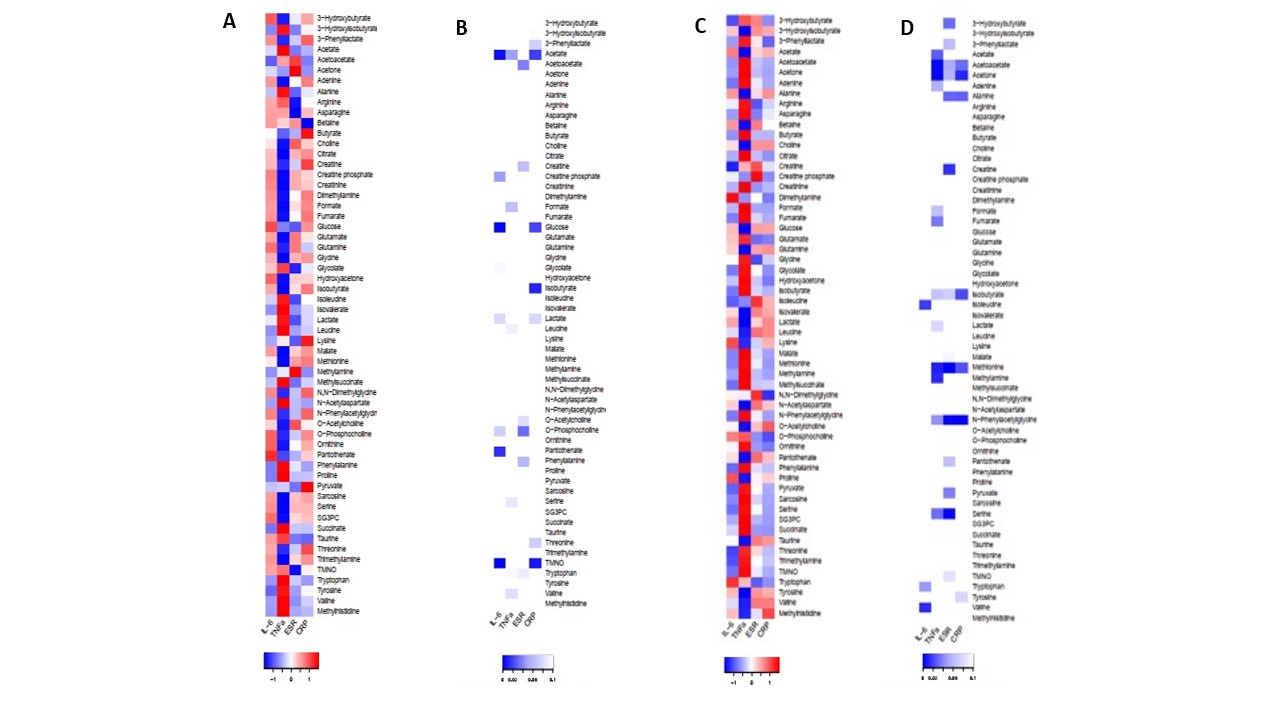 Figure 2. Pearson correlation adjusted by age, gender and BMI (body mass index) at baseline between proinflammatory cytokines and metabolites obtained by 1H-NMR. A) The strength of association of each pair were used to form a cluster heatmap to lend insight into which cytokine were correlated with which group of polar metabolites in patients with PMR or C) EORA neg. B) Correlation significant p-values for PMR or D) EORA neg.
Figure 2. Pearson correlation adjusted by age, gender and BMI (body mass index) at baseline between proinflammatory cytokines and metabolites obtained by 1H-NMR. A) The strength of association of each pair were used to form a cluster heatmap to lend insight into which cytokine were correlated with which group of polar metabolites in patients with PMR or C) EORA neg. B) Correlation significant p-values for PMR or D) EORA neg.
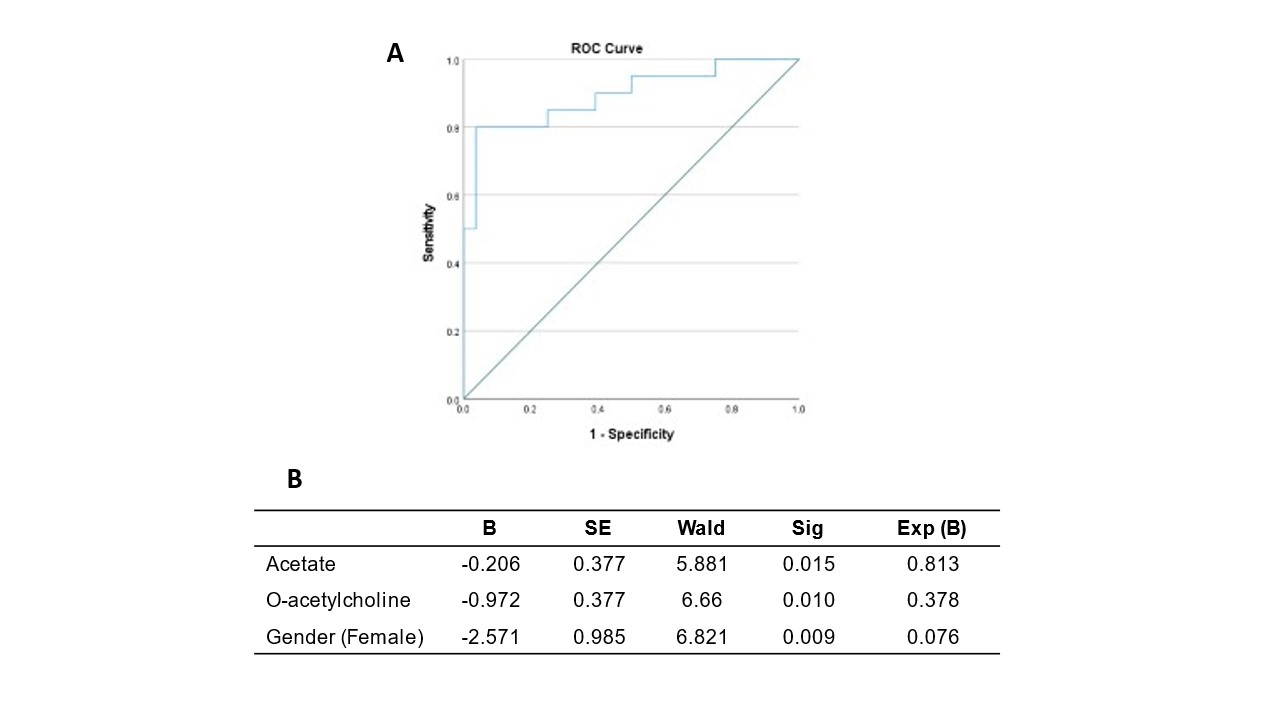 Figure 3. A) Receiver operating characteristic curve and B) Binary Logistic regression Model. PMR was consider the principal outcome. The logistic model used significant polar metabolites (p < 0.05) and gender. The model showed an area under curve of 0.895 with a sensibility= 80% and specificity= 96.4%; p < 0.001.
Figure 3. A) Receiver operating characteristic curve and B) Binary Logistic regression Model. PMR was consider the principal outcome. The logistic model used significant polar metabolites (p < 0.05) and gender. The model showed an area under curve of 0.895 with a sensibility= 80% and specificity= 96.4%; p < 0.001.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cedeno M, Murillo Saich J, Coras R, Brandy-Garcia A, Prior-Español A, Mateo L, Martinez-Morillo M, Guma M. Serum Metabolomic Profiling Identifies Potential Biomarkers in Arthritis in the Elderly [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-metabolomic-profiling-identifies-potential-biomarkers-in-arthritis-in-the-elderly/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-metabolomic-profiling-identifies-potential-biomarkers-in-arthritis-in-the-elderly/
