Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 14, 2023
Title: (2095–2140) RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, and Outcomes Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Alarmins are endogenous cytokines released following cellular damage and physiologic stress to promote homeostasis through tissue inflammation, remodeling, and fibrosis. Alarmins may facilitate maladaptive responses that play a role in the development of chronic inflammatory diseases, including RA (Ebina-Shibuya R, Nat Rev Immunol 2023). Whereas studies have implicated alarmins in cardiovascular disease (CVD) pathogenesis, it is unknown whether they may serve as a marker of CVD risk in RA. We examined associations of serum alarmin concentrations with CVD in a prospective RA cohort.
Methods: In a multicenter, prospective cohort of US Veterans with RA, we identified MACE (myocardial infarction, coronary revascularization, stroke, or CVD-related death) and heart failure (HF) hospitalizations before and after registry enrollment using validated administrative algorithms in linked VA, Medicare, and National Death Index data. From banked serum at registry enrollment, we measured the alarmins IL-25, IL-33, and thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) using U-PLEX immunoassay (Meso Scale Discovery). Given their distributions, IL-33 and TSLP concentrations were log-transformed and standardized (per 1 SD).Detectable IL-25 was categorized into tertiles (undetectable values as referent). Cross-sectional associations of alarmin concentrations with prevalent CVD were examined in multivariable logistic regression models. We then followed participants without prevalent CVD from registry enrollment to incident MACE, HF hospitalization, death, or end of study (12/2020). Associations of circulating alarmin concentrations with incident CVD events were tested in multivariable Cox regression models, adjusting for age, sex, race/ethnicity, smoking status, body mass index, DAS28, hypertension, diabetes, lung disease, LDL cholesterol, statin use, NSAID use, and aspirin use.
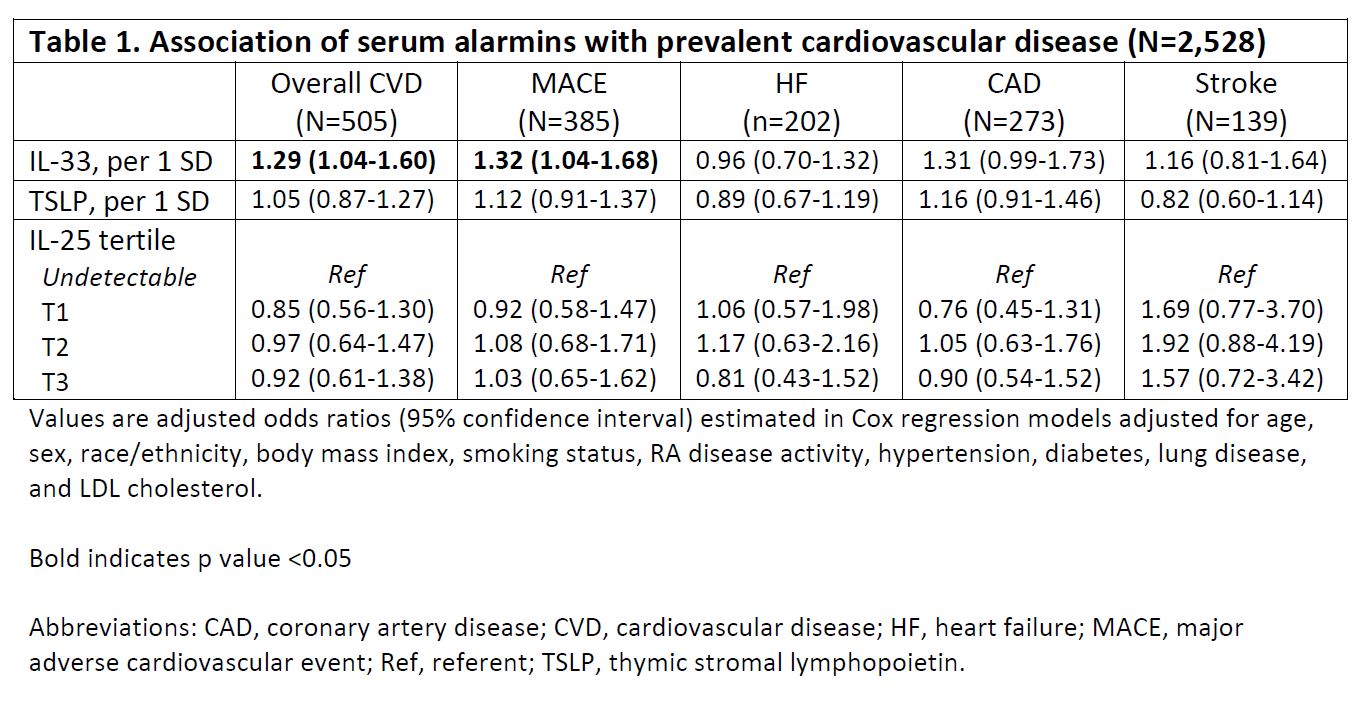
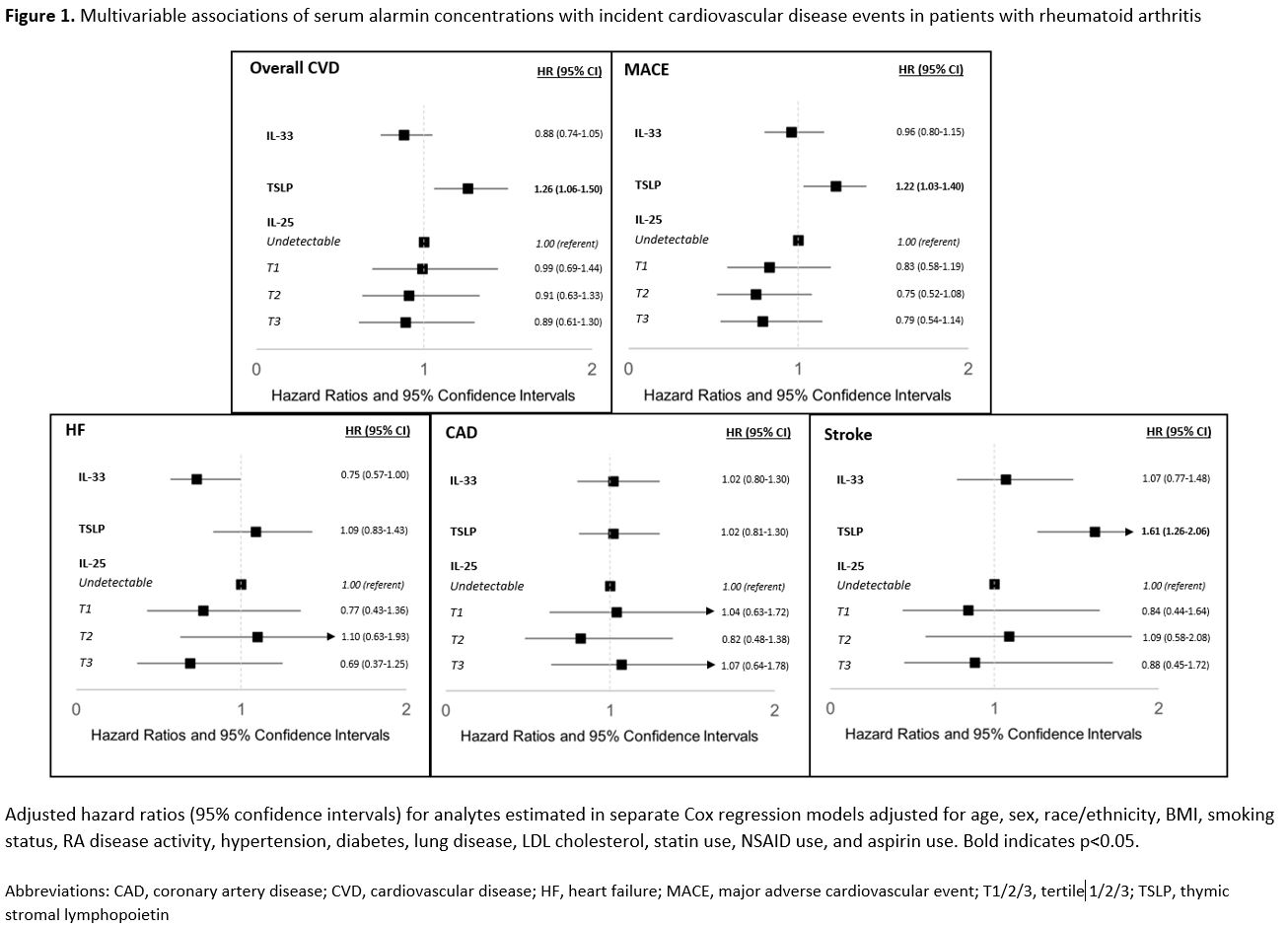
Results: Among 2,528 patients (mean age 64 years, 88% male, mean DAS28 3.6), 505 (20.0%) patients had prevalent MACE or HF. We observed CVD outcomes in 414 (20.5%) of the remaining 2,023 patients over a mean follow up of 7.3 years. After multivariable adjustment, IL-33, but not TSLP or IL-25, concentrations were associated with an increased odds of prevalent CVD (Table 1; aOR 1.29 [1.04-1.60] per 1 SD increase) and MACE (aOR 1.32 [1.04-1.68]). For incident disease, TSLP concentrations were most strongly associated with CVD risk (Figure 1; aHR 1.26, [1.06-1.50]), which was driven by its association with stroke (aHR 1.61 [1.26-2.06]) and MACE (aHR 1.22 [1.03-1.20]). A trend toward an inverse association between IL-33 and HF was observed, otherwise no associations were seen between IL-33 or IL-25 with incident CVD in fully adjusted models.
Conclusion: In this large, multicenter, prospective RA cohort, serum IL-33 concentration was independently associated with prevalent CVD, whereas TSLP concentration was associated with incident CVD, particularly stroke and MACE. These findings suggest that alterations in endogenous alarmins occurring in RA may contribute to RA-associated CVD risk. Further study is warranted to determine whether serum alarmins can improve CVD risk stratification in RA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Johnson T, Yang Y, Roul P, Duryee M, Hunter C, Baker J, Sauer B, Cannon G, Joseph A, Wysham K, Lenert A, Thiele G, Poole J, Mikuls T, England B. Serum Alarmin Concentrations and Risk of Incident Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events and Heart Failure in a Multicenter, Prospective Rheumatoid Arthritis Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-alarmin-concentrations-and-risk-of-incident-major-adverse-cardiovascular-events-and-heart-failure-in-a-multicenter-prospective-rheumatoid-arthritis-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serum-alarmin-concentrations-and-risk-of-incident-major-adverse-cardiovascular-events-and-heart-failure-in-a-multicenter-prospective-rheumatoid-arthritis-cohort/