Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a relatively frequent manifestation of Sjögren’s Syndrome (pSS), potentially presenting with a wide spectrum of clinical-radiological characteristics. Anti-Ro52 autoantibodies have been recently recognized as a risk factor for ILD in pSS. However, little is known about the relationship between circulating autoantibodies and clinical characteristics of pSS-ILD patients.
Aim of the study was: 1. to compare pSS-ILD patients with non-ILD pSS patients and 2. to investigate the impact of serology on the pulmonary phenotype of pSS-ILD patients.
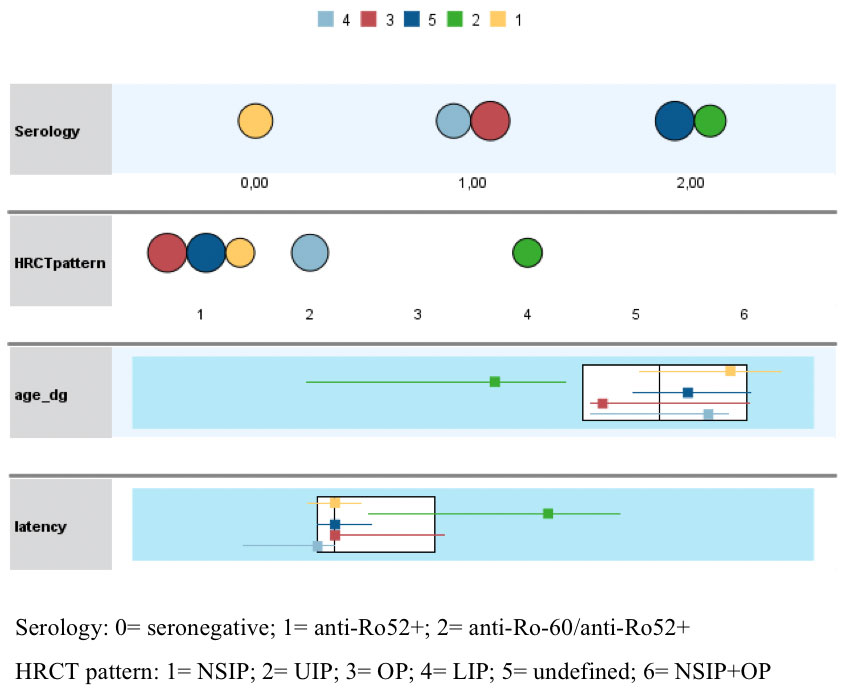
Methods: This was a monocentric observational study, including pSS patients (2016 ACR/EULAR criteria) in follow-up from 2012 to 2022. Demographic, clinical, biological, and imaging data updated to last follow-up visit were collected. ILD presence for all cases was confirmed by an expert radiologist based on HRCT chest findings. She assessed HRCT patterns, ILD extension and severity by Warrick score. Anti-Ro60 and anti-Ro52 were assessed by immunoblotting. A two-step cluster analysis was performed to identify ILD subgroups using anti-Ro60 and anti-Ro52 positivity status, HRCT pattern, age at pSS diagnosis and latency from ILD onset to pSS diagnosis or viceversa. Differences in Warrick score and functional tests between the subgroups were assessed.
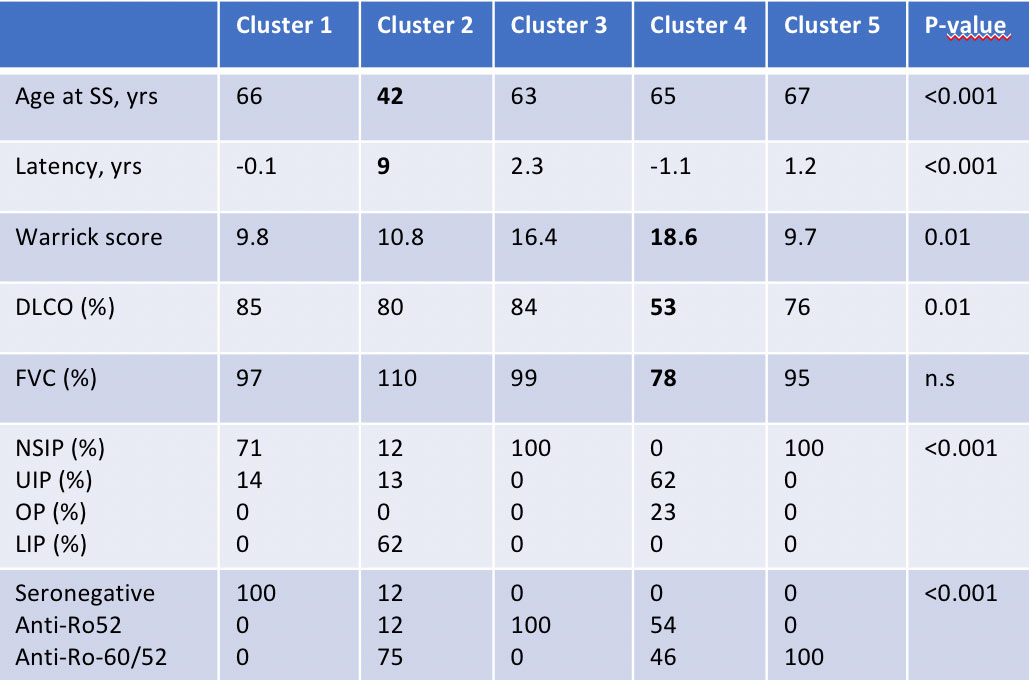
Results: 615 pSS patients were included. Out of them 51 (8.3%) presented ILD. Compared to non-ILD patients, pSS-ILD patients were significantly older (p< 0.0001), had a higher ESSDAI at baseline (p< 0.001) and a higher frequency of isolated anti-Ro52 antibodies (p< 0.001). Cluster analysis identified 5 subgroups in ILD patients (Fig. 1a and 1b). ILD tended to precede the diagnosis of pSS in clusters 1 and 4, whereas tended to occur during the disease course in clusters 2, 3 and 5. Clusters 1 was characterized predominantly by a seronegative status and a NSIP pattern whereas cluster 4 by isolated-Ro52 and a UIP pattern. The latter presented the most severe abnormalities in functional tests (p=0.02) and tended to present the worst Warrick score (p=0.08). Clusters 3 and 5 were both characterized by a predominant NSIP pattern, generally occurring within the first 5 years of the disease; however, cluster 3 was generally characterized by isolated anti-Ro52 whereas cluster 5 predominantly by antiRo60/anti-Ro52 positivity. Cluster 2 patients were the youngest (p< 0.001), they were anti-Ro60/Ro52 positive and presented the longest average time from pSS to ILD diagnosis (p< 0.001). All the 4 LIP cases in our cohort were included in cluster 2.
Conclusion: In this study we highlighted a significant association between pSS-ILD patients’ serological profile and pulmonary phenotype in terms of clinical presentation, severity and imaging patterns.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
La Rocca G, Ferro F, Fulvio G, Fonzetti S, Navarro García I, Elefante E, Romei C, Mosca M, Baldini C. Serology Driven Pulmonary Phenotype Characterization of Sjögren Syndrome-associated Interstitial Lung Disease: A Monocentric Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serology-driven-pulmonary-phenotype-characterization-of-sjogren-syndrome-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-a-monocentric-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serology-driven-pulmonary-phenotype-characterization-of-sjogren-syndrome-associated-interstitial-lung-disease-a-monocentric-cohort-study/