Background/Purpose: Pain is associated with diagnosed osteoarthritis (OA), but little clinically association is found between joint integrity and the pain the individual patient experience. Peripheral and central pain mechanisms are suggested to play roles in OA-pain. Patients experiencing pain for longer periods can become sensitized; hence lesser stimulus is need for the patient to feel pain in the affected site and other remote places of the body (spreading sensitization). Biochemical markers mirroring the pathological processes in OA may aid in the linking of pain mechanisms and tissue integrity. This study investigate the link between the mechanistic, experimental pain biomarkers and serological biochemical markers of inflammation (CRPM), connective tissue turnover (C1M) and synovium (C3M) to investigate underlying causes of knee OA-pain.
Methods: A cross-sectional study of 281 participants recruited from Northern Denmark, age 42-80, with varying degrees of symptomatic knee OA (rated on a 0-100 visual analog scale, max pain for the last 24hours). Serological markers were measured in fasting serum samples: high sensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP) and matrix metalloproteinase-mediated degradation of CRP (CRPM) and type I (C1M; connective tissue) and III collagen (C3M: synovium). Patients were divided into groups depending on sensitization; 1) sensitized, 2) moderate and 3) non-sensitized. Pressure pain thresholds (PPT) and conditioning pain modulation (CPM) were assessed from the knee, arm and leg. One-way analysis of variance with a Bonferroni post-hoc-test was used. Results are shown as mean (SD).
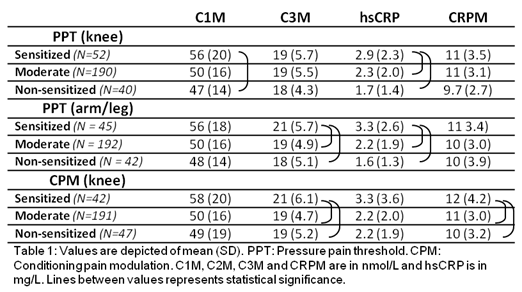
Results: Compared with un-sensitized patients C1M and hsCRP were higher in patients with localized knee sensitization (p=0.047 and p=0.001, respectively) and C3M and hsCRP were higher in patients with spreading sensitization (p=0.018 and p=0.001, respectively). CRPM was higher in patients with developed centralized sensitization (p=0.006). Interestingly, the percentage of males was higher in the non-sensitized groups and the percentage of female was higher in the sensitized groups.
Conclusion: Associations between pain sensitization and serological markers of structural integrity (C1M, C3M) and inflammation (hsCRP and CRPM,) were found. These results indicate that pain in OA is highly related to inflammation and structural integrity.
Disclosure:
A. S. Siebuhr,
Nordic Bisocience,
3;
L. Arendt-Nielsen,
None;
T. N. Eskehave,
None;
M. A. Karsdal,
Nordic Biosciece,
1,
Nordic Bioscience Diagnostic,
3;
K. K. Petersen,
None;
O. Simonsen,
None;
A. C. Bay-Jensen,
Nordic Bioscience Diagnostic,
3.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/serological-markers-of-structural-integrity-and-inflammation-is-associated-with-pain-in-osteoarthritis/