Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 19, 2024
Title: Abstracts: Muscle Biology, Myositis & Myopathies – Basic & Clinical Science II
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies (IIM) are a group of systemic autoimmune inflammatory muscle disorders characterized by symmetrical skeletal muscle weakness and accelerated fatigue. Although signs of inflammatory cell infiltrates in the muscles are commonly seen, correlation lacks between the degree of infiltrates and muscle weakness or fatigue. The mechanisms causing the muscle weakness in IIM remain unclear. Considering the systemic inflammation involved in IIM, our hypothesis proposes that blood-borne factors contribute to muscle dysfunction by affecting the contractile apparatus within muscle fibers.
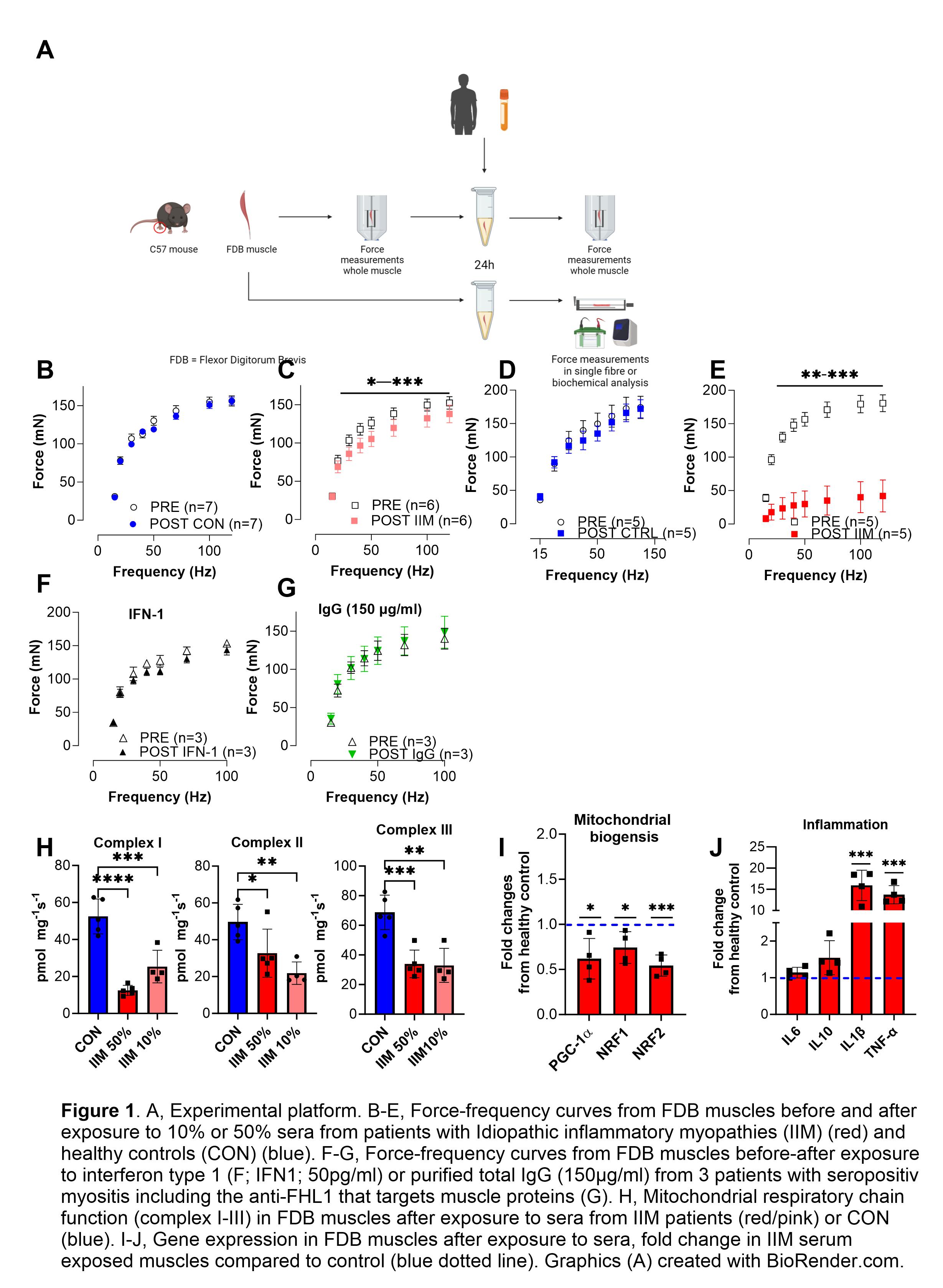
Methods: Isolated whole flexor digitorum brevis (FDB) muscles from female mice (C57BL/6JRj) were incubated for 24h in DMEM buffer containing either 10% or 50% of serum from patients with IIM (n=5) or from healthy controls (n=2) (Fig 1B-E). Muscle force-frequency measurements were assessed before and after incubation of the muscles via electrical stimulations at increasing frequencies (15-100Hz). Interferon-1 (IFN1) and myositis autoantibodies (e.g. FHL1) have been implied in the pathogenesis of IIM. In some expreriments we incubated muscles with IFN1 (Fig1F) or total IgG from seropositive IIM patients (Fig 1G). Mitochondrial respiration in permeabilized muscles was assessed with high-resolution respirometry (Oroboros). qPCR was used to measure gene expression in incubated muscles.
Results: In whole muscles exposed to sera from patients with IIM, we found a significantly reduced force generation in a serum-dose dependent manner that was not observed after incubation in healthy control sera (Fig 1B-E; p< 0.05). Incubation with IFN1 or IIM patient IgG did not affect muscle force (Fig1F-G). The activity of mitochondrial respiratory chain (complex I-III) was reduced (Fig 1H; P< 0.05), and mitochondrial biogenesis regulatory genes (PGC1α, NRF1/2; P< 0.05) displayed lower expression (Fig 1I) after incubation with IIM sera when compared to healthy sera, indicating metabolic stress. IIM serum incubation induced the gene expression for some inflammatory cytokines (IL1b & TNF; P< 0.05), suggesting that local cytokine production within the muscle fibers (Fig 1J).
Conclusion: Sera from patients with IIM can initiate a phenotype of inflammatory activation, muscle weakness and metabolic dysfunction in an intact isolated healthy skeletal muscle preparation. By using isolated mouse muscle preparations in sera from human patients with IIM, we have developed an experimental platform to study mechanisms that could contribute to muscle weakness in patients with IIM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Leijding C, Kaewin S, Andreasson K, Schiffer T, Galindo-Feria A, Horuluoglu B, Carlstrom M, Gastaldello S, Alexanderson H, Lundberg I, Andersson D. Sera from Patients with Idiopathic Inflammatory Myopathy Induces Muscle Weakness, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Induction of Cytokines in Isolated Skeletal Muscle [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sera-from-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy-induces-muscle-weakness-mitochondrial-dysfunction-and-induction-of-cytokines-in-isolated-skeletal-muscle/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/sera-from-patients-with-idiopathic-inflammatory-myopathy-induces-muscle-weakness-mitochondrial-dysfunction-and-induction-of-cytokines-in-isolated-skeletal-muscle/