Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 12, 2023
Title: (0325–0344) Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The 2021 EULAR guidelines on self-management have made recommendations (rec) to aid with the implementation of self-management strategies in inflammatory arthritis (IA) (1). Their aim is to support patients and encourage a patient-centred care approach which can improve both patient experience and outcomes in IA. Self-management can increase self-efficacy which can in turn improve adherence and outcomes for several self-management strategies (2). The objectives of this project were two fold; 1) to assess the implementation of self-management recommendations into routine clinical care of IA patients at a large tertiary rheumatology centre in London and 2) to explore how implementation (or not) of these recommendations may affect self-efficacy.
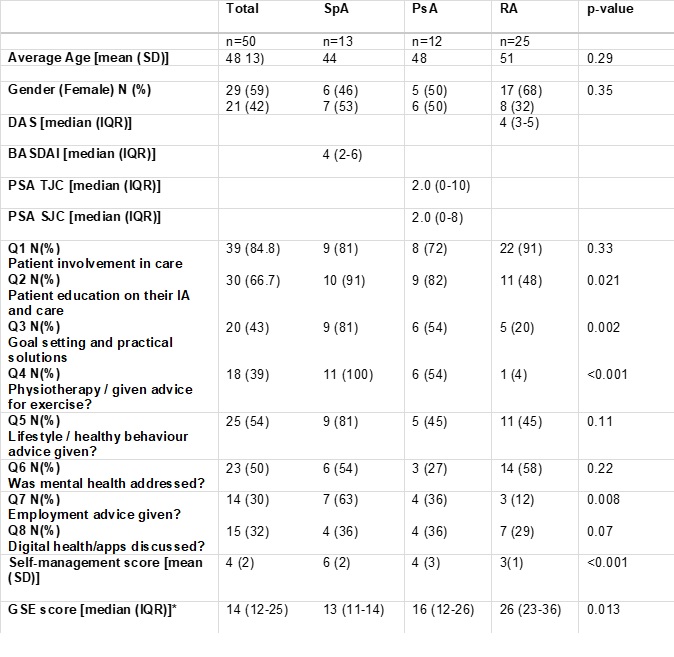
Methods: A retrospective analysis of the records of patients attending IA clinics at a large tertiary centre in London was undertaken from January 2022 to November 2022. Inclusion criteria included a diagnosis of either RA, PsA or AS. Specific questions addressing the uptake of the 2021 EULAR recommendations were developed (Table 1). The electronic notes were reviewed by two fellows who additionally interviewed patients via telephone, to explore whether the recommendations were addressed at their clinical encounter with the health care professional. Questions to the patients included specific ones addressing self-efficacy using the validated general self-efficacy (GSE) scale. Comparisons between groups were done with χ² tests, paired T-tests and Wilcoxon’s Rank sum where appropriate.
Results: Fifty patients were included: 50% with RA, 24% with PsA and 26% with SpA. The mean (SD) age of participants was 48 (13) years. The median DAS was 4 (3-5) in RA, SJC and TJC was 2.0 (0.0-10.0) and 2.0 (0.0-8.0) respectively in PsA patients with the median BASDAI of 4 (2-6) in SpA (Table 1). The median GSE was 14 (12-25), where a higher score indicates more self-efficacy. 78% of patients reported feeling involved in the planning of their care and were made aware of the multidisciplinary team (rec 1). 30% felt they were given enough information on disease management (rec 2). Goals and practical points on physical and psychological interventions (rec 3) were mentioned to 50%. For patients where >50% of the self-management recommendations were addressed the mean GSE was 12.64 compared to a mean of 10.52 when < 50% of self-management recommendations were addressed.
Conclusion: This study demonstrates that self-management recommendations are not fully and consistently addressed in routine clinics. Furthermore, patient self-efficacy was low/moderate suggesting that clinicians need to do better at discussing and supporting self-management strategies to improve self-efficacy which may also improve disease outcomes.
*GSE score – Ranges from 10_40, where a higher score indicates more self-efficacy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ali S, Ioasaf K, Katie B, Rutherford A, Steer S, Nikiphorou E. Self-management Strategies and Self-efficacy in Patients Living with Inflammatory Arthritis: Findings from a Quality Improvement Project in a Tertiary Centre [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/self-management-strategies-and-self-efficacy-in-patients-living-with-inflammatory-arthritis-findings-from-a-quality-improvement-project-in-a-tertiary-centre/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/self-management-strategies-and-self-efficacy-in-patients-living-with-inflammatory-arthritis-findings-from-a-quality-improvement-project-in-a-tertiary-centre/