Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: We previously reported on the incidence of shared treatment goal discussions which are associated with disease activity (DA) improvement and satisfaction within rheumatology care. Building on our previous reports, we aimed to gain insight into the nature of discordance in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment goals and explore its relationship to patient satisfaction with care.
Methods: An anonymous online questionnaire was presented in 2019 on a secure survey system. U.S. residents ≥18 years of age with a self-reported RA diagnosis by a medical professional responded to questions on demographics, DA, diagnosis and DMARD history, and RA treatment goals. Participants were asked how their providers’ RA treatment goals differed from their own. Responses were assessed and coded thematically using qualitative content analysis to identify reasons their goals differed from their providers’. Responses were also coded for strong emotion, poor communication, and difference in outcome expectation (high or low). Relationships between patient demographics and discordance in treatment goals and patient satisfaction were assessed using Chi-square tests for categorical variables and Kruskal-Wallis tests for continuous variables.
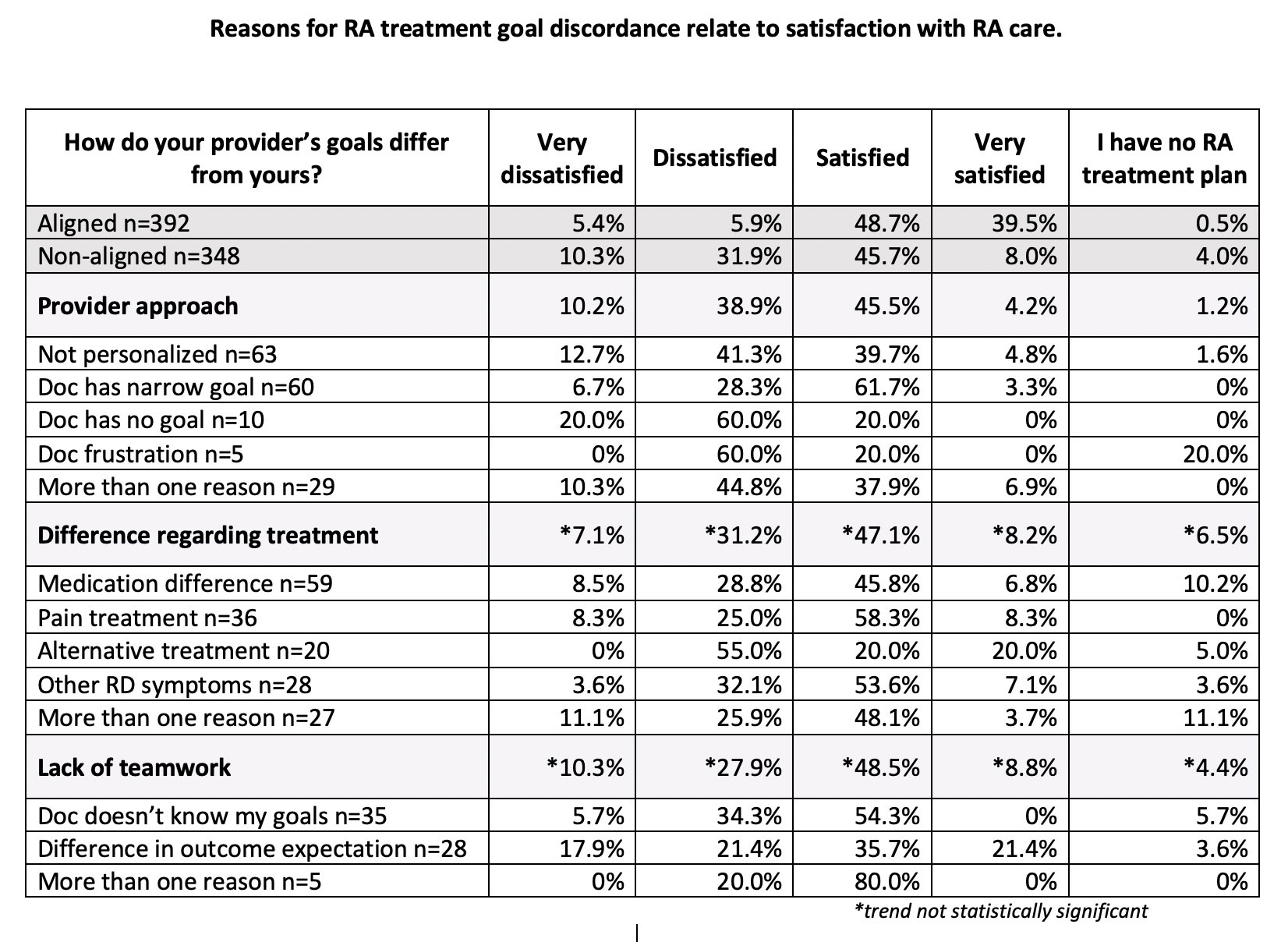
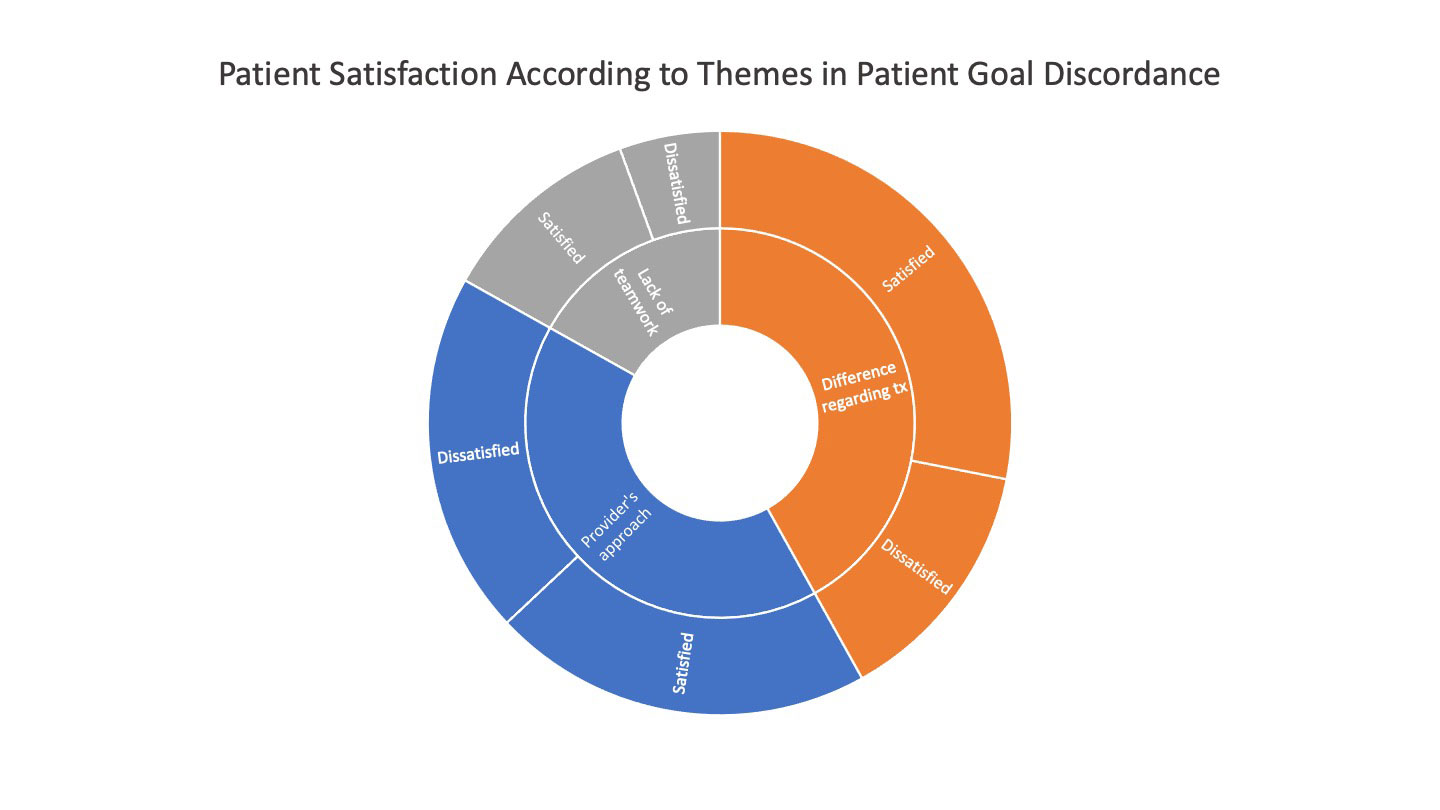
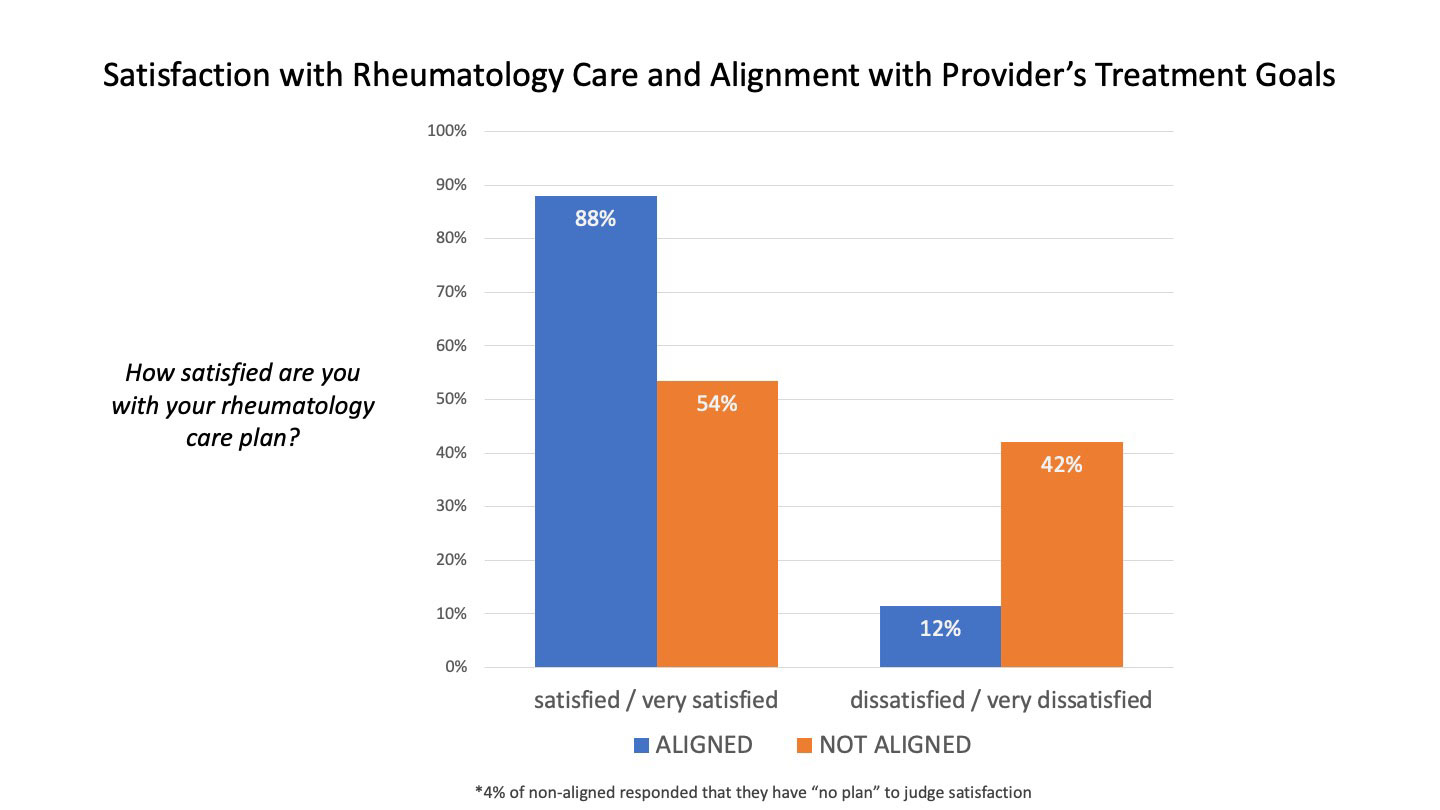
Results: The questionnaire was completed by 907 RA patients (90% women), with 58 (11) years mean (SD) age and 11 (10) years since diagnosis. 82% (n=740) responded to the question “How do you think your healthcare provider’s treatment goals differ from your own goals?”. Of those, 53% (n=392) did not differ (“aligned” with their providers’ goals); 47% (n=348) reported one or more reasons they differed with respect to treatment goals (“non-aligned”). Patient satisfaction was highest in those aligned with their providers’ goals (88%), compared to those non-aligned (54%, p< .0001). Among those non-aligned, major themes were providers’ approach (PA, 48%), differences regarding treatment (DT, 49%) and lack of teamwork (LT, 20%). Dissatisfaction was highest within the PA theme, with 49% dissatisfaction compared to only 36% in the non-PA group (p=0.002).
Conclusion: This survey found previously unreported associations between patient satisfaction with RA treatment and discordance with provider’s treatment goals. Our study is unique in that patients are asked about discordance with provider’s goals and their satisfaction with care. Further research should seek greater insight to patient concerns in RA treatment goals and investigate their significance in RA treatment satisfaction.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
O'Neill K, Sinicrope P, Crowson C, Marks K, Giblon R, Myasoedova E, Davis J. Satisfaction with Rheumatoid Arthritis Care Is Related to Discordance with Providers’ Treatment Goals and Patients’ Reasons for Disagreement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/satisfaction-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-care-is-related-to-discordance-with-providers-treatment-goals-and-patients-reasons-for-disagreement/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/satisfaction-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-care-is-related-to-discordance-with-providers-treatment-goals-and-patients-reasons-for-disagreement/